VIPER22AS-E Datasheet
... The VDD pin voltage range extends from 9 V to 38 V. This feature offers a great flexibility in design to achieve various behaviors. In Figure 4 on page 7 a forward configuration has been chosen to supply the device with two benefits: ...
... The VDD pin voltage range extends from 9 V to 38 V. This feature offers a great flexibility in design to achieve various behaviors. In Figure 4 on page 7 a forward configuration has been chosen to supply the device with two benefits: ...
EE 101 Lab 4 Digital Signals
... P2. Turn on the function generator and set the controls to create a pulse waveform with a 1 kHz repetition frequency, 20 % duty cycle, 5 volt peak-to-peak amplitude and an offset such that the pulse waveform is zero volts during the low portions and +5 volts at the high portions. To set the Tek AF ...
... P2. Turn on the function generator and set the controls to create a pulse waveform with a 1 kHz repetition frequency, 20 % duty cycle, 5 volt peak-to-peak amplitude and an offset such that the pulse waveform is zero volts during the low portions and +5 volts at the high portions. To set the Tek AF ...
Bipolar Transistor PNP 160V, 1.5A TP/TP-FA
... customer' s products or equipment. To verify symptoms and states that cannot be evaluated in an independent device, the customer should always evaluate and test devices mounted in the customer' s products or equipment. SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. assumes no responsibility for equipment failures tha ...
... customer' s products or equipment. To verify symptoms and states that cannot be evaluated in an independent device, the customer should always evaluate and test devices mounted in the customer' s products or equipment. SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. assumes no responsibility for equipment failures tha ...
Introduction to circuit analysis Classification of Materials Electric
... – An ideal voltage source maintains a prescribed voltage regardless of the current in the device. – An ideal current source maintains a prescribed current regardless of the voltage across the device. – A resistor constrains its voltage and current to be proportional to each other: v = iR (Ohm’s law) ...
... – An ideal voltage source maintains a prescribed voltage regardless of the current in the device. – An ideal current source maintains a prescribed current regardless of the voltage across the device. – A resistor constrains its voltage and current to be proportional to each other: v = iR (Ohm’s law) ...
Monte Carlo Simulation of Device Variations
... mismatch error. In order to simulate this, each line of code calling a transistor is “flattened” into the equivalent number of transistors so that each transistor’s parameters can be randomized separately. This model is accurate for DC analyses but has some shortcomings with parasitic capacitances i ...
... mismatch error. In order to simulate this, each line of code calling a transistor is “flattened” into the equivalent number of transistors so that each transistor’s parameters can be randomized separately. This model is accurate for DC analyses but has some shortcomings with parasitic capacitances i ...
STGW30NC60VD
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
Logic signal voltage levels
... TTL gates operate on a nominal power supply voltage of 5 volts, +/- 0.25 volts. Ideally, a TTL "high" signal would be 5.00 volts exactly, and a TTL "low" signal 0.00 volts exactly. However, real TTL gate circuits cannot output such perfect voltage levels, and are designed to accept "high" and "low" ...
... TTL gates operate on a nominal power supply voltage of 5 volts, +/- 0.25 volts. Ideally, a TTL "high" signal would be 5.00 volts exactly, and a TTL "low" signal 0.00 volts exactly. However, real TTL gate circuits cannot output such perfect voltage levels, and are designed to accept "high" and "low" ...
DATA SHEET PBSS5320T 20 V, 3 A
... All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner. The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without notice. No ...
... All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner. The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without notice. No ...
Wide tunable CMOS active inductor
... This allows us to use a smaller NMOS device and broaden the operating frequency range of the inductive impedance. The positive feedback generates negative resistance, which reduces the inductor loss and, in turn, increases the Q factor. Bandpass filter/amplifier: In a novel design approach, two active ...
... This allows us to use a smaller NMOS device and broaden the operating frequency range of the inductive impedance. The positive feedback generates negative resistance, which reduces the inductor loss and, in turn, increases the Q factor. Bandpass filter/amplifier: In a novel design approach, two active ...
We analyze circuits for several reasons • Understand how they work
... Task is clear by inspection When dealing with more complex networks Other tools are available Mesh Equations Let’s look at what we have been calling loop analysis in more detail Planar Networks ...
... Task is clear by inspection When dealing with more complex networks Other tools are available Mesh Equations Let’s look at what we have been calling loop analysis in more detail Planar Networks ...
Name: Date: ______ ___ 1. A series RL circuit is connected to an
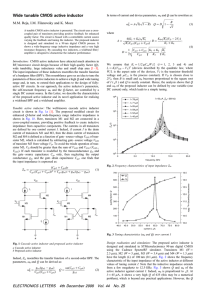
... ___ 15. In the diagram, the function y(t) = ym sin (ωt) is plotted as a solid curve. The other three curves have the form y(t) = ym sin (ωt + φ), where φ is between –π/2 and + π/2. Rank the curves according to the value of φ, from the most negative to the most positive. ...
... ___ 15. In the diagram, the function y(t) = ym sin (ωt) is plotted as a solid curve. The other three curves have the form y(t) = ym sin (ωt + φ), where φ is between –π/2 and + π/2. Rank the curves according to the value of φ, from the most negative to the most positive. ...
Prelab06
... An ideal EMF device maintains a constant potential difference across its terminals; we denote the EMF E by an arrow pointing from the negative to positive terminals; Real (non-ideal) EMF devices are modeled as an ideal EMF with an internal resistance in series; the potential difference across th ...
... An ideal EMF device maintains a constant potential difference across its terminals; we denote the EMF E by an arrow pointing from the negative to positive terminals; Real (non-ideal) EMF devices are modeled as an ideal EMF with an internal resistance in series; the potential difference across th ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.