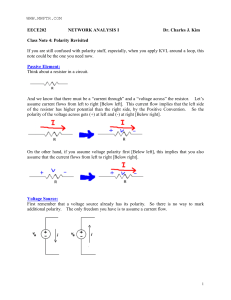
Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifiers
... RE and RL are as shown in the figure. Design a bias-stable circuit to achieve the maximum undistorted swing in the output voltage if the total instantaneous C-E voltage is to remain in the range 1 ≤ vCE ≤ 8 V and the minimum collector current is to be iC (min) = 0.1 mA. ...
... RE and RL are as shown in the figure. Design a bias-stable circuit to achieve the maximum undistorted swing in the output voltage if the total instantaneous C-E voltage is to remain in the range 1 ≤ vCE ≤ 8 V and the minimum collector current is to be iC (min) = 0.1 mA. ...
ESMT/EMP
... The AD22653 is a 2-Vrms cap-less stereo line driver. The device is ideal for single supply electronics. Cap-less design can eliminate output dc-blocking capacitors for better low frequency response and save cost. The AD22653 is capable of delivering 2-Vrms output into a 10kΩ load with 3.3V supply. T ...
... The AD22653 is a 2-Vrms cap-less stereo line driver. The device is ideal for single supply electronics. Cap-less design can eliminate output dc-blocking capacitors for better low frequency response and save cost. The AD22653 is capable of delivering 2-Vrms output into a 10kΩ load with 3.3V supply. T ...
SDD450 - ssousa.com
... The SDD450 consists of a Photo Darlington transistor optically coupled to a light emitting diode. Optical coupling between the input LED and output Photo Darlington allows for high isolation levels while maintaining low-level DC signal control capability. The SDD450 provides an optically isolated me ...
... The SDD450 consists of a Photo Darlington transistor optically coupled to a light emitting diode. Optical coupling between the input LED and output Photo Darlington allows for high isolation levels while maintaining low-level DC signal control capability. The SDD450 provides an optically isolated me ...
ET161 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... Class A Power Analysis Class B Power Analysis Power Amp with Driver JFET Bias JFET Amplifiers ...
... Class A Power Analysis Class B Power Analysis Power Amp with Driver JFET Bias JFET Amplifiers ...
File - N@Y@
... If the coordinates of the operating point of a CE amplifier using fixed bias or base resistor method of biasing are Vce=6v and Ic=1mA,determine the value of R c and RB. Derive an expression for the stability factor of a collector –to –base bias circuit. Mention the disadvantage of collector –to-base ...
... If the coordinates of the operating point of a CE amplifier using fixed bias or base resistor method of biasing are Vce=6v and Ic=1mA,determine the value of R c and RB. Derive an expression for the stability factor of a collector –to –base bias circuit. Mention the disadvantage of collector –to-base ...
RevExII
... In the circuit below which resistors must have the same current flowing through them? Do not assume that the resistors are identical. RII-8 ...
... In the circuit below which resistors must have the same current flowing through them? Do not assume that the resistors are identical. RII-8 ...
Watt`s Law Practice Worksheet Key
... Solve the following problems using Ohm’s Law and Watt’s Law as appropriate. 1. A 12 volt battery is providing a circuit current of 25 ma. If this is the only power source in the circuit, what is the equivalent circuit resistance? ___480Ω____________________________ 2. In the above circuit, how much ...
... Solve the following problems using Ohm’s Law and Watt’s Law as appropriate. 1. A 12 volt battery is providing a circuit current of 25 ma. If this is the only power source in the circuit, what is the equivalent circuit resistance? ___480Ω____________________________ 2. In the above circuit, how much ...
CIRCUITS WORKSHEET
... 8) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown. 9) Determine the resistance of resistor R shown in the diagram. Questions 10 through 12 refer to the following: A 3.0-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor, R, and two ammeters, A1 and A2, are connected as shown below with a 12-volt source. Am ...
... 8) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown. 9) Determine the resistance of resistor R shown in the diagram. Questions 10 through 12 refer to the following: A 3.0-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor, R, and two ammeters, A1 and A2, are connected as shown below with a 12-volt source. Am ...
Annex A (IEEE_1246).
... conductor, and the distance between the energized and deenergized conductors. Once the deenergized conductor is grounded there no longer exists a significant potential difference between the conductor and ground. However, unlike the case of the floating conductor, there is now a path for charging cu ...
... conductor, and the distance between the energized and deenergized conductors. Once the deenergized conductor is grounded there no longer exists a significant potential difference between the conductor and ground. However, unlike the case of the floating conductor, there is now a path for charging cu ...
Power Quality Issues
... Defines the total harmonic content of current or voltage Ratio of the RMS of the harmonic content to the RMS of the Fundamental, as % of Fundamental ...
... Defines the total harmonic content of current or voltage Ratio of the RMS of the harmonic content to the RMS of the Fundamental, as % of Fundamental ...
HVTC Product Information
... designed for PD testing on e. g. transformers, semiconducters, and micro samples. Depending on the built-in HV transformer, testing up to 20 kVrms is possible. The test chamber provides sufficient space to test samples up to a maximum size of 500x500x400 mm³. The main components of this system are: ...
... designed for PD testing on e. g. transformers, semiconducters, and micro samples. Depending on the built-in HV transformer, testing up to 20 kVrms is possible. The test chamber provides sufficient space to test samples up to a maximum size of 500x500x400 mm³. The main components of this system are: ...
Electricity - Mr. Meserve`s Class
... Electrical Potential is the energy stored ready to do work. It is measured in volts, is represented as V, and is determined by the source in a circuit. Electrical Flow is the flow of energy from a high potential point to a low potential point. This flow is called the current, is measured in ampere ...
... Electrical Potential is the energy stored ready to do work. It is measured in volts, is represented as V, and is determined by the source in a circuit. Electrical Flow is the flow of energy from a high potential point to a low potential point. This flow is called the current, is measured in ampere ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.
![SpiceAss[2] - simonfoucher.com](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007214569_1-1b3e0e1e96d8c8a37166cbdff9c4eb24-300x300.png)