Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in
... The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with the ...
... The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with the ...
fundamental unit of life biology
... In 1838, a German Botanist Schleiden announced that all plants are composed of cells and in 1839, German Zoologist Schwann made some statements for animals. These announcements led to the formulation of cell theory, which “holds that all living matter, form the simplest of unicellular organisms to v ...
... In 1838, a German Botanist Schleiden announced that all plants are composed of cells and in 1839, German Zoologist Schwann made some statements for animals. These announcements led to the formulation of cell theory, which “holds that all living matter, form the simplest of unicellular organisms to v ...
Harmful and Helpful Protists Station 6
... 1. Select one harmful protist and one helpful protist from the list below (or another approved by your instructor). 2. Using the Internet or research materials provided by your instructor, research to discover the following: a. A brief overview of each protist b. Determine the effect of each protist ...
... 1. Select one harmful protist and one helpful protist from the list below (or another approved by your instructor). 2. Using the Internet or research materials provided by your instructor, research to discover the following: a. A brief overview of each protist b. Determine the effect of each protist ...
cells review ppt
... defective ribosome assembly in the nucleolus C. Cilia are found in the respiratory system and flagella move sperm; if dynein doesn’t function, these can’t move and do their job Campbell Self quiz ...
... defective ribosome assembly in the nucleolus C. Cilia are found in the respiratory system and flagella move sperm; if dynein doesn’t function, these can’t move and do their job Campbell Self quiz ...
Cells - SignatureIBBiology
... ancestral cell form which all other cells have arisen by descent. (origin of cellular life). This relationship of common ancestor suggest therefore that all organisms are related. ...
... ancestral cell form which all other cells have arisen by descent. (origin of cellular life). This relationship of common ancestor suggest therefore that all organisms are related. ...
Cell Division
... Consists of two processes: mitosis and cytokinesis During mitosis, the chromosomes divide and are distributed into two daughter nuclei During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided into two These two processes result in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells ...
... Consists of two processes: mitosis and cytokinesis During mitosis, the chromosomes divide and are distributed into two daughter nuclei During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm is divided into two These two processes result in the production of two genetically identical daughter cells ...
Reynolds School District
... In most species, cleavage produces a raspberry-shaped mass of 16 to 64 cells. Then, the mass becomes a hollow ball of cells called a blastula. – The hollow cavity is the blastocoel. ...
... In most species, cleavage produces a raspberry-shaped mass of 16 to 64 cells. Then, the mass becomes a hollow ball of cells called a blastula. – The hollow cavity is the blastocoel. ...
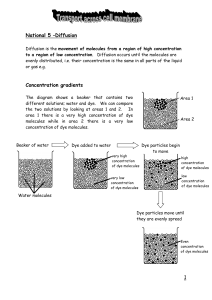
High - eduBuzz.org
... Both diffusion and osmosis are passive processes that don’t require a lot of energy. Sometimes some substances enter or leave cells against a concentration gradient and this does need energy. This is known as Active Transport. National 5- Active transport The cell membrane is made up of phospholipid ...
... Both diffusion and osmosis are passive processes that don’t require a lot of energy. Sometimes some substances enter or leave cells against a concentration gradient and this does need energy. This is known as Active Transport. National 5- Active transport The cell membrane is made up of phospholipid ...
Biology 20 Student Notes Ciculatory System To Evolution_1
... respiration. Decomposers release organic material back into carbon dioxide. Abiotic component ~ carbon dioxide is mostly stored as carbonic acid in water and the release via volcanic eruptions Disruption by human activity ~ release of stored organic (deforestation) and inorganic (fossil fuels) c ...
... respiration. Decomposers release organic material back into carbon dioxide. Abiotic component ~ carbon dioxide is mostly stored as carbonic acid in water and the release via volcanic eruptions Disruption by human activity ~ release of stored organic (deforestation) and inorganic (fossil fuels) c ...
Lecture 5
... Biology 103 - Main points/Questions 1. How do plants keep growing for their entire lives? 2. How do animal cells differentiate? ...
... Biology 103 - Main points/Questions 1. How do plants keep growing for their entire lives? 2. How do animal cells differentiate? ...
01st lecture
... is a staining method for microscopic preparates. Cells are stained with chrystal violet and iodine, decolorized with alcohol and investigated under microscope. Cell walls colored violet-blue are identified as Gram-positive, Gram-negative cells remain pink. ...
... is a staining method for microscopic preparates. Cells are stained with chrystal violet and iodine, decolorized with alcohol and investigated under microscope. Cell walls colored violet-blue are identified as Gram-positive, Gram-negative cells remain pink. ...
Kingdom Animalia - Hastings High School
... • Include animals such as Reptiles, Amphibians, Mammals, Fish, and Birds ...
... • Include animals such as Reptiles, Amphibians, Mammals, Fish, and Birds ...
Kingdom Animalia - Hastings High School
... • Include animals such as Reptiles, Amphibians, Mammals, Fish, and Birds ...
... • Include animals such as Reptiles, Amphibians, Mammals, Fish, and Birds ...
document
... • eg. insects like grasshoppers • An internal system allows to maintain a moist environment • Consists of external pores called “spiracles” controlled by valves • Connected to internal network of tubes called ...
... • eg. insects like grasshoppers • An internal system allows to maintain a moist environment • Consists of external pores called “spiracles” controlled by valves • Connected to internal network of tubes called ...
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing
... proper regulation of cell cycle is so key to life that the genes for these regulatory proteins have been highly conserved through evolution the genes are basically the same in yeast, insects, plants & animals (including humans) ...
... proper regulation of cell cycle is so key to life that the genes for these regulatory proteins have been highly conserved through evolution the genes are basically the same in yeast, insects, plants & animals (including humans) ...
Exam review F14
... 1. Make a table with the following cell parts. In the second column give the function of the cell part and in the third column sketch what it looks like. Nucleus, nucleolus, ribosome, mitochondria, vacuole, golgi, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vesicle, SER, RER, cell wall, chloroplast. (the last two are ...
... 1. Make a table with the following cell parts. In the second column give the function of the cell part and in the third column sketch what it looks like. Nucleus, nucleolus, ribosome, mitochondria, vacuole, golgi, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vesicle, SER, RER, cell wall, chloroplast. (the last two are ...
RNA polymerase I
... • 8 - 14 distinct subunits; visible in EM • differ in sensitivities to a-amanitin, – highly toxic octapeptide (8 linked amino acids) – from common poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides – also the source of microfilament toxin, phalloidin – Pol II is very sensitive, pol I not affected, pol III medium ...
... • 8 - 14 distinct subunits; visible in EM • differ in sensitivities to a-amanitin, – highly toxic octapeptide (8 linked amino acids) – from common poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides – also the source of microfilament toxin, phalloidin – Pol II is very sensitive, pol I not affected, pol III medium ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 46 TEK 7.12B: Human Organ Systems
... processes food into glucose that every cell of the body uses as food, and the respiratory system processes air and filters out the oxygen that every cell of the body needs to “burn” the glucose to create energy. Neither system could complete their jobs without the circulatory system delivering the g ...
... processes food into glucose that every cell of the body uses as food, and the respiratory system processes air and filters out the oxygen that every cell of the body needs to “burn” the glucose to create energy. Neither system could complete their jobs without the circulatory system delivering the g ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... Analogous characters the same function but different underlying construction. Homologous characters different functions, but show an anatomical similarity inherited from a common ancestor. ...
... Analogous characters the same function but different underlying construction. Homologous characters different functions, but show an anatomical similarity inherited from a common ancestor. ...
AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology Specification Specification
... reproducibility and validity of the data obtained must be considered. Societal aspects of scientific evidence A judgement or decision relating to social-scientific issues may be biased, or may not be based on evidence alone, as other societal factors may be relevant. Limitations of scientific eviden ...
... reproducibility and validity of the data obtained must be considered. Societal aspects of scientific evidence A judgement or decision relating to social-scientific issues may be biased, or may not be based on evidence alone, as other societal factors may be relevant. Limitations of scientific eviden ...
What is an animal? Part 1
... number of nematocysts discharging into the skin and to reduce the harmful effects of the venom. If stung by a jellyfish, the victim should carefully remove the tentacles that adhere to the skin by using sand, clothing, towels, seaweed or other available materials. As long as tentacles remain on the ...
... number of nematocysts discharging into the skin and to reduce the harmful effects of the venom. If stung by a jellyfish, the victim should carefully remove the tentacles that adhere to the skin by using sand, clothing, towels, seaweed or other available materials. As long as tentacles remain on the ...
Bio 101 Biology I
... evolutionary genetics, and the genetics of common diseases. Survey of human genetic conditions with an emphasis on the underlying molecular biology. MBG 324 Plant Molecular Biology and Genetics (3+0)3 This course emphasizes genetic transformation methodology, gene expression systems and strategies f ...
... evolutionary genetics, and the genetics of common diseases. Survey of human genetic conditions with an emphasis on the underlying molecular biology. MBG 324 Plant Molecular Biology and Genetics (3+0)3 This course emphasizes genetic transformation methodology, gene expression systems and strategies f ...
MBG 304 Molecular Genetics of Eukaryotes (3+0)3
... evolutionary genetics, and the genetics of common diseases. Survey of human genetic conditions with an emphasis on the underlying molecular biology. MBG 324 Plant Molecular Biology and Genetics (3+0)3 This course emphasizes genetic transformation methodology, gene expression systems and strategies f ...
... evolutionary genetics, and the genetics of common diseases. Survey of human genetic conditions with an emphasis on the underlying molecular biology. MBG 324 Plant Molecular Biology and Genetics (3+0)3 This course emphasizes genetic transformation methodology, gene expression systems and strategies f ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.