The chemistry and metallurgy of beryllium
... consider its toxicity and the hazards involved with the continual production and usage of the metal, its oxide and alloys. Beryllium is extremely toxic, both as a carcin ogen and as an initiator of acute and chronic beryllium disease (CBD). 3·5 Although beryllium is considered a car cinogen, its c ...
... consider its toxicity and the hazards involved with the continual production and usage of the metal, its oxide and alloys. Beryllium is extremely toxic, both as a carcin ogen and as an initiator of acute and chronic beryllium disease (CBD). 3·5 Although beryllium is considered a car cinogen, its c ...
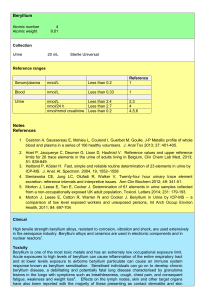
Beryllium Notes References
... High tensile strength beryllium alloys, resistant to corrosion, vibration and shock, are used extensively in the aerospace industry. Beryllium alloys and ceramics are used in electronic components and in nuclear reactors1. Toxicity Beryllium is one of the most toxic metals and has an extremely low o ...
... High tensile strength beryllium alloys, resistant to corrosion, vibration and shock, are used extensively in the aerospace industry. Beryllium alloys and ceramics are used in electronic components and in nuclear reactors1. Toxicity Beryllium is one of the most toxic metals and has an extremely low o ...