The Underground Economy - Causes, Extent, Approaches
... One should not think of the underground economy public policy is multifaceted and potentially signifias only black markets or smuggling on irregular marcant, and has been much debated by economists and kets. The irregular economy mainly includes othernon-economists. One standard criticism against th ...
... One should not think of the underground economy public policy is multifaceted and potentially signifias only black markets or smuggling on irregular marcant, and has been much debated by economists and kets. The irregular economy mainly includes othernon-economists. One standard criticism against th ...
Optimal Monetary Policy in Open Economies
... e.g., Curdia and Woodford (2009). Analogous trade-o¤s naturally and most plausibly arise in open economies in the form of misalignments in the terms of trade (the relative price of imports in terms of exports) or the real exchange rate (the international relative price of consumption), as well as i ...
... e.g., Curdia and Woodford (2009). Analogous trade-o¤s naturally and most plausibly arise in open economies in the form of misalignments in the terms of trade (the relative price of imports in terms of exports) or the real exchange rate (the international relative price of consumption), as well as i ...
The weakness of business investment in the
... which makes them less suitable for use as collateral, while problems of asymmetric information increase to obtain financing, in comparison with tangible assets. Accordingly, this type of investment is related to the increase in liquid resources of non-financial firms that has occurred during the cri ...
... which makes them less suitable for use as collateral, while problems of asymmetric information increase to obtain financing, in comparison with tangible assets. Accordingly, this type of investment is related to the increase in liquid resources of non-financial firms that has occurred during the cri ...
Trying to Make Sense of the Principle of Effective Demand
... equivalent to maximization of the realized profit or to realization of the maximum profit respectively. (Since all of this plays an important role in my own reinterpretation of the Principle of Effective Demand I relegate an in-depth discussion of these topics to the third section of this paper.) If ...
... equivalent to maximization of the realized profit or to realization of the maximum profit respectively. (Since all of this plays an important role in my own reinterpretation of the Principle of Effective Demand I relegate an in-depth discussion of these topics to the third section of this paper.) If ...
Intersectoral Linkages, Diverse Information, and Aggregate
... observe their own productivity, which is idiosyncratic to their sector, the price of their output, and the prices of those goods that are inputs in their production.4 If firms use only a small subset of all intermediate inputs, as is realistically the case, then they will have only a limited local s ...
... observe their own productivity, which is idiosyncratic to their sector, the price of their output, and the prices of those goods that are inputs in their production.4 If firms use only a small subset of all intermediate inputs, as is realistically the case, then they will have only a limited local s ...
Utility Maximization
... If this does not hold, a household would be better off reallocating expenditures Marginal utility per dollar indicates addition in total utility from spending an additional dollar on a commodity If marginal utility per dollar for one commodity is higher than that for another commodity Household ca ...
... If this does not hold, a household would be better off reallocating expenditures Marginal utility per dollar indicates addition in total utility from spending an additional dollar on a commodity If marginal utility per dollar for one commodity is higher than that for another commodity Household ca ...
Infrastructure and Social Welfare in Metropolitan America
... works in the productivity literature implies that employees will choose to arrive early at work, increasing their output. But at least some workers will likely claim at least a portion of the time for themselves, by eating breakfast with their families or reading the paper longer each morning. This ...
... works in the productivity literature implies that employees will choose to arrive early at work, increasing their output. But at least some workers will likely claim at least a portion of the time for themselves, by eating breakfast with their families or reading the paper longer each morning. This ...
Textbook of Economics
... that many students have deficiencies in mathematics as many of them had finished high school years ago. Therefore where mathematics is necessary a Math Box is included. Each chapter is followed by Numerical Examples that can be used in seminars to practice the acquired knowledge. The examples and th ...
... that many students have deficiencies in mathematics as many of them had finished high school years ago. Therefore where mathematics is necessary a Math Box is included. Each chapter is followed by Numerical Examples that can be used in seminars to practice the acquired knowledge. The examples and th ...
Entrepreneurship and economic development: Theory - UNU
... For instance Shane and Venkataraman (2000) define an `opportunity' as when goods can be sold at a profit. From a development perspective this is inadequate because it implies that utility from ...
... For instance Shane and Venkataraman (2000) define an `opportunity' as when goods can be sold at a profit. From a development perspective this is inadequate because it implies that utility from ...
11 PERFECT COMPETITION
... multiplied by 2). Total cost is $30, so economic profit is −$10. Pat’s shutdown point is at a price of $10 a pizza. The shutdown point is the price that equals minimum average variable cost. To calculate total variable cost, subtract total fixed cost ($10, which is total cost at zero output) from to ...
... multiplied by 2). Total cost is $30, so economic profit is −$10. Pat’s shutdown point is at a price of $10 a pizza. The shutdown point is the price that equals minimum average variable cost. To calculate total variable cost, subtract total fixed cost ($10, which is total cost at zero output) from to ...
12.2 Utility Functions and Probabilities
... this decision should be independentof how much consumption you will have in the other state of nature-how much wealth you will have if the house is not destroyed. For the house will either burn down or it won't. If it happens to burn down, then the value of extra wealth shouldn't depend on how much ...
... this decision should be independentof how much consumption you will have in the other state of nature-how much wealth you will have if the house is not destroyed. For the house will either burn down or it won't. If it happens to burn down, then the value of extra wealth shouldn't depend on how much ...
Chapter 1
... 56. You have one dollar to spend on a vending machine snack. A bag of chips will cost you $1 and the candy bar will also cost you $1. If you choose the bag of chips, the opportunity cost of buying the chips is: A. $1 plus the enjoyment you would have received from the candy bar. B. $2 minus the enjo ...
... 56. You have one dollar to spend on a vending machine snack. A bag of chips will cost you $1 and the candy bar will also cost you $1. If you choose the bag of chips, the opportunity cost of buying the chips is: A. $1 plus the enjoyment you would have received from the candy bar. B. $2 minus the enjo ...
The Optimal Composition of Public Spending in a Deep Recession
... based on optimal fiscal plans in which only public consumption is adjusted, as is the case in existing studies. When we exclude public investment from the set of policy instruments that are available to the policymaker, the optimal plan is such that the cumulative increase in public spending is vir ...
... based on optimal fiscal plans in which only public consumption is adjusted, as is the case in existing studies. When we exclude public investment from the set of policy instruments that are available to the policymaker, the optimal plan is such that the cumulative increase in public spending is vir ...
Other-Regarding Preferences in General Equilibrium - U
... As separability is necessary and sufficient, we characterize completely the kind of ORP that do not affect market behaviour. It is thus possible to compare the outcomes of a general-equilibrium model with ORP to those of a classical model in which each agent maximizes a utility function that depends ...
... As separability is necessary and sufficient, we characterize completely the kind of ORP that do not affect market behaviour. It is thus possible to compare the outcomes of a general-equilibrium model with ORP to those of a classical model in which each agent maximizes a utility function that depends ...
Optimally Sticky Prices
... social surplus with the consumers, but the shares are the same whether the consumers are all uninformed or all informed. In the presence of additional assumptions about preferences (e.g., quadratic), it is possible to derive qualitative but testable implications of our models. For given preferences ...
... social surplus with the consumers, but the shares are the same whether the consumers are all uninformed or all informed. In the presence of additional assumptions about preferences (e.g., quadratic), it is possible to derive qualitative but testable implications of our models. For given preferences ...
Econ 1000: Mod 4, Lecture 8 - Leona Craig Art Gallery, Red
... wages, they will be able to buy 10% less, in goods and services, with their money. If people who want to work and earn a living are unable to find employment, they will not be able to buy anything or they will have to dip into their savings from past earnings, if they have any. The person loses well ...
... wages, they will be able to buy 10% less, in goods and services, with their money. If people who want to work and earn a living are unable to find employment, they will not be able to buy anything or they will have to dip into their savings from past earnings, if they have any. The person loses well ...
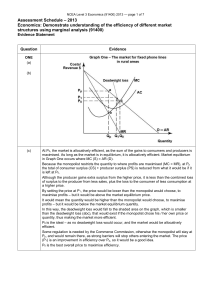
Assessment Schedule – 2013
... This means that market supply in Graph Five shifts in the long run to SLR, causing the market price to fall. Since the perfect competitor accepts the market price, the price they receive also falls (as does their MR). Since MR is now less than MC at Q1, they will not want to produce this quantity – ...
... This means that market supply in Graph Five shifts in the long run to SLR, causing the market price to fall. Since the perfect competitor accepts the market price, the price they receive also falls (as does their MR). Since MR is now less than MC at Q1, they will not want to produce this quantity – ...