State Intervention – Growth and Development
... Since the financial crisis of 2008 many countries have struggled to maintain manageable budget deficits as their economies contract. With revenue down from reduced economic activity and increasing expenditure on items such as social welfare, governments around the world are either tightening their b ...
... Since the financial crisis of 2008 many countries have struggled to maintain manageable budget deficits as their economies contract. With revenue down from reduced economic activity and increasing expenditure on items such as social welfare, governments around the world are either tightening their b ...
Sectors of the economy
... The Market Market: A place or situation where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services Market in the Economy: Goods and Services Market: Traditional sense of market Exchange prices for items Resource Market: Producer use recourse inputs Inputs of production are capital, enterprise, land and la ...
... The Market Market: A place or situation where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services Market in the Economy: Goods and Services Market: Traditional sense of market Exchange prices for items Resource Market: Producer use recourse inputs Inputs of production are capital, enterprise, land and la ...
Chapter 12.3 Notes
... increase investment + capital deepening if the imports consist of investment goods(structures + equipment) rather than consumer goods Technological Progress -an increase in efficiency gained by producing more output without using more inputs -factors contributing to technological progress -Scientifi ...
... increase investment + capital deepening if the imports consist of investment goods(structures + equipment) rather than consumer goods Technological Progress -an increase in efficiency gained by producing more output without using more inputs -factors contributing to technological progress -Scientifi ...
Modernization Theory Rostow`s Stages of Economic Growth
... Stage 1 Traditional Society - The economy is dominated by subsistence activity. Output is consumed by producers; it is not traded. Trade is barter where goods are exchanged directly for other goods. Agriculture is the most important industry. Production is labour intensive using only limited quantit ...
... Stage 1 Traditional Society - The economy is dominated by subsistence activity. Output is consumed by producers; it is not traded. Trade is barter where goods are exchanged directly for other goods. Agriculture is the most important industry. Production is labour intensive using only limited quantit ...
Ch. 2 Economics Systems
... What is a mixed economy? There is no such thing as a pure free enterprise (market) economy. In the US, govt. controls a bunch of stuff. 10. Why is a mixed economy not considered a major economic system along with free enterprise and ...
... What is a mixed economy? There is no such thing as a pure free enterprise (market) economy. In the US, govt. controls a bunch of stuff. 10. Why is a mixed economy not considered a major economic system along with free enterprise and ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... Self correcting The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
... Self correcting The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
Economics Notes
... What does GDP mean? The value of all goods and services produced by a country in a set time; it measures the economic health of a country. What is GDP per capita? The average income of a household in one year What are entrepreneurs? People who take risks to start their own business Why are they impo ...
... What does GDP mean? The value of all goods and services produced by a country in a set time; it measures the economic health of a country. What is GDP per capita? The average income of a household in one year What are entrepreneurs? People who take risks to start their own business Why are they impo ...
“Classical” economic theory and “Keynesian
... Self correcting The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
... Self correcting The very act of producing goods generates an amount of income = to the value of the goods produced. “Supply Creates Its Own Demand” There will always be sufficient consumption Works as a “LONG RUN” view ...
Economic Systems
... Working Economic Systems • Market Economy- economic system in which decisions of production and consumption are made by individuals, it is a voluntary system of exchange in a marketplace, guided by self interest. – Market is based on the competition between producers for the dollars of consumers – ...
... Working Economic Systems • Market Economy- economic system in which decisions of production and consumption are made by individuals, it is a voluntary system of exchange in a marketplace, guided by self interest. – Market is based on the competition between producers for the dollars of consumers – ...
Fiscal Policy - Mr. Catalano
... • Many people are getting laid off from their jobs • People have less discretionary income, so aggregate demand (spending) is down • Businesses continue to suffer and are forced to lay off more and more workers ...
... • Many people are getting laid off from their jobs • People have less discretionary income, so aggregate demand (spending) is down • Businesses continue to suffer and are forced to lay off more and more workers ...
Unit 1 Notes - Alvinisd.net
... Ricardo argued that there is mutual benefit from trade even if one party (e.g. resource-rich country, highly-skilled artisan) is more productive in every possible area than its trading counterpart (e.g. resource-poor country, unskilled laborer). As long as each concentrates on the activities where i ...
... Ricardo argued that there is mutual benefit from trade even if one party (e.g. resource-rich country, highly-skilled artisan) is more productive in every possible area than its trading counterpart (e.g. resource-poor country, unskilled laborer). As long as each concentrates on the activities where i ...
Economics Unit 3 Markets
... (a) strong government control of the economy. (b) limited government intervention in the economy. (c) no government intervention in the economy. (d) government control of manufacturing only. ...
... (a) strong government control of the economy. (b) limited government intervention in the economy. (c) no government intervention in the economy. (d) government control of manufacturing only. ...
Factors of Economic Growth
... between businesses. Can you think of businesses that compete by producing similar products? ...
... between businesses. Can you think of businesses that compete by producing similar products? ...
Economic Activity
... Economic Systems answer these questions… What will be produced? How much will be produced? How will it be distributed? What will it cost? ...
... Economic Systems answer these questions… What will be produced? How much will be produced? How will it be distributed? What will it cost? ...
Economic Understandings
... Government planners 4. In a market economy, how are decisions made? Consumers and the market 5. Who takes the financial risk in starting a new business in a market economy? Individual business people 6. Why do most countries have a mixed economy? Most economies have found they need a mix of free mar ...
... Government planners 4. In a market economy, how are decisions made? Consumers and the market 5. Who takes the financial risk in starting a new business in a market economy? Individual business people 6. Why do most countries have a mixed economy? Most economies have found they need a mix of free mar ...
Choices
... Economists only consider events if there is a market transaction. Economists are less concerned about how many cows we have standing on four feet as they are about how many cows are brought to market. ...
... Economists only consider events if there is a market transaction. Economists are less concerned about how many cows we have standing on four feet as they are about how many cows are brought to market. ...
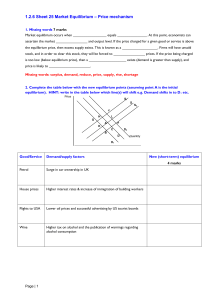
Homework C due 8th May51.5 KB
... ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is known as a __________________. Firms will have unsold stock, and in order to clear this stock, they will be forced to __________ ...
... ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is known as a __________________. Firms will have unsold stock, and in order to clear this stock, they will be forced to __________ ...
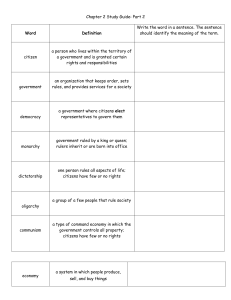
Chapter 2 Study Guide: Part 2 Word Definition Write the word in a
... a group of a few people that rule society ...
... a group of a few people that rule society ...
Chapter 13 vocabulary - Econ
... 19. Demandpull theory- theory that inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds existing supplies ...
... 19. Demandpull theory- theory that inflation occurs when demand for goods and services exceeds existing supplies ...
SEM_I-301
... economy, including full and part-time workers, managers, public employees, and professional people. ...
... economy, including full and part-time workers, managers, public employees, and professional people. ...
Gloom, despair and agony on me
... the economy. It can’t increase spending or cut taxes because of debt and deficits. It can’t lower interest rates much further because they are so low already. Moreover, if government could come up with a plan to stimulate growth, gridlock among the Democrats and the Republicans would prevent its imp ...
... the economy. It can’t increase spending or cut taxes because of debt and deficits. It can’t lower interest rates much further because they are so low already. Moreover, if government could come up with a plan to stimulate growth, gridlock among the Democrats and the Republicans would prevent its imp ...