Answers - Pearson-Global
... (a) The prices of CDs in Tamer’s shop have been falling recently. He has not been able to sell the CDs because people do not want to buy them. This is because many people prefer to download music from the internet and listen to it using an iPod. Tamer has lowered prices to encourage his customers to ...
... (a) The prices of CDs in Tamer’s shop have been falling recently. He has not been able to sell the CDs because people do not want to buy them. This is because many people prefer to download music from the internet and listen to it using an iPod. Tamer has lowered prices to encourage his customers to ...
Whence Reform? A Critique of the Stiglitz Perspective
... inputs (of labour and capital), and to enable them to respond flexibly in future to changes in supply and demand conditions. Of course, if real wages were perfectly flexible and labour and capital resources were perfectly moveable, then no fall of output would be necessary. However, they are not, an ...
... inputs (of labour and capital), and to enable them to respond flexibly in future to changes in supply and demand conditions. Of course, if real wages were perfectly flexible and labour and capital resources were perfectly moveable, then no fall of output would be necessary. However, they are not, an ...
Ch15.aggregate demand - Emporia State University
... • The long-run aggregate-supply curve is vertical at the natural rate of output, which is the production of goods and services that an economy achieves in the long run when unemployment is at its normal rate. – This level of production is also referred to as potential output or full-employment outpu ...
... • The long-run aggregate-supply curve is vertical at the natural rate of output, which is the production of goods and services that an economy achieves in the long run when unemployment is at its normal rate. – This level of production is also referred to as potential output or full-employment outpu ...
PDF
... follows, time will also be money, since we choose the wage rate as the numeraire. Some agents additionally receive a share of firm profits. Agents owning only labor we call laborers; those • owning labor and profit shares we call capitalists. consumer/laborers) and i ...
... follows, time will also be money, since we choose the wage rate as the numeraire. Some agents additionally receive a share of firm profits. Agents owning only labor we call laborers; those • owning labor and profit shares we call capitalists. consumer/laborers) and i ...
"Policies to promote entrepreneurship"
... society and the economy and this view underlies much of the general policy support for enterprise in society mentioned at the start of this paper. This view can also be seen as suggesting that entrepreneurship is temporary and when s/he ceases to develop new products or services or develop the organ ...
... society and the economy and this view underlies much of the general policy support for enterprise in society mentioned at the start of this paper. This view can also be seen as suggesting that entrepreneurship is temporary and when s/he ceases to develop new products or services or develop the organ ...
TRANSNATIONAL MARKETS AND THE POLANYI PROBLEM
... specialised machines that require a steady flow of marketable resources in inputs and outputs. In order to keep the productive circuit running smoothly and profitable, then, labour, land and money needed to be turned into commodities that would be readily available on demand. This is the technologic ...
... specialised machines that require a steady flow of marketable resources in inputs and outputs. In order to keep the productive circuit running smoothly and profitable, then, labour, land and money needed to be turned into commodities that would be readily available on demand. This is the technologic ...
krugman_mods_3e_irm_micro_econ_mod20
... from the doughnut holes. If you like, bring something for them to drink (say, orange juice) and discuss complements! Once your final data is recorded, calculate total utility and graph total and marginal utility. If you don’t want to bring food to class, or if you have no volunteers for the exercise ...
... from the doughnut holes. If you like, bring something for them to drink (say, orange juice) and discuss complements! Once your final data is recorded, calculate total utility and graph total and marginal utility. If you don’t want to bring food to class, or if you have no volunteers for the exercise ...
The impact of international capital flows on the South Africa... since the end of apartheid Seeraj Mohamed
... improved access to credit for productive investment and employment creation. Instead, easier access to credit has supported existing negative trends in the economy. For example, the exuberance in the stock market experienced from the early-1990s that led to higher share prices seems to have continu ...
... improved access to credit for productive investment and employment creation. Instead, easier access to credit has supported existing negative trends in the economy. For example, the exuberance in the stock market experienced from the early-1990s that led to higher share prices seems to have continu ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... National Bureau of Economic Research
... observed investment. In fact, the correlation is, I believe, a little bit negative. Central to the subject of this conference is that the amount of capital that that calculation reveals is about double the recorded amount of capital. In other words, we have as much intangible capital as we have tang ...
... observed investment. In fact, the correlation is, I believe, a little bit negative. Central to the subject of this conference is that the amount of capital that that calculation reveals is about double the recorded amount of capital. In other words, we have as much intangible capital as we have tang ...
The Composition of Capital Inflows When Emerging
... firms. Domestic agents take the world interest rate as given. There are two kinds of foreign agents: the aforementioned multinational firms who search to purchase domestic firms and the global credit market of one-period bonds that determines the world real interest rate. Unlike the domestic firms t ...
... firms. Domestic agents take the world interest rate as given. There are two kinds of foreign agents: the aforementioned multinational firms who search to purchase domestic firms and the global credit market of one-period bonds that determines the world real interest rate. Unlike the domestic firms t ...
Investment Hangover and the Great Recessionâ
... will analyze situations in which the economy starts with excess residential capital, h0 > h (see Eq. (16) below). This assumption can be thought of as capturing an unmodeled overbuilding episode that took place before the start of our model. We are agnostic about the reason for overbuilding, which c ...
... will analyze situations in which the economy starts with excess residential capital, h0 > h (see Eq. (16) below). This assumption can be thought of as capturing an unmodeled overbuilding episode that took place before the start of our model. We are agnostic about the reason for overbuilding, which c ...
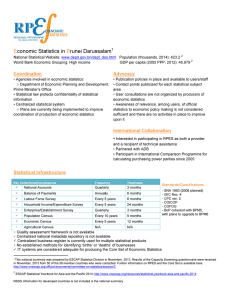
E B conomic Statistics in runei Darussalam
... Standards/Classifications - SNA 1993 (2008 planned) - ISIC Rev. 4 - CPC ver. 2 - COICOP - COFOG - BoP coherent with BPM5, with plans to upgrade to BPM6 ...
... Standards/Classifications - SNA 1993 (2008 planned) - ISIC Rev. 4 - CPC ver. 2 - COICOP - COFOG - BoP coherent with BPM5, with plans to upgrade to BPM6 ...
Capital Flight and the Hollowing Out of the Philippine Economy in
... of basic human needs, including human development.1 Moreover, it is argued that a neoliberal environment benefits everyone rather than only an influential segment in society. Proponents of neoliberal economic policies also argue that this idea is self-evident and it will be realized if, for example, ...
... of basic human needs, including human development.1 Moreover, it is argued that a neoliberal environment benefits everyone rather than only an influential segment in society. Proponents of neoliberal economic policies also argue that this idea is self-evident and it will be realized if, for example, ...
Rothbard on Consumer Sovereignty and His Implicit Rejection of
... In economic theory, the classical “theorem” was transformed by the Austrian theory of value and cost. In its most advance formulation, the entrepreneur function represents all of the distinctly human use of means – i.e., production of goods. The entrepreneur earns profit (ibid.: 252). The ultimate s ...
... In economic theory, the classical “theorem” was transformed by the Austrian theory of value and cost. In its most advance formulation, the entrepreneur function represents all of the distinctly human use of means – i.e., production of goods. The entrepreneur earns profit (ibid.: 252). The ultimate s ...
Text of Chapter 4 from Perman et al
... generations. The first question that then arises is: what are the interests of future generations? The next question then is: how do we look after those interests? This second question itself involves two stages. First, the identification of current policy objectives that look after future interests ...
... generations. The first question that then arises is: what are the interests of future generations? The next question then is: how do we look after those interests? This second question itself involves two stages. First, the identification of current policy objectives that look after future interests ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TOWARDS A THEORY OF FIRM ENTRY
... augmenting standard VAR models with measures of new …rm incorporations and net business formation. Second, we build a stylized sticky price model of monetary policy when …rm entry is endogenous. Firms must prepay a (possibly time-varying) …xed cost in the period prior to production, which is the cos ...
... augmenting standard VAR models with measures of new …rm incorporations and net business formation. Second, we build a stylized sticky price model of monetary policy when …rm entry is endogenous. Firms must prepay a (possibly time-varying) …xed cost in the period prior to production, which is the cos ...
Algebraic Production Functions and Their Uses Before Cobb
... production functions developed hand-in-hand with the theory of marginal productivity. That theory progressed from eighteenth century statements of the law of diminishing returns to late nineteenth and early twentieth century proofs of the product-exhaustion theorem. Each stage saw production functio ...
... production functions developed hand-in-hand with the theory of marginal productivity. That theory progressed from eighteenth century statements of the law of diminishing returns to late nineteenth and early twentieth century proofs of the product-exhaustion theorem. Each stage saw production functio ...
From Capital Control to Capital`s Control : Political Economy of
... we will examine next section. In addition, capital controls have been implemented effectively in reality even in the 90s in Chile and Malaysia.4 Of course, faced with this critic and reality that mere financial opening and international capital flows are apt to destabilize economies, neoclassicals ...
... we will examine next section. In addition, capital controls have been implemented effectively in reality even in the 90s in Chile and Malaysia.4 Of course, faced with this critic and reality that mere financial opening and international capital flows are apt to destabilize economies, neoclassicals ...
Medium Term Business Cycles in Developing Countries
... frequency component and a medium term component. The high frequency component captures ‡uctuations with periods smaller than 8 years while the medium term component captures ‡uctuations with periods between 8 and 50 years. We use a Hodrick-Prescott …lter to isolate ‡uctuations at the high frequency ...
... frequency component and a medium term component. The high frequency component captures ‡uctuations with periods smaller than 8 years while the medium term component captures ‡uctuations with periods between 8 and 50 years. We use a Hodrick-Prescott …lter to isolate ‡uctuations at the high frequency ...