View updating Rule
... update, and delete operators. This means that data can be retrieved from a relational database in sets constructed of data from multiple rows and/or multiple tables. This rule states that insert, update, and delete operations should be supported for any retrievable set rather than just for a single ...
... update, and delete operators. This means that data can be retrieved from a relational database in sets constructed of data from multiple rows and/or multiple tables. This rule states that insert, update, and delete operations should be supported for any retrievable set rather than just for a single ...
Database Management Systems
... 1. Simplified design process for the application programmer o In the context of a distributed database (DB spread over several machines in a network) the work of the application program becomes extremely cumbersome o The DBMS allows the application software to be written as though the database was s ...
... 1. Simplified design process for the application programmer o In the context of a distributed database (DB spread over several machines in a network) the work of the application program becomes extremely cumbersome o The DBMS allows the application software to be written as though the database was s ...
South NM Land Links Project - New Mexico State University
... acreage, previous land use, cost/exchange (i.e. rent, sell, share crop, trade, other…) – wanted land: acreage, previous land-use (vegetables, herbs, orchard, beekeeping, organic, pesticide use…), payment/exchange – Other… appropriate associative tables ...
... acreage, previous land use, cost/exchange (i.e. rent, sell, share crop, trade, other…) – wanted land: acreage, previous land-use (vegetables, herbs, orchard, beekeeping, organic, pesticide use…), payment/exchange – Other… appropriate associative tables ...
Relational Calculus
... Algebra and safe calculus have same expressive power, leading to the notion of relational completeness. ...
... Algebra and safe calculus have same expressive power, leading to the notion of relational completeness. ...
Building Applications using SQL Azure
... • CTP cluster has throttling limits turned up to allow for building logic into apps for handling this case • Build in retry logic especially if you expect very high throughput demands • Consider scaling out for high throughput scenarios ...
... • CTP cluster has throttling limits turned up to allow for building logic into apps for handling this case • Build in retry logic especially if you expect very high throughput demands • Consider scaling out for high throughput scenarios ...
Object Composition and Reuse in a Distributed Multimedia
... Object Composition and Reuse in a Distributed Multimedia Database This paper proposes a distributed multimedia database. We use object-oriented methodology with the support of multimedia networking technologies in the design and implementation of our system. The database supports an easy to reuse me ...
... Object Composition and Reuse in a Distributed Multimedia Database This paper proposes a distributed multimedia database. We use object-oriented methodology with the support of multimedia networking technologies in the design and implementation of our system. The database supports an easy to reuse me ...
PPT
... Replicate data over a number of database systems User interact with replicas to balance the workload of the entire system Data update over the entire system is not in the same scope the transactions; the system will propagate the update later for the purpose of better respond time ...
... Replicate data over a number of database systems User interact with replicas to balance the workload of the entire system Data update over the entire system is not in the same scope the transactions; the system will propagate the update later for the purpose of better respond time ...
Chapter 5 Relational Algebra
... INSERT - provides a list of attribute values for a new tuple in a relation. This operator is the same as SQL. DELETE - provides a condition on the attributes of a relation to determine which tuple(s) to remove from the relation. This operator is the same as SQL. MODIFY - changes the values of one or ...
... INSERT - provides a list of attribute values for a new tuple in a relation. This operator is the same as SQL. DELETE - provides a condition on the attributes of a relation to determine which tuple(s) to remove from the relation. This operator is the same as SQL. MODIFY - changes the values of one or ...
XML Data Storage
... – Non-relational data stores • Flat files – Natural for storing XML – But has all problems discussed in Chapter 1 (no concurrency, no recovery, …) • XML database – Database built specifically for storing XML data, supporting DOM model and declarative querying – Currently no commercial-grade systems ...
... – Non-relational data stores • Flat files – Natural for storing XML – But has all problems discussed in Chapter 1 (no concurrency, no recovery, …) • XML database – Database built specifically for storing XML data, supporting DOM model and declarative querying – Currently no commercial-grade systems ...
Hiring in Databases - UBC Department of Computer Science
... Laks V.S. Lakshmanan Dept. of Computer Science Univ. of British Columbia ...
... Laks V.S. Lakshmanan Dept. of Computer Science Univ. of British Columbia ...
comp426-f14-18-Databases
... – Non-identifying attributes are dependent on the entity’s unique identifier. • Rule of thumb: if the same value appears multiple times for a particular attribute, think hard if what you really need is another entity. • In particular, if the same value for the same attribute for two different instan ...
... – Non-identifying attributes are dependent on the entity’s unique identifier. • Rule of thumb: if the same value appears multiple times for a particular attribute, think hard if what you really need is another entity. • In particular, if the same value for the same attribute for two different instan ...
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS 1. Define Database
... P⇒Q means if P is true then Q must be true. 41. Write short notes on domain relational calculus The domain relational calculus uses domain variables that take on values from an attribute domain rather than values for entire tuple. 42. Define query language? A query is a statement requesting the retr ...
... P⇒Q means if P is true then Q must be true. 41. Write short notes on domain relational calculus The domain relational calculus uses domain variables that take on values from an attribute domain rather than values for entire tuple. 42. Define query language? A query is a statement requesting the retr ...
The Worlds of Database Systems
... – Providing a unified view to the database user even if data comes from different sources(legacy databases) using different structures to represent information – Data Warehouses copy information from many legacy databases with appropriate translation to a central ...
... – Providing a unified view to the database user even if data comes from different sources(legacy databases) using different structures to represent information – Data Warehouses copy information from many legacy databases with appropriate translation to a central ...
Lab Session-II CS121 Summer
... Start with a root node (root is at the top as opposed to natural trees) One child is shown on left and the other one is shown on right The children can also have maximum two ...
... Start with a root node (root is at the top as opposed to natural trees) One child is shown on left and the other one is shown on right The children can also have maximum two ...
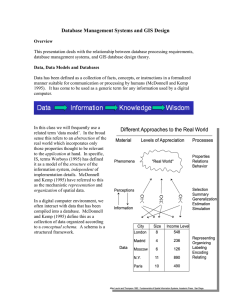
Database Management Systems and GIS Design
... GIS Design To place topics of database and DBMS design in a context for GIS, Worboys (1995) has developed a model for GIS database design. The model responds to the requirements of all information systems and extends it at the beginning to understand the area of use or application domain at hand. T ...
... GIS Design To place topics of database and DBMS design in a context for GIS, Worboys (1995) has developed a model for GIS database design. The model responds to the requirements of all information systems and extends it at the beginning to understand the area of use or application domain at hand. T ...
hypermedia database model
... Data Integrity: It is difficult to place data integrity constraints across multiple data files. Application-Data independence: In the file environment, the applications and their associated data files are dependent on each other. The numerous problems arising from the file environment approach ...
... Data Integrity: It is difficult to place data integrity constraints across multiple data files. Application-Data independence: In the file environment, the applications and their associated data files are dependent on each other. The numerous problems arising from the file environment approach ...
Chapter 17
... clause that identifies ‘compiled code’ in operating system’s file storage. ORDBMS will provide method to dynamically link this object file into the DBMS so that it can be invoked when required. Procedure for this is outside bounds of SQL standard and is left as implementation-defined. ...
... clause that identifies ‘compiled code’ in operating system’s file storage. ORDBMS will provide method to dynamically link this object file into the DBMS so that it can be invoked when required. Procedure for this is outside bounds of SQL standard and is left as implementation-defined. ...
DIS Topic 02: Project Initiation
... SQL, the “Structured Query Language”, has become the standard language for data manipulation in relational databases SQL is a non-procedural language - it specifies what is to be done, not how it is to be done Relatively easy to use for simple queries ...
... SQL, the “Structured Query Language”, has become the standard language for data manipulation in relational databases SQL is a non-procedural language - it specifies what is to be done, not how it is to be done Relatively easy to use for simple queries ...
CS3311 – Advanced Database Systems
... Multimedia data storage and management. Content-based querying and retrieval. Meta-data generation and use. ...
... Multimedia data storage and management. Content-based querying and retrieval. Meta-data generation and use. ...
CS263Lecture1
... • Relational databases views all data in the form of tables • Each column represents an attribute, e.g. the Customer table has attributes ID, Name, Address..etc. • Relationships between entities are represented by values stored in columns of the corresponding tables, e.g. Customer_ID is an attribute ...
... • Relational databases views all data in the form of tables • Each column represents an attribute, e.g. the Customer table has attributes ID, Name, Address..etc. • Relationships between entities are represented by values stored in columns of the corresponding tables, e.g. Customer_ID is an attribute ...
Relational model
The relational model for database management is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by Edgar F. Codd. In the relational model of a database, all data is represented in terms of tuples, grouped into relations. A database organized in terms of the relational model is a relational database.The purpose of the relational model is to provide a declarative method for specifying data and queries: users directly state what information the database contains and what information they want from it, and let the database management system software take care of describing data structures for storing the data and retrieval procedures for answering queries.Most relational databases use the SQL data definition and query language; these systems implement what can be regarded as an engineering approximation to the relational model. A table in an SQL database schema corresponds to a predicate variable; the contents of a table to a relation; key constraints, other constraints, and SQL queries correspond to predicates. However, SQL databases deviate from the relational model in many details, and Codd fiercely argued against deviations that compromise the original principles.