File
... Monetary Policy – regulation of the money supply by the Federal Reserve System Policy that attempts to stabilize the economy by controlling interest rates and the supply of money • Created in 1913 consisting of a 7-member board of governors serving by appointment of the President for staggered 14-ye ...
... Monetary Policy – regulation of the money supply by the Federal Reserve System Policy that attempts to stabilize the economy by controlling interest rates and the supply of money • Created in 1913 consisting of a 7-member board of governors serving by appointment of the President for staggered 14-ye ...
ENV 536: Environmental Economics and Policy (Lecture 4
... Even if consumers could be induced to express their WTP for a public good, it is highly likely that the resulting demand price would underestimate the true benefits. ...
... Even if consumers could be induced to express their WTP for a public good, it is highly likely that the resulting demand price would underestimate the true benefits. ...
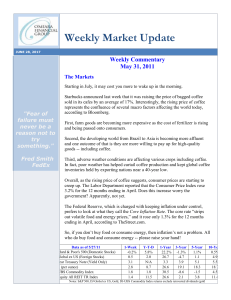
Weekly Market Update - O`Meara Financial Group
... contracts on 19 physical commodities and was launched on July 14, 1998. * The DJ Equity All REIT TR Index measures the total return performance of the equity subcategory of the Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) industry as calculated by Dow Jones. * Yahoo! Finance is the source for any reference t ...
... contracts on 19 physical commodities and was launched on July 14, 1998. * The DJ Equity All REIT TR Index measures the total return performance of the equity subcategory of the Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) industry as calculated by Dow Jones. * Yahoo! Finance is the source for any reference t ...
Folie 1
... 1. The following shall be prohibited as incompatible with the common market: all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between Member States and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or dis ...
... 1. The following shall be prohibited as incompatible with the common market: all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between Member States and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or dis ...
2014 answers - The University of Auckland
... on interest earnings on savings deposits, since interest rates are likely to fall. ...
... on interest earnings on savings deposits, since interest rates are likely to fall. ...
Lecture
... – Any P. optimum can be reached by a p.c.e. with transfers (but only if everyone can use the transfers to adjust consumption!) ...
... – Any P. optimum can be reached by a p.c.e. with transfers (but only if everyone can use the transfers to adjust consumption!) ...
Boxer-ltr-10-27-09.pdf
... Advocacy that is included in the House bill. We agree that this office should be empowered to address long-term climate change policy and its impact on consumers and intercede on their behalf as needed. However, we are concerned that an assured funding stream is needed to guarantee this important co ...
... Advocacy that is included in the House bill. We agree that this office should be empowered to address long-term climate change policy and its impact on consumers and intercede on their behalf as needed. However, we are concerned that an assured funding stream is needed to guarantee this important co ...
Demand - Bank of England
... (b) Data are to 2011 Q4. Includes survey measures of investment intentions from the Bank’s Agents (companies’ intended changes in investment over the next twelve months), BCC (net percentage balance of companies who say they have increased planned investment in plant and machinery over the past thre ...
... (b) Data are to 2011 Q4. Includes survey measures of investment intentions from the Bank’s Agents (companies’ intended changes in investment over the next twelve months), BCC (net percentage balance of companies who say they have increased planned investment in plant and machinery over the past thre ...
Financial Market Crisis as a Phenomenon of - Fritz Breuss
... Between 1929 and 2009, annual average growth of nominal GDP of 6.3 percent was somewhat higher than that of the Dow Jones Index of 4.7 percent. The data base for the period of the Great Depression 1929 to 1933 was probably less than reliable for both series, hence the results may be somewhat distort ...
... Between 1929 and 2009, annual average growth of nominal GDP of 6.3 percent was somewhat higher than that of the Dow Jones Index of 4.7 percent. The data base for the period of the Great Depression 1929 to 1933 was probably less than reliable for both series, hence the results may be somewhat distort ...
Comparing GDP across Countries
... – Ex. Your Swiss food company projects that it can at most get a 20% share of the market for Mexican processed foodstuffs. Converting the size of Mexico’s processed food expenditures from Pesos to Swiss Francs is useful info for estimating profits. . ...
... – Ex. Your Swiss food company projects that it can at most get a 20% share of the market for Mexican processed foodstuffs. Converting the size of Mexico’s processed food expenditures from Pesos to Swiss Francs is useful info for estimating profits. . ...
Expansionary Effects of the Welfare State in a Small Open Economy
... varieties ( xi , i ∈ [0, N ]) that can be thought of as consisting of highly specialised producer services and other intangible inputs such as knowledge. The larger is the mass of intermediates N, the higher will be the degree of specialisation in production and the resulting aggregate efficiency. T ...
... varieties ( xi , i ∈ [0, N ]) that can be thought of as consisting of highly specialised producer services and other intangible inputs such as knowledge. The larger is the mass of intermediates N, the higher will be the degree of specialisation in production and the resulting aggregate efficiency. T ...
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT7 – Business Economics INDICATIVE SOLUTION
... v) Free market - A free market is one in which there is no government intervention; instead, individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions. In a free market, consumers choose what to buy (or demand), while producers choose what to produce (or supply) and how to pro ...
... v) Free market - A free market is one in which there is no government intervention; instead, individual producers and consumers are free to make their own economic decisions. In a free market, consumers choose what to buy (or demand), while producers choose what to produce (or supply) and how to pro ...
Analyze the connection between levels of
... LG1: Interpret data to determine levels of development and standard of living in various societies, analyze the connection between levels of development and economic activities and compare how people satisfy their needs through the production of goods and services. ...
... LG1: Interpret data to determine levels of development and standard of living in various societies, analyze the connection between levels of development and economic activities and compare how people satisfy their needs through the production of goods and services. ...
Econ101.Ch.1.A
... B. The second big question is “When is the pursuit of selfinterest also in the social interest?” 1. People make choices in their own self-interest—they make choices they think are best for their own well-being. a) The incentives surrounding an individual’s choice amongst available alternatives influ ...
... B. The second big question is “When is the pursuit of selfinterest also in the social interest?” 1. People make choices in their own self-interest—they make choices they think are best for their own well-being. a) The incentives surrounding an individual’s choice amongst available alternatives influ ...
INFLATION
... SAYS THAT WITH INFLATION OF 3% PER YEAR, PRICES WILL DOUBLE IN ABOUT 72/3 = 24 YEARS. ...
... SAYS THAT WITH INFLATION OF 3% PER YEAR, PRICES WILL DOUBLE IN ABOUT 72/3 = 24 YEARS. ...
Marginal Utility – the extra usefulness or satisfaction people get from
... Markets • Markets – exchanges between buyers and sellers. • Supply – questions faced by sellers in those exchanges are related to how much to sell and at what price. • Demand – questions faced by buyers – the amount of goods and services consumers are willing to buy at various prices at a particul ...
... Markets • Markets – exchanges between buyers and sellers. • Supply – questions faced by sellers in those exchanges are related to how much to sell and at what price. • Demand – questions faced by buyers – the amount of goods and services consumers are willing to buy at various prices at a particul ...
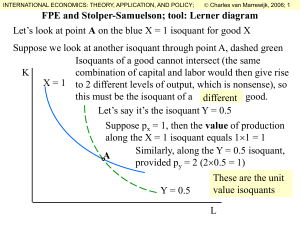
Factor Price Equalization and Stolper
... This determines exactly the values 1/r and 1/w K X=1 This implies that if trade between two countries equalizes the prices of final goods and these two countries have 1/r identical CRS production functions, then the reward to factors of production B w and r are also equalized (FPE) C Y = 0.5 1/w ...
... This determines exactly the values 1/r and 1/w K X=1 This implies that if trade between two countries equalizes the prices of final goods and these two countries have 1/r identical CRS production functions, then the reward to factors of production B w and r are also equalized (FPE) C Y = 0.5 1/w ...
land policy the turn point to the renovation in vietnam
... Ministry of Natural Resources & Environment of Vietnam ...
... Ministry of Natural Resources & Environment of Vietnam ...
Aggregate Demand - Business-TES
... I: Capital Investment – This is investment spending by companies on capital goods such as new plant and equipment and buildings. Investment also includes spending on working capital such as stocks of finished goods and work in progress. Capital investment spending in the UK typically accounts for be ...
... I: Capital Investment – This is investment spending by companies on capital goods such as new plant and equipment and buildings. Investment also includes spending on working capital such as stocks of finished goods and work in progress. Capital investment spending in the UK typically accounts for be ...
General Year 12 sample course outline - SCSA
... This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that ...
... This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that ...
Sample Question Paper 3 Subject: Economics Time: 3 Hours
... Marks for questions are indicated against each. Question number 1-5 and 17 – 21 are very short answer questions carrying one mark each. They are required to be answered in one sentence each. Question number 6-10 and 22 – 26 are short-answer questions carrying three marks each. Answers to them should ...
... Marks for questions are indicated against each. Question number 1-5 and 17 – 21 are very short answer questions carrying one mark each. They are required to be answered in one sentence each. Question number 6-10 and 22 – 26 are short-answer questions carrying three marks each. Answers to them should ...
Slides Class 5 - Rosella Nicolini
... The Weber Location-Production Model • Transfer-oriented firm: transport cost is the dominant factor in the location decision The firm chooses the location that minimizes total transport costs Two types of cost: - Procurement cost is the cost of transporting raw materials from the input source to ...
... The Weber Location-Production Model • Transfer-oriented firm: transport cost is the dominant factor in the location decision The firm chooses the location that minimizes total transport costs Two types of cost: - Procurement cost is the cost of transporting raw materials from the input source to ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... (Marginal) Private cost (MC) is the cost of an economic activity directly borne by the immediate producer or consumer. (It excludes externalities). Marginal external cost is the cost of producing an additional unit of a G or S that falls on people other than the producer or consumer. (Marginal) soci ...
... (Marginal) Private cost (MC) is the cost of an economic activity directly borne by the immediate producer or consumer. (It excludes externalities). Marginal external cost is the cost of producing an additional unit of a G or S that falls on people other than the producer or consumer. (Marginal) soci ...