Complex Waveforms
... In previous work, a.c. supplies have been assumed to be sinusoidal, this being a form of alternating quantity commonly encountered in electrical engineering. However, many supply waveforms are not sinusoidal. For example, sawtooth generators produce ramp waveforms, and rectangular waveforms may be p ...
... In previous work, a.c. supplies have been assumed to be sinusoidal, this being a form of alternating quantity commonly encountered in electrical engineering. However, many supply waveforms are not sinusoidal. For example, sawtooth generators produce ramp waveforms, and rectangular waveforms may be p ...
Rebirth of Negative-Sequence Quantities in Protective Relaying
... conductor, the protective relay is unable to measure zero-sequence currents. ...
... conductor, the protective relay is unable to measure zero-sequence currents. ...
Harmonic detection and filtering : pdf
... A typical crest factor for the current drawn by non-linear loads is much greater than 2. Its value can range from 1.5 to 2 or even up to 5 in critical situations. A very high crest factor indicates that high overcurrents occur from time to time. These overcurrents, detected by the protection devices ...
... A typical crest factor for the current drawn by non-linear loads is much greater than 2. Its value can range from 1.5 to 2 or even up to 5 in critical situations. A very high crest factor indicates that high overcurrents occur from time to time. These overcurrents, detected by the protection devices ...
PD166017T1F Data Sheet INTELLIGENT POWER DEVICE
... In case of a reverse voltage is applied to the device, the N-Ch MOSFET will turn on only if a reverse current can flow from IN pin through RCC and if |VCC – VIN| voltage is in range of 8 V (TYP). In above conditions, power dissipation in the driver is generated by N-Ch Mosfet as well as RCC and RIS0 ...
... In case of a reverse voltage is applied to the device, the N-Ch MOSFET will turn on only if a reverse current can flow from IN pin through RCC and if |VCC – VIN| voltage is in range of 8 V (TYP). In above conditions, power dissipation in the driver is generated by N-Ch Mosfet as well as RCC and RIS0 ...
MAX5946 Dual PCI Express, Hot-Plug Controller General Description
... PCI Express™ applications. The device provides hotplug control for 12V, 3.3V, and 3.3V auxiliary supplies of two PCI express slots. The MAX5946’s logic inputs/outputs allow interfacing directly with the system hot-plug management controller or through an SMBus™ with an external I/O expander. An inte ...
... PCI Express™ applications. The device provides hotplug control for 12V, 3.3V, and 3.3V auxiliary supplies of two PCI express slots. The MAX5946’s logic inputs/outputs allow interfacing directly with the system hot-plug management controller or through an SMBus™ with an external I/O expander. An inte ...
ADM3202 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Transmitter (Driver) Inputs. These inputs accept TTL/CMOS levels. Transmitter (Driver) Outputs. These are RS-232 signal levels (typically ±9 V). Receiver Inputs. These inputs accept RS-232 signal levels. An internal 5 kΩ pull-down resistor to GND is connected on each input. Receiver Outputs. These a ...
... Transmitter (Driver) Inputs. These inputs accept TTL/CMOS levels. Transmitter (Driver) Outputs. These are RS-232 signal levels (typically ±9 V). Receiver Inputs. These inputs accept RS-232 signal levels. An internal 5 kΩ pull-down resistor to GND is connected on each input. Receiver Outputs. These a ...
2. Capacitor
... Parallel Plate Capacitor A parallel plate capacitor is a simple example of the factors affecting a capacitor. A simple capacitor can be made from two identical plates of conductive materials, separated a distance apart. The capacitance is then directly proportional to the area of the plates and inve ...
... Parallel Plate Capacitor A parallel plate capacitor is a simple example of the factors affecting a capacitor. A simple capacitor can be made from two identical plates of conductive materials, separated a distance apart. The capacitance is then directly proportional to the area of the plates and inve ...
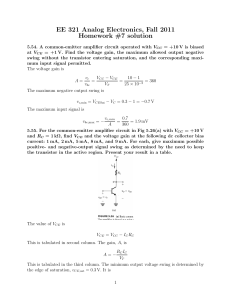
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2011 Homework #7 solution
... and RC = 1 kΩ, find VCE and the voltage gain at the following dc collector bias current: 1 mA, 2 mA, 5 mA, 8 mA, and 9 mA. For each, give maximum possible positive- and negative-output signal swing as determined by the need to keep the transistor in the active region. Present your result in a table. ...
... and RC = 1 kΩ, find VCE and the voltage gain at the following dc collector bias current: 1 mA, 2 mA, 5 mA, 8 mA, and 9 mA. For each, give maximum possible positive- and negative-output signal swing as determined by the need to keep the transistor in the active region. Present your result in a table. ...
Leakage Current Reduction in CMOS VLSI Circuits by Input Vector
... have relied on scaling down the supply voltage to reduce the dynamic power dissipation. Maintaining the transistor switching speeds requires a proportionate downscaling of the transistor threshold voltages in lock step with the supply voltage reduction. However, threshold voltage scaling results in ...
... have relied on scaling down the supply voltage to reduce the dynamic power dissipation. Maintaining the transistor switching speeds requires a proportionate downscaling of the transistor threshold voltages in lock step with the supply voltage reduction. However, threshold voltage scaling results in ...
64-Position Up/Down Control Digital Potentiometer AD5227
... coefficient to 5 ppm/°C except at low value codes where RW dominates. ...
... coefficient to 5 ppm/°C except at low value codes where RW dominates. ...
Lecture 5: DC motors
... Solutions to the problems with commutation 1. Commutating poles or interpoles To avoid sparkling at the brushes while the machine’s load changes, instead of adjusting the brushes’ position, it is possible to introduce small poles (commutating poles or interpoles) between the main ones to make the v ...
... Solutions to the problems with commutation 1. Commutating poles or interpoles To avoid sparkling at the brushes while the machine’s load changes, instead of adjusting the brushes’ position, it is possible to introduce small poles (commutating poles or interpoles) between the main ones to make the v ...
Dual, Wideband, High Output Current Operational Amplifier with Active Off-Line Control OPA2673 FEATURES
... Specified on ±6V supplies (to support +12V operation), the OPA2673 also supports up to +13V single or ±6.5V dual supplies. Video applications benefit from a very high output current to drive up to 10 parallel video loads (15Ω) with < 0.1%/0.1° dG/dΦ nonlinearity. ...
... Specified on ±6V supplies (to support +12V operation), the OPA2673 also supports up to +13V single or ±6.5V dual supplies. Video applications benefit from a very high output current to drive up to 10 parallel video loads (15Ω) with < 0.1%/0.1° dG/dΦ nonlinearity. ...
MAX5922 +48V, Single-Port Network Power Switch For Power
... (MAX5922A) or 28V (MAX5922B/C) internally. After successfully discovering and classifying a PD, the MAX5922 enters startup mode. During startup, the MAX5922 limits the output voltage and current slew rate to minimize EMI (electromagnetic interference). The MAX5922 has an integrated 0.45Ω N-channel p ...
... (MAX5922A) or 28V (MAX5922B/C) internally. After successfully discovering and classifying a PD, the MAX5922 enters startup mode. During startup, the MAX5922 limits the output voltage and current slew rate to minimize EMI (electromagnetic interference). The MAX5922 has an integrated 0.45Ω N-channel p ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.