Syllabus
... Visual Basic & the Oracle DBMS. A stepped approach will be used to gradually and incrementally complete the project within schedule. Also, students will have the opportunity to learn the Oracle Database Management System. Oracle’s interactive tool SQL*PLUS that allows the user to create and manipula ...
... Visual Basic & the Oracle DBMS. A stepped approach will be used to gradually and incrementally complete the project within schedule. Also, students will have the opportunity to learn the Oracle Database Management System. Oracle’s interactive tool SQL*PLUS that allows the user to create and manipula ...
How is database integrity assured within the relational database
... What is a computer file system, and what are its problems? What are the DBMS functions, and why are they important? Describe the database environment and the different types of database systems. What is a Database Model? Why is database design so important? What is data redundancy and which characte ...
... What is a computer file system, and what are its problems? What are the DBMS functions, and why are they important? Describe the database environment and the different types of database systems. What is a Database Model? Why is database design so important? What is data redundancy and which characte ...
A little history…
... – when you tell NHibernate to “save” an object – when you ask NHibernate to search/load objects – can also create all database tables if desired ...
... – when you tell NHibernate to “save” an object – when you ask NHibernate to search/load objects – can also create all database tables if desired ...
What is a Database Management System?
... Basic Concepts • Basic concepts – Different types of DBMS – Advantages over file systems – Two famous RDBMS prototypes ...
... Basic Concepts • Basic concepts – Different types of DBMS – Advantages over file systems – Two famous RDBMS prototypes ...
CS 338 The Relational Data Model and Relational Database
... • Relational database state (instance) of the schema is a set of relation states which satisfy the specified integrity constraints • All integrity constraints must be satisfied for the database to be valid • Each relational DBMS has a Data Definition Language ...
... • Relational database state (instance) of the schema is a set of relation states which satisfy the specified integrity constraints • All integrity constraints must be satisfied for the database to be valid • Each relational DBMS has a Data Definition Language ...
Data Dependence An application program that deals with data
... statement S2 still works properly. That’s because in S1 the value 's01' is assigned to the first column, whichever column that is; in S2 the value 's01' is assigned to the StudentId column, wherever that column appears in the table. The DBMS supports data independence here by making S2 possible in i ...
... statement S2 still works properly. That’s because in S1 the value 's01' is assigned to the first column, whichever column that is; in S2 the value 's01' is assigned to the StudentId column, wherever that column appears in the table. The DBMS supports data independence here by making S2 possible in i ...
Data Modeling using XML Schemas
... on mywpi (limited) + discussion boards (discuss among fellow students) + viewing of grades ...
... on mywpi (limited) + discussion boards (discuss among fellow students) + viewing of grades ...
Syllabus for CSCI 6441: Database Management Systems GWU
... There will be opportunities to individually select and investigate one database topic more deeply. Students will be expected to present their findings to the class. Although presentation skills will not be graded per se, a comfort with public speaking will help make this less arduous. The stated pre ...
... There will be opportunities to individually select and investigate one database topic more deeply. Students will be expected to present their findings to the class. Although presentation skills will not be graded per se, a comfort with public speaking will help make this less arduous. The stated pre ...
Normalisation
... Only need to check for BCNF is when there is more than one candidate key for a relation and at least one of is composite ...
... Only need to check for BCNF is when there is more than one candidate key for a relation and at least one of is composite ...
Nguyen, Yen P
... hold many smaller classes) Object model the real world better than the relational tuples ...
... hold many smaller classes) Object model the real world better than the relational tuples ...
The History of Databases
... independence between programs on the one hand and machine representation on the other.”(Codd 1970) ...
... independence between programs on the one hand and machine representation on the other.”(Codd 1970) ...
Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
... The digital revolution implies abundant and rich data easily available as never before. As the volume of data grows, extracting information gets more and more challenging and the only way to deal with this complexity is through computing and expertise in programming environments. The recent explosio ...
... The digital revolution implies abundant and rich data easily available as never before. As the volume of data grows, extracting information gets more and more challenging and the only way to deal with this complexity is through computing and expertise in programming environments. The recent explosio ...
You have already learned three of most important terms in data
... Page 1 of 1 Access 2003 Handout #3 ...
... Page 1 of 1 Access 2003 Handout #3 ...
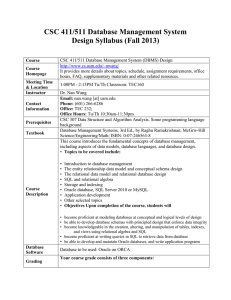
CSC 411/511 Database Management System Design Syllabus (Fall
... CSC 307 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis. Some programming language background Database Management Systems, 3rd Ed., by Raghu Ramakrishnan; McGrw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math; ISBN: 0-07-246563-8 This course introduces the fundamental concepts of database management, including aspects of data ...
... CSC 307 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis. Some programming language background Database Management Systems, 3rd Ed., by Raghu Ramakrishnan; McGrw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math; ISBN: 0-07-246563-8 This course introduces the fundamental concepts of database management, including aspects of data ...
database - CyberInfrastructure and Geospatial Information Laboratory
... o Each tuple contains as many values as there are attributes in the relation scheme o Each data item is drawn from the domain for its attribute o The order of tuples is not significant o Tuples in a relation are all distinct from each other ...
... o Each tuple contains as many values as there are attributes in the relation scheme o Each data item is drawn from the domain for its attribute o The order of tuples is not significant o Tuples in a relation are all distinct from each other ...
Chapter 12 Representing Data Elements
... – How to represent SQL datatypes as fields – How to represent tuples as records – How to represent collections or records in blocks of memory – How to represent and store relations as collections of blocks – How to cope with record sizes – What if the size of a record changes due to updating ...
... – How to represent SQL datatypes as fields – How to represent tuples as records – How to represent collections or records in blocks of memory – How to represent and store relations as collections of blocks – How to cope with record sizes – What if the size of a record changes due to updating ...
Relational model
The relational model for database management is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by Edgar F. Codd. In the relational model of a database, all data is represented in terms of tuples, grouped into relations. A database organized in terms of the relational model is a relational database.The purpose of the relational model is to provide a declarative method for specifying data and queries: users directly state what information the database contains and what information they want from it, and let the database management system software take care of describing data structures for storing the data and retrieval procedures for answering queries.Most relational databases use the SQL data definition and query language; these systems implement what can be regarded as an engineering approximation to the relational model. A table in an SQL database schema corresponds to a predicate variable; the contents of a table to a relation; key constraints, other constraints, and SQL queries correspond to predicates. However, SQL databases deviate from the relational model in many details, and Codd fiercely argued against deviations that compromise the original principles.