100學年度基礎學科會考
... ( ) 6. The table above gives the demand schedule for snow peas. If the price of snow peas falls from $4.00 to $3.00 a bushel, total revenue will (A) increase because demand is inelastic in this range. (B) increase because demand is elastic in this range. (C) decrease because demand is elastic in thi ...
... ( ) 6. The table above gives the demand schedule for snow peas. If the price of snow peas falls from $4.00 to $3.00 a bushel, total revenue will (A) increase because demand is inelastic in this range. (B) increase because demand is elastic in this range. (C) decrease because demand is elastic in thi ...
PPT Resources and Natural Capital
... Ecological processes have no formal value Still important though waste elimination, flood & erosion control, nitrogen fixation, photosynthesis Essential for existence but taken for granted ...
... Ecological processes have no formal value Still important though waste elimination, flood & erosion control, nitrogen fixation, photosynthesis Essential for existence but taken for granted ...
Answer the following questions on business organizations
... 11. What is a production possibilities curve and what does it show? The production possibilities curve that shows alternative ways to use an economy’s resources (pg. 13). Can display opportunity cost 12. How do you explain a point on the production possibilities curve? Resources used efficiently 13. ...
... 11. What is a production possibilities curve and what does it show? The production possibilities curve that shows alternative ways to use an economy’s resources (pg. 13). Can display opportunity cost 12. How do you explain a point on the production possibilities curve? Resources used efficiently 13. ...
word document - European Commission
... Herewith we confirm that we will not use the data, specified here above, from the common Eurostat/OECD PPP programme, for any kind of publication and will not make them public in any form. We are aware that we can use the data only for our internal research purposes and we will refrain from providin ...
... Herewith we confirm that we will not use the data, specified here above, from the common Eurostat/OECD PPP programme, for any kind of publication and will not make them public in any form. We are aware that we can use the data only for our internal research purposes and we will refrain from providin ...
eThekwini SMME Strategy - eThekwini Municipality
... disproportionately to their numerical share. This, however, should in no way distract from the organic linkages between SMEs and large firms. All large enterprises rely heavily on SMEs' performance for supply and demand reasons. ...
... disproportionately to their numerical share. This, however, should in no way distract from the organic linkages between SMEs and large firms. All large enterprises rely heavily on SMEs' performance for supply and demand reasons. ...
Economics (25-1)
... • For a country’s long-run growth, education is at least as important as investment in physical capital. – In the United States, each year of schooling raises a person’s wage, on average, by about 10 percent. – Thus, one way the government can enhance the standard of living is to provide schools and ...
... • For a country’s long-run growth, education is at least as important as investment in physical capital. – In the United States, each year of schooling raises a person’s wage, on average, by about 10 percent. – Thus, one way the government can enhance the standard of living is to provide schools and ...
Rules - Economics
... produce. Then, once every firm has decided how much to produce, production takes place and you have to choose the price at which you will sell your goods. For pedagogic reasons and to allow you to correct potential pricing mistakes, you will play the "sales part" twice (but this does not correspond ...
... produce. Then, once every firm has decided how much to produce, production takes place and you have to choose the price at which you will sell your goods. For pedagogic reasons and to allow you to correct potential pricing mistakes, you will play the "sales part" twice (but this does not correspond ...
The `Marginal Revolution` in Economics against the Labour Theory
... no unemployment, and full equilibrium prevails. Hence, any reallocation of resources by governments will break the ‘equilibrium’, for, according to Pareto’s optimality criterion, you cannot make one better off without making another worse off. Thus, governments need not bother about futile economic ...
... no unemployment, and full equilibrium prevails. Hence, any reallocation of resources by governments will break the ‘equilibrium’, for, according to Pareto’s optimality criterion, you cannot make one better off without making another worse off. Thus, governments need not bother about futile economic ...
Indonesia DDO - World Bank Treasury
... unique US$2 billion development policy loan (DPL) with a Deferred Drawdown Option (DDO) for Indonesia. The government could draw down the loan if market conditions deteriorated and its access to international or domestic financial markets became restricted. Indonesia itself imposed conditions for wi ...
... unique US$2 billion development policy loan (DPL) with a Deferred Drawdown Option (DDO) for Indonesia. The government could draw down the loan if market conditions deteriorated and its access to international or domestic financial markets became restricted. Indonesia itself imposed conditions for wi ...
Chapter 11 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... GDP measures the market value of final goods and services produced within a country’s border during a given time period ...
... GDP measures the market value of final goods and services produced within a country’s border during a given time period ...
The broad social goals that relate to economics
... Productive efficiency alone cannot indicate the most appropriate decision to make. An economy may possess productive efficiency in producing good A, for example, but if consumers do not want good A and prefer good B instead, then it would not be allocatively efficient to produce good A. Economics or ...
... Productive efficiency alone cannot indicate the most appropriate decision to make. An economy may possess productive efficiency in producing good A, for example, but if consumers do not want good A and prefer good B instead, then it would not be allocatively efficient to produce good A. Economics or ...
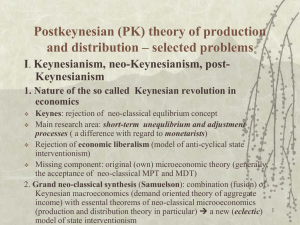
II.1. Critique of MPT/MDT
... classical economy, neoricardianism) Concept of the so called real capital (as the critique of NCE approach towards the capital ) Capital which exists at a given point of time is the (physical) embodiment of time of labor of past periods Capital represents this part of labor resource (in terms of lab ...
... classical economy, neoricardianism) Concept of the so called real capital (as the critique of NCE approach towards the capital ) Capital which exists at a given point of time is the (physical) embodiment of time of labor of past periods Capital represents this part of labor resource (in terms of lab ...
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE 1 GRAAD 12 GRADE 12
... The effect of increasing living standards result in the trading of more goods and services Allows industries that have a comparative advantage with a lower opportunity cost It increases economic efficiency and prevent wasting resources Each country that is best suited for specific goods and ...
... The effect of increasing living standards result in the trading of more goods and services Allows industries that have a comparative advantage with a lower opportunity cost It increases economic efficiency and prevent wasting resources Each country that is best suited for specific goods and ...
Competitive Markets
... resources. In the real world this is rare. Perfect competition is bases on certain assumptions. Flower markets are a perfectly competitive market. The customer chooses whose plants are the best on the market. Pricing makes a different and so does the freshness and types of plants are carried. Also t ...
... resources. In the real world this is rare. Perfect competition is bases on certain assumptions. Flower markets are a perfectly competitive market. The customer chooses whose plants are the best on the market. Pricing makes a different and so does the freshness and types of plants are carried. Also t ...
Where is in the interaction of forms of capital?
... are marginalised. • Without an interaction of capitals, how can inter and ...
... are marginalised. • Without an interaction of capitals, how can inter and ...
Macro_online_chapter_09_14e
... Recognize how the resource market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the loanable funds market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the foreign exchange market is connected to the goods and services market. ...
... Recognize how the resource market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the loanable funds market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the foreign exchange market is connected to the goods and services market. ...
No: 2009-12 31 March 2009 SUMMARY OF THE MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MEETING
... 2. Energy prices dropped by 0.82 percent in February, and annual inflation in this subgroup eased to 13.74 percent, chiefly owing to falling natural gas and solid fuel prices. Yet, the exchange rate-driven sharp rise in fuel and bottled gas prices limited the downtrend in energy price inflation. 3. ...
... 2. Energy prices dropped by 0.82 percent in February, and annual inflation in this subgroup eased to 13.74 percent, chiefly owing to falling natural gas and solid fuel prices. Yet, the exchange rate-driven sharp rise in fuel and bottled gas prices limited the downtrend in energy price inflation. 3. ...
Problems with Neoclassical Growth Model:
... price. Since population is growing and there is a large surplus labor supply in existence, any improvement in technology for the primary industries will likely result in lower cost-a benefit to the primary importing countries. The advice given is usually to increase the production of primary goods ...
... price. Since population is growing and there is a large surplus labor supply in existence, any improvement in technology for the primary industries will likely result in lower cost-a benefit to the primary importing countries. The advice given is usually to increase the production of primary goods ...
conference abstracts
... basic infrastructure and whose residents are currently experiencing a double-dose of austerity. During the economic storm brought on by the end of socialism, Mongolians faced a void left by the sudden withdrawal of state. After the brief mining boom around 2012, the economy is again stalling. Follow ...
... basic infrastructure and whose residents are currently experiencing a double-dose of austerity. During the economic storm brought on by the end of socialism, Mongolians faced a void left by the sudden withdrawal of state. After the brief mining boom around 2012, the economy is again stalling. Follow ...
Social Cooperation and the Process of Economic
... For instance, in an institutional setting like that which characterized East and Central Europe during the 1990s, where there were ineffective courts and insecure property rights, we would expect entrepreneurs to direct their efforts elsewhere from above ground markets ...
... For instance, in an institutional setting like that which characterized East and Central Europe during the 1990s, where there were ineffective courts and insecure property rights, we would expect entrepreneurs to direct their efforts elsewhere from above ground markets ...
Finance, financialization and compressed development
... Minsky synthesises Schumpeter and Keynes: ‘There is not only a price level of current output, but also a price level of capital and financial assets’ (1992: 106) – investment occurs when profits are foreseen in both spheres. Minsky also notes, however, that the Schumpeterian entrepreneur is acti ...
... Minsky synthesises Schumpeter and Keynes: ‘There is not only a price level of current output, but also a price level of capital and financial assets’ (1992: 106) – investment occurs when profits are foreseen in both spheres. Minsky also notes, however, that the Schumpeterian entrepreneur is acti ...