Feudal Japan
... be lords on different parts of land and they would look after the land These feudal lords were called ...
... be lords on different parts of land and they would look after the land These feudal lords were called ...
View - Legal Precedents
... for the Grantee to make a sub-grant of the land. The Grants of land were made on certain terms and conditions know as services and incidents. These were the precursors of the modern taxes as a means for the Crown to raise revenue. As part of the grant the Grantee had to perform services for the Gran ...
... for the Grantee to make a sub-grant of the land. The Grants of land were made on certain terms and conditions know as services and incidents. These were the precursors of the modern taxes as a means for the Crown to raise revenue. As part of the grant the Grantee had to perform services for the Gran ...
1. Kings and nobles didn`t know how to protect their land, and they
... 3 items that were exchanged, financial obligations, and lord obligations, equaling a complicated system, and supply military supplies 4. In some situations something may The lords “group” that he was in have happened to the lord of the charge of had to ransom for the lord ...
... 3 items that were exchanged, financial obligations, and lord obligations, equaling a complicated system, and supply military supplies 4. In some situations something may The lords “group” that he was in have happened to the lord of the charge of had to ransom for the lord ...
Zoey Choi 7C Feudalism Notes Feudal and Manorial Systems
... • Knights were usually paid for their services with land • Land given to knight for services was called a fief • Anyone accepting fief was called vassal • Person from whom he accepted fief was his lord • Historians call system of exchanging land fro service the Feudal system, or feudalism Feudal Obl ...
... • Knights were usually paid for their services with land • Land given to knight for services was called a fief • Anyone accepting fief was called vassal • Person from whom he accepted fief was his lord • Historians call system of exchanging land fro service the Feudal system, or feudalism Feudal Obl ...
Chapter 19 Vocabulary Name Medieval Europe/Middle Ages Period
... who have sworn loyalty to the lord; political order; under feudalism, nobles governed and protected people in return for services (p. 523, pp. 548-549) ...
... who have sworn loyalty to the lord; political order; under feudalism, nobles governed and protected people in return for services (p. 523, pp. 548-549) ...
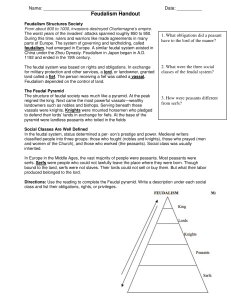
The feudal system
... •In return for the land they had been given by the King, the Barons had to serve on the royal council, pay rent and provide the King with Knights for military service when he demanded it. ...
... •In return for the land they had been given by the King, the Barons had to serve on the royal council, pay rent and provide the King with Knights for military service when he demanded it. ...
Barons in Scotland

In Scotland, a Baron is the head of a ""feudal"" barony (also known as prescriptive barony). This used to be attached to a particular piece of land on which was the ""caput"" (Latin meaning 'head'), or the essence of the barony, normally a building, such as a castle or manor house. Accordingly, the owner of the piece of land containing the ""caput"" was the Baron or Baroness. The Court of the Lord Lyon recognises a person possessing the dignity of baron under certain conditions, this being the status of a minor baron, recognized by the crown as noble, but not a peer. Scottish feudal baronies may be passed to any person, of either sex, by inheritance or conveyance.Scotland has a distinct legal system within the United Kingdom. Historically, in the Kingdom of Scotland, the Lord Lyon King of Arms, as the Sovereign’s Minister in matters armorial, is at once Herald and Judge.The Scottish equivalent of an English baron is a Lord of Parliament.