Introduction to Quantum Entanglement
... follows that it is not satisfied at least principle of quantum mechanics. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen came to the conclusion that some quantum effects travel faster than light, which is contradiction to the theory of relativity. The presented experiment is called the EPR paradox. In response to the ...
... follows that it is not satisfied at least principle of quantum mechanics. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen came to the conclusion that some quantum effects travel faster than light, which is contradiction to the theory of relativity. The presented experiment is called the EPR paradox. In response to the ...
Quantum connection and Poincare19 e-
... The present paper is aimed at analysing some aspects of the general relativistic classical and quantum mechanics on a curved spacetime with absolute time, in terms of recent formulations of a finite order Lagrangian bicomplex [Kru90, Kru95] and of a covariant approach to classical and quantum mechan ...
... The present paper is aimed at analysing some aspects of the general relativistic classical and quantum mechanics on a curved spacetime with absolute time, in terms of recent formulations of a finite order Lagrangian bicomplex [Kru90, Kru95] and of a covariant approach to classical and quantum mechan ...
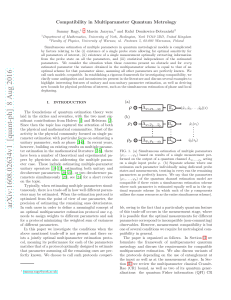
A Common Fallacy in Quantum Mechanics: Retrocausality David Ellerman
... polarization of the incident beam. But since no collapsing measurement was in fact made in P or its inverse, the original beam can be the output of an analyzer loop. Very few textbooks realize there is even a problem with presenting a polarization analyzer such as a calcite crystal as creating two b ...
... polarization of the incident beam. But since no collapsing measurement was in fact made in P or its inverse, the original beam can be the output of an analyzer loop. Very few textbooks realize there is even a problem with presenting a polarization analyzer such as a calcite crystal as creating two b ...
Matematiska institutionen Department of Mathematics Covering the sphere with noncontextuality inequalities
... In the beginning of the 20th century, some physical phenomena could not be explained by classical physics, for example the ultra-violet disaster of any classical model of of black-body radiation, and the photoelectric effect. There were many other phenomena that were unexplainable, for more see for ...
... In the beginning of the 20th century, some physical phenomena could not be explained by classical physics, for example the ultra-violet disaster of any classical model of of black-body radiation, and the photoelectric effect. There were many other phenomena that were unexplainable, for more see for ...
The uncertainty relations in quantum mechanics
... and in spite of the fact that the views on QM of the two founding fathers, Heisenberg and Bohr, are often clubbed as the ‘Copenhagen interpretation’, there is considerable difference between their views on uncertainty relation, wave–particle duality and Bohr’s complementarity principle (BCP, to be d ...
... and in spite of the fact that the views on QM of the two founding fathers, Heisenberg and Bohr, are often clubbed as the ‘Copenhagen interpretation’, there is considerable difference between their views on uncertainty relation, wave–particle duality and Bohr’s complementarity principle (BCP, to be d ...
A Priori Probability and Localized Observers
... in the interpretation of quantum mechanics (particles, eigenvalues, wave-functions) and the von Neumann algebras associated with localized regions of space-time, which are focused on by mathematical physicists interested in the conceptual foundations of relativistic quantum field theories. The purpo ...
... in the interpretation of quantum mechanics (particles, eigenvalues, wave-functions) and the von Neumann algebras associated with localized regions of space-time, which are focused on by mathematical physicists interested in the conceptual foundations of relativistic quantum field theories. The purpo ...
Statistical Mechanics to Disordered Quantum Optimization
... Thus, in Chapter 2, we review the classical complexity theory necessary to understand the important statement that P 6= NP and its more recent quantum generalization BQP 6= QMA. These complexity theoretic conjectures essentially assert that there exist natural classes of problems (called NP-complet ...
... Thus, in Chapter 2, we review the classical complexity theory necessary to understand the important statement that P 6= NP and its more recent quantum generalization BQP 6= QMA. These complexity theoretic conjectures essentially assert that there exist natural classes of problems (called NP-complet ...
Polarization statistics
... integvration the other variables not describing polarization properties. We hace compared the result with other distribution analogous to the s-ordered but directly introduced on the Poincaré sphere, referred to as SU(2) distributions, instead from being derived after distributions for the complex a ...
... integvration the other variables not describing polarization properties. We hace compared the result with other distribution analogous to the s-ordered but directly introduced on the Poincaré sphere, referred to as SU(2) distributions, instead from being derived after distributions for the complex a ...
Silicon nanophotonics for scalable quantum coherent feedback
... framework based on input-output theory has been developed for modeling networks of quantum systems connected by electromagnetic fields [–]. Such networks can be designed to operate as autonomous devices for quantum information tasks, e.g., quantum state preparation and stabilization [–], as well ...
... framework based on input-output theory has been developed for modeling networks of quantum systems connected by electromagnetic fields [–]. Such networks can be designed to operate as autonomous devices for quantum information tasks, e.g., quantum state preparation and stabilization [–], as well ...
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics
... are the result of the entanglement of feelings of discontent and fear in the presence of dogs. Albeit this example may seem a little trivial at this time, the connection to system dynamics will become clearer as the central argument is developed. We will now delve into scientific research. Recent de ...
... are the result of the entanglement of feelings of discontent and fear in the presence of dogs. Albeit this example may seem a little trivial at this time, the connection to system dynamics will become clearer as the central argument is developed. We will now delve into scientific research. Recent de ...
Excerpt. - Dover Publications
... there is really no meaning to combine the results of noncommuting operators such as Lx , Ly , and L45◦ . These measurements are incompatible and mutually exclusive.” Nevertheless, Eq. 10.10 for expectation values is still true, owing to the validity of the additivity postulate in quantum mechanics, ...
... there is really no meaning to combine the results of noncommuting operators such as Lx , Ly , and L45◦ . These measurements are incompatible and mutually exclusive.” Nevertheless, Eq. 10.10 for expectation values is still true, owing to the validity of the additivity postulate in quantum mechanics, ...
Compatibility in Multiparameter Quantum Metrology
... metrology from the single parameter case can already be discussed at the classical level. Assuming we’ve already chosen a probe state and a measurement, it may happen that the resulting FI matrix is non-diagonal. This means that the estimators for the parameters will not be independent. Considering ...
... metrology from the single parameter case can already be discussed at the classical level. Assuming we’ve already chosen a probe state and a measurement, it may happen that the resulting FI matrix is non-diagonal. This means that the estimators for the parameters will not be independent. Considering ...
Quantum computing
Quantum computing studies theoretical computation systems (quantum computers) that make direct use of quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. Quantum computers are different from digital computers based on transistors. Whereas digital computers require data to be encoded into binary digits (bits), each of which is always in one of two definite states (0 or 1), quantum computation uses quantum bits (qubits), which can be in superpositions of states. A quantum Turing machine is a theoretical model of such a computer, and is also known as the universal quantum computer. Quantum computers share theoretical similarities with non-deterministic and probabilistic computers. The field of quantum computing was initiated by the work of Yuri Manin in 1980, Richard Feynman in 1982, and David Deutsch in 1985. A quantum computer with spins as quantum bits was also formulated for use as a quantum space–time in 1968.As of 2015, the development of actual quantum computers is still in its infancy, but experiments have been carried out in which quantum computational operations were executed on a very small number of quantum bits. Both practical and theoretical research continues, and many national governments and military agencies are funding quantum computing research in an effort to develop quantum computers for civilian, business, trade, and national security purposes, such as cryptanalysis.Large-scale quantum computers will be able to solve certain problems much more quickly than any classical computers that use even the best currently known algorithms, like integer factorization using Shor's algorithm or the simulation of quantum many-body systems. There exist quantum algorithms, such as Simon's algorithm, that run faster than any possible probabilistic classical algorithm.Given sufficient computational resources, however, a classical computer could be made to simulate any quantum algorithm, as quantum computation does not violate the Church–Turing thesis.