A Behavioral Model for DC-DC Converters using Modelica
... environment. Simulation results are given. A theoreti- be built where every switching cycle is taken into accal method for tuning the simulation model to a phys- count. However, the goal of our modeling effort is to emulate the behavior of a commercial dc/dc conical converter is presented. verter wh ...
... environment. Simulation results are given. A theoreti- be built where every switching cycle is taken into accal method for tuning the simulation model to a phys- count. However, the goal of our modeling effort is to emulate the behavior of a commercial dc/dc conical converter is presented. verter wh ...
AN028: Building an Auto-Ranging DMM with the ICL7103A
... For example, type B can be implemented with analog gating, whereas, type A cannot. However, type B requires some form of input protection to prevent destructive breakdown when high voltage is applied. The designer must also consider the potential hazards of four additional sources of leakage current ...
... For example, type B can be implemented with analog gating, whereas, type A cannot. However, type B requires some form of input protection to prevent destructive breakdown when high voltage is applied. The designer must also consider the potential hazards of four additional sources of leakage current ...
ADP5135 Preliminary Data Sheet Triple 1800 mA Buck Regulators
... buck switching frequency is always constant and does not change with the load current. If the MODE pin is at logic low level, the switching regulators operate in auto PWM/PSM mode. In this mode, the regulators operate at fixed PWM frequency when the load current is above the PSM current threshold. W ...
... buck switching frequency is always constant and does not change with the load current. If the MODE pin is at logic low level, the switching regulators operate in auto PWM/PSM mode. In this mode, the regulators operate at fixed PWM frequency when the load current is above the PSM current threshold. W ...
Combined Voltage and Current Output Terminal
... Although it was not tested in this design, a footprint was included for an external R SET resistor (R1). Unless the RSET resistor is populated, there are not any passive components that require high precision for this design. If an external RSET resistor is used with this design then it should be ch ...
... Although it was not tested in this design, a footprint was included for an external R SET resistor (R1). Unless the RSET resistor is populated, there are not any passive components that require high precision for this design. If an external RSET resistor is used with this design then it should be ch ...
... is shown in Figure 3. The output voltage keeps the shape of the dynamic current, but they are stretched in time. This stretch in time is useful for further processing. The main advantage is the speed of test, where only two write operations are required as compared to March tests, where minimum 4 op ...
XB1117 Series
... 2. Stability and load regulation The XB1117 series requires a load capacitor between the VOUT pin and the GND pin to provide phase compensation thereby ensuring stability of the output voltage. Either a tantalum capacitor of more than 10μF (TYP.) or an aluminum electrolytic capacitor of more than 50 ...
... 2. Stability and load regulation The XB1117 series requires a load capacitor between the VOUT pin and the GND pin to provide phase compensation thereby ensuring stability of the output voltage. Either a tantalum capacitor of more than 10μF (TYP.) or an aluminum electrolytic capacitor of more than 50 ...
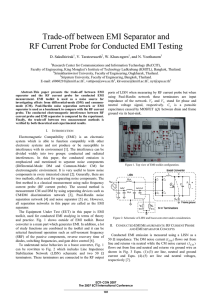
Trade-off between EMI Separator and D. Sakulhirirak , V. Tarateeraseth
... From Fig. 8, when the applied current (I) is equal to (or less than) its critical current(IC) value, both sides of the sample are connected by the superconduction parts. Then, the resistance of sample does not appear. But when I>IC, superconduction part will be cut-off, because weak point region is ...
... From Fig. 8, when the applied current (I) is equal to (or less than) its critical current(IC) value, both sides of the sample are connected by the superconduction parts. Then, the resistance of sample does not appear. But when I>IC, superconduction part will be cut-off, because weak point region is ...
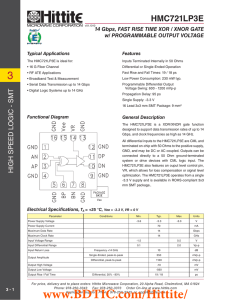
MAX1733/MAX1734 Low-Voltage, Step-Down DC-DC Converters in SOT23 General Description
... output voltage is out of regulation, the error comparator begins a switching cycle by turning on the high-side switch. This switch remains on until the minimum ontime of 400ns expires and the output voltage regulates or the current-limit threshold is exceeded. Once off, the high-side switch remains ...
... output voltage is out of regulation, the error comparator begins a switching cycle by turning on the high-side switch. This switch remains on until the minimum ontime of 400ns expires and the output voltage regulates or the current-limit threshold is exceeded. Once off, the high-side switch remains ...
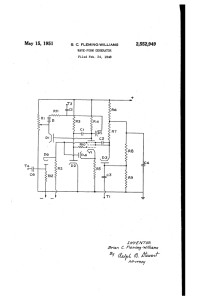
May l5, 1951 B. c. FLEMlNG-wlLLsAMs 2,552,949 Brian C. Fleming
... lows during which it cannot be caused again ex' between the tapping on potentiometer Rl and the cept by a stillV larger pulse than that which is-d'e‘ cathode of this diode to provide an'ad'equate im'-l termined by the value of the steady bi'as applied pedance for the nring pulse to build up on. to d ...
... lows during which it cannot be caused again ex' between the tapping on potentiometer Rl and the cept by a stillV larger pulse than that which is-d'e‘ cathode of this diode to provide an'ad'equate im'-l termined by the value of the steady bi'as applied pedance for the nring pulse to build up on. to d ...
Subject: Power Electronics & Industrial Control Content Developed by :
... determined by the external load. The magnitude of gate current has a very strong effect on the value of the break over voltage as shown in the figure. The right hand side figure in the inset shows a typical plot of the forward break over voltage (V ...
... determined by the external load. The magnitude of gate current has a very strong effect on the value of the break over voltage as shown in the figure. The right hand side figure in the inset shows a typical plot of the forward break over voltage (V ...
Chapter 21 AC Circuits
... Recall that a capacitor C with Voltage V across it has charge Q=CV Current I= dQ/dt = C dV/dt In a circuit with a capacitor and resistor in parallel the voltage across the resistor must equal opposite that across the capacitor Hence Vc = -VR or Q/C = -IR or Q/C + IR = 0 (note the current I thru the ...
... Recall that a capacitor C with Voltage V across it has charge Q=CV Current I= dQ/dt = C dV/dt In a circuit with a capacitor and resistor in parallel the voltage across the resistor must equal opposite that across the capacitor Hence Vc = -VR or Q/C = -IR or Q/C + IR = 0 (note the current I thru the ...
Ch 15 Circuits and Domestic Electricity
... (RA) connected in series with two resistors R1 and R2. (a) Small resistance circuit (R1 = 0.1 ): (i) Total resistance = R1 + RA (ii) Since R1 is comparable to RA, the total resistance is increased. (iii)The current passing through and the voltage across the resistor decrease. (b) Large resistance c ...
... (RA) connected in series with two resistors R1 and R2. (a) Small resistance circuit (R1 = 0.1 ): (i) Total resistance = R1 + RA (ii) Since R1 is comparable to RA, the total resistance is increased. (iii)The current passing through and the voltage across the resistor decrease. (b) Large resistance c ...
UCC28019A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Output voltage sense: An external resistor-divider network connected from this pin to the PFC output voltage provides feedback sensing for regulation to the internal 5-V reference voltage. A small capacitor from this pin to GND filters high-frequency noise. Standby mode disables the controller and d ...
... Output voltage sense: An external resistor-divider network connected from this pin to the PFC output voltage provides feedback sensing for regulation to the internal 5-V reference voltage. A small capacitor from this pin to GND filters high-frequency noise. Standby mode disables the controller and d ...
S1-3-15 - Series vs. Parallel
... In this activity, you will construct your own series and parallel circuits and explore the current flow and the voltage differences in your circuits. You will use resistors as well as light bulbs in these circuits. Resistors and light bulbs both restrict the amount of current that can flow through t ...
... In this activity, you will construct your own series and parallel circuits and explore the current flow and the voltage differences in your circuits. You will use resistors as well as light bulbs in these circuits. Resistors and light bulbs both restrict the amount of current that can flow through t ...
3.1.3 AS Level – Current Electricity Notes – LJ (2010) Detail lifted
... positive terminal as opposite charges attract. They do not just experience a pull from the positive terminal – they are also pulled by the ions in the lattice – therefore there is not simply a flow of electrons in one direction – they are pulled in all directions – just more in one direction than an ...
... positive terminal as opposite charges attract. They do not just experience a pull from the positive terminal – they are also pulled by the ions in the lattice – therefore there is not simply a flow of electrons in one direction – they are pulled in all directions – just more in one direction than an ...
BD9302FP
... For output capacitor, select the allowable ripple voltage VPP or the allowable drop voltage at a sharp change of load, whichever larger for the capacitor. The output ripple voltage can be obtained according to the formula shown below. ...
... For output capacitor, select the allowable ripple voltage VPP or the allowable drop voltage at a sharp change of load, whichever larger for the capacitor. The output ripple voltage can be obtained according to the formula shown below. ...
TPS255xx Precision Adjustable Current-Limited
... The TPS2552/53 and TPS2552-1/53-1 respond to overcurrent conditions by limiting their output current to the IOS levels shown in Figure 24. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and reduces the output voltage accordingly. Two possible overload condi ...
... The TPS2552/53 and TPS2552-1/53-1 respond to overcurrent conditions by limiting their output current to the IOS levels shown in Figure 24. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and reduces the output voltage accordingly. Two possible overload condi ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.