Vertical Agreements: Motivation and Impact
... operating at the same level of the production or distribution chain, i.e., competing firms) and vertical agreements. After World War II, this approach found support in a number of empirical studies that tended to show a positive relationship between dense market structures and price and profit level ...
... operating at the same level of the production or distribution chain, i.e., competing firms) and vertical agreements. After World War II, this approach found support in a number of empirical studies that tended to show a positive relationship between dense market structures and price and profit level ...
Stock Prices as a Leading Indicator of Economic activity
... formulation of monetary policy. Central banks are moving away from policies based on the management of intermediate targets and towards frameworks defined in terms of the ultimate policy objectives using indicators or information variables to guide policy towards those objectives. Monetary policy ha ...
... formulation of monetary policy. Central banks are moving away from policies based on the management of intermediate targets and towards frameworks defined in terms of the ultimate policy objectives using indicators or information variables to guide policy towards those objectives. Monetary policy ha ...
Business Cycle Accounting
... models with various types of frictions, is equivalent to a prototype model with various types of time-varying wedges that distort the equilibrium decisions of agents operating in otherwise competitive markets. At face value, these wedges look like time-varying productivity, labor income taxes, inves ...
... models with various types of frictions, is equivalent to a prototype model with various types of time-varying wedges that distort the equilibrium decisions of agents operating in otherwise competitive markets. At face value, these wedges look like time-varying productivity, labor income taxes, inves ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES BUSINESS CYCLE ACCOUNTING V.V. Chari Patrick J. Kehoe
... Our method has two components: an equivalence result and an accounting procedure. The equivalence result is that a large class of models, including models with various types of frictions, are equivalent to a prototype model with various types of time-varying wedges that distort the equilibrium decis ...
... Our method has two components: an equivalence result and an accounting procedure. The equivalence result is that a large class of models, including models with various types of frictions, are equivalent to a prototype model with various types of time-varying wedges that distort the equilibrium decis ...
the aggregate market
... The basic setup, shape, and position of the aggregate demand curve on a graph. The AD curve shows the negative relationship between the price level and real GDP. What causes the negative slope of the AD curve--namely: 1) the real-balance effect, 2) the interest-rate effect, and 3) the net-export eff ...
... The basic setup, shape, and position of the aggregate demand curve on a graph. The AD curve shows the negative relationship between the price level and real GDP. What causes the negative slope of the AD curve--namely: 1) the real-balance effect, 2) the interest-rate effect, and 3) the net-export eff ...
Financial Collateral and Macroeconomic Amplification∗
... relates to Oehmke (2014), who analyzes the dynamics of repo liquidations in the presence of …nancial intermediaries’default. Unlike our model, the liquidation strategies of repo lenders are driven both by strategic considerations and by lenders’ balance sheet constraints. Parlatore (2015) provides a ...
... relates to Oehmke (2014), who analyzes the dynamics of repo liquidations in the presence of …nancial intermediaries’default. Unlike our model, the liquidation strategies of repo lenders are driven both by strategic considerations and by lenders’ balance sheet constraints. Parlatore (2015) provides a ...
FAILING FIRMS AND SUCCESSFUL ENTREPRENEURS: SERIAL
... This leads us to the central question of this paper: Given what we think we know about firm success and failure, namely that most firms fail, can we say anything about the possible success or failure of entrepreneurs? In the following pages we argue that irrespective of what we might believe the fa ...
... This leads us to the central question of this paper: Given what we think we know about firm success and failure, namely that most firms fail, can we say anything about the possible success or failure of entrepreneurs? In the following pages we argue that irrespective of what we might believe the fa ...
Mega Quiz File (ECO401) Shahzad Sadiq Attock VU Group
... this would reduce the purchasing power of labourers as consumers. This in turn would bleaken firms’ prospects of selling more goods, hence inducing them to cut their investment (and hence labour) demand. the unemployment was caused by frictional and structural factors. wages would fall more than req ...
... this would reduce the purchasing power of labourers as consumers. This in turn would bleaken firms’ prospects of selling more goods, hence inducing them to cut their investment (and hence labour) demand. the unemployment was caused by frictional and structural factors. wages would fall more than req ...
Sharing a Ride on the Commodities Roller Coaster
... GDP for a pool of 13 small EMEs using simple averages.1 In the years that preceded the crisis income increased up to 4 percentage points above its trend while commodities did so by more than 50 points. The financial crisis materialized in a sharp fall in economic activity, with real output bottoming ...
... GDP for a pool of 13 small EMEs using simple averages.1 In the years that preceded the crisis income increased up to 4 percentage points above its trend while commodities did so by more than 50 points. The financial crisis materialized in a sharp fall in economic activity, with real output bottoming ...
AP Economics
... A. Explicit and Implicit Costs 5 Point Total 1 Point- definition of explicit costs (traditional out of pocket costs) 1 Point- Example showing explicit costs (costs to a firm or a consumer) 1 Point- definition of implicit costs (opportunity costs that a firm or person must “pay” to themselves) 1 Poi ...
... A. Explicit and Implicit Costs 5 Point Total 1 Point- definition of explicit costs (traditional out of pocket costs) 1 Point- Example showing explicit costs (costs to a firm or a consumer) 1 Point- definition of implicit costs (opportunity costs that a firm or person must “pay” to themselves) 1 Poi ...
- Rainer Maurer
... ■ The formation of neoclassical theory cannot be attributed to a single person – contrary to the Keynesian theory. ■ Neoclassical theory emerged over the centuries and embraces the ideas about the working mechanisms of a market economy of several generations of economists. ■ Common for all these eco ...
... ■ The formation of neoclassical theory cannot be attributed to a single person – contrary to the Keynesian theory. ■ Neoclassical theory emerged over the centuries and embraces the ideas about the working mechanisms of a market economy of several generations of economists. ■ Common for all these eco ...
kalecki`s long-run theory of effective demand
... innovation, Kalecki’s 1939 model avoids the main problem of dynamical linear models, whereby a small change in the value of the parameters may radically change the nature of the solution; especially by changing cycles of constant amplitude into a solution giving rise to explosive or damped cycles. I ...
... innovation, Kalecki’s 1939 model avoids the main problem of dynamical linear models, whereby a small change in the value of the parameters may radically change the nature of the solution; especially by changing cycles of constant amplitude into a solution giving rise to explosive or damped cycles. I ...
Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, 8e
... economyʹs output was the sum of four types of spending: consumer expenditure, planned investment spending, government spending, and net exports. B) Keynes recognized that equilibrium would occur in the economy when total quantity of output supplied equals quantity of output demanded (Y ad ), that is ...
... economyʹs output was the sum of four types of spending: consumer expenditure, planned investment spending, government spending, and net exports. B) Keynes recognized that equilibrium would occur in the economy when total quantity of output supplied equals quantity of output demanded (Y ad ), that is ...
Globalization - Russell Trenholme
... leaders of other advanced industrialized nations. Free trade continues to be nearly universally defended, although many of the accompanying doctrines of the “Washington Consensus”—deregulation, privatization, and fiscal austerity—have yet to recover their former status. Since this book is principall ...
... leaders of other advanced industrialized nations. Free trade continues to be nearly universally defended, although many of the accompanying doctrines of the “Washington Consensus”—deregulation, privatization, and fiscal austerity—have yet to recover their former status. Since this book is principall ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES RATIONAL INFLATIONARY BUBBLES Herschel i. Grossman
... difference equation that is obtained by setting the solution to the associated homogeneous equation equal to zero. They define other solutions to the homogeneous equation to be the rational.bubbles component of the price level. Defined in this way, the market—fundamentals component relates the curre ...
... difference equation that is obtained by setting the solution to the associated homogeneous equation equal to zero. They define other solutions to the homogeneous equation to be the rational.bubbles component of the price level. Defined in this way, the market—fundamentals component relates the curre ...
PDF
... While a feedlot may be in a packer’s primary market area, this masks much potential instability in the relationship between the feedlot and the packer. As noted by Gort (1963), a given industry may be quite concentrated but still competitive, if the stability of relationships within the industry is ...
... While a feedlot may be in a packer’s primary market area, this masks much potential instability in the relationship between the feedlot and the packer. As noted by Gort (1963), a given industry may be quite concentrated but still competitive, if the stability of relationships within the industry is ...
Theory of Consumer Behavior
... Mr. H. Gossen, a German economist, was first to explain this law in 1854. Alfred Marshal later on restated this law in the following words: “The additional benefit which a person derives from an increase of his stock of a thing diminishes with every increase in the stock that already has”. ...
... Mr. H. Gossen, a German economist, was first to explain this law in 1854. Alfred Marshal later on restated this law in the following words: “The additional benefit which a person derives from an increase of his stock of a thing diminishes with every increase in the stock that already has”. ...
Thermal Treatment and Incineration of Wastes
... Clarity regarding vision for ports Lead in time of investment Significant development plans Expedite administrative process for developments ...
... Clarity regarding vision for ports Lead in time of investment Significant development plans Expedite administrative process for developments ...
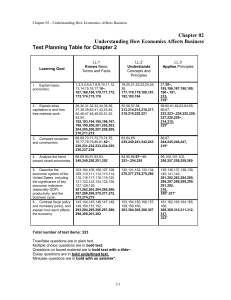
Chapter 02 Understanding How Economics Affects Business
... western suburb of Chicago, Illinois. One of the benefits of her arrangement was that she could attend the community college near her family's residence. When she arrived at her new job, she experienced the differences from a predominately socialist nation and a capitalist nation. Abby noted that pub ...
... western suburb of Chicago, Illinois. One of the benefits of her arrangement was that she could attend the community college near her family's residence. When she arrived at her new job, she experienced the differences from a predominately socialist nation and a capitalist nation. Abby noted that pub ...
Principles Of Economics
... Material from the First Edition’s Chapters 1 and 2 have been reworked and condensed into Chapter 1, to more clearly and efficiently prepare students for the economic way of thinking and the approach to learning economics used in the text. Chapter 2 presents comparative advantage as the basis for exc ...
... Material from the First Edition’s Chapters 1 and 2 have been reworked and condensed into Chapter 1, to more clearly and efficiently prepare students for the economic way of thinking and the approach to learning economics used in the text. Chapter 2 presents comparative advantage as the basis for exc ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... National Bureau of Economic Research
... Under this principle, nonmarket goods and services should be treated as if they were produced and consumed as market activities. The accounts would include a full set of current and capital accounts, modeled after those of systems of market-based accounts. Nordhaus emphasizes that the single most im ...
... Under this principle, nonmarket goods and services should be treated as if they were produced and consumed as market activities. The accounts would include a full set of current and capital accounts, modeled after those of systems of market-based accounts. Nordhaus emphasizes that the single most im ...