Regents Biology - I Heart Science
... Is a monocyte derivative. Phagocytosis (engulfment and digestion) of cellular debris and pathogens, and stimulation of lymphocytes and other immune cells that respond to the pathogen. ...
... Is a monocyte derivative. Phagocytosis (engulfment and digestion) of cellular debris and pathogens, and stimulation of lymphocytes and other immune cells that respond to the pathogen. ...
Chapt 6 Study Guide (Word)
... Many important activities that occur between cells and the extracellular environment that involve the plasma membrane are fully explored in this chapter. To a large extent the protein and phospholipid molecules that make up much of the chemical composition of the plasma membrane regulate the passage ...
... Many important activities that occur between cells and the extracellular environment that involve the plasma membrane are fully explored in this chapter. To a large extent the protein and phospholipid molecules that make up much of the chemical composition of the plasma membrane regulate the passage ...
Body_Systems_Overview_T
... 1. What is the main function of the reproductive system? The joining of gametes to produce offspring and to produce secondary sex characteristics in males and females. 2. What is produced in the ovary? Eggs (ovum) 3. Name the main male and female hormone produced and give its function. Female: estro ...
... 1. What is the main function of the reproductive system? The joining of gametes to produce offspring and to produce secondary sex characteristics in males and females. 2. What is produced in the ovary? Eggs (ovum) 3. Name the main male and female hormone produced and give its function. Female: estro ...
File - Mizzou Pre
... DNA is a polymer of nucleotides o Nucleotide: nitrogen base, five carbon sugar deoxyribose, phosphate group Purines – adenine, guanine (double ring)—2 H bonds (AT2, GC3) Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine (singe ring) – 3 H bonds (to remember: CUT the PYE) A nucleoside is just the sugar+base o T ...
... DNA is a polymer of nucleotides o Nucleotide: nitrogen base, five carbon sugar deoxyribose, phosphate group Purines – adenine, guanine (double ring)—2 H bonds (AT2, GC3) Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine (singe ring) – 3 H bonds (to remember: CUT the PYE) A nucleoside is just the sugar+base o T ...
cell growth, division, and reproduction
... a. Internal regulators are proteins that respond to events inside a cell i. they allow the cell cycle to proceed only once certain processes have happened inside the cell b. External regulators are proteins that respond to events outside the cell i. they direct cells to speed up or slow down the cel ...
... a. Internal regulators are proteins that respond to events inside a cell i. they allow the cell cycle to proceed only once certain processes have happened inside the cell b. External regulators are proteins that respond to events outside the cell i. they direct cells to speed up or slow down the cel ...
ch_44 water balance - Valhalla High School
... Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: ...
... Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: ...
gene duplications
... • The much slower rate of mutation at sites that do affect molecular function is consistent with the view that most nonsynonymous mutations are disadvantageous and are eliminated from the population by natural selection. • In general, the more essential a molecule is for cell function, the slower t ...
... • The much slower rate of mutation at sites that do affect molecular function is consistent with the view that most nonsynonymous mutations are disadvantageous and are eliminated from the population by natural selection. • In general, the more essential a molecule is for cell function, the slower t ...
Biology revision notes
... connected to the brain by the nerves of the nervous system. The nervous system The nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord (called the central nervous system, CNS) and all of the nerves connected to the CNS. Each of the nerves consists of a bundle of nerve cells. Each nerve cell c ...
... connected to the brain by the nerves of the nervous system. The nervous system The nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord (called the central nervous system, CNS) and all of the nerves connected to the CNS. Each of the nerves consists of a bundle of nerve cells. Each nerve cell c ...
Essential Biology 06.4 Gas Exchange Core
... Highlight all objective 1 command terms in yellow and complete these before class. Highlight all objective 2 and 3 command terms in green – these will be part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid pri ...
... Highlight all objective 1 command terms in yellow and complete these before class. Highlight all objective 2 and 3 command terms in green – these will be part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid pri ...
Melrose Public Schools
... 2.7 Describe how the process of meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells. Explain the importance of this process in sexual reproduction, and how gametes form diploid zygotes in the process of fertilization. 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the orga ...
... 2.7 Describe how the process of meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells. Explain the importance of this process in sexual reproduction, and how gametes form diploid zygotes in the process of fertilization. 4. Anatomy and Physiology Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the orga ...
FUNGI
... Heterokaryon - A vegetative hyphae containing nuclei from more than one individual Heterokaryotic - Hetero refers to different; and karyo refers to the nuclei. Heterokaryotic means that there are nuclei from different individuals in the same hyphae. Homothallic - Refers to species in which individua ...
... Heterokaryon - A vegetative hyphae containing nuclei from more than one individual Heterokaryotic - Hetero refers to different; and karyo refers to the nuclei. Heterokaryotic means that there are nuclei from different individuals in the same hyphae. Homothallic - Refers to species in which individua ...
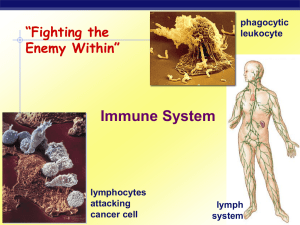
Wanganui High School
... Their surface antigens are seen as “foreign” by the body’s white blood cells which make antibodies. Antibodies are specific – eg when flu virus mutates the body has to make new antibodies for it which is why we can get flu time and time again. WANGANUI HIGH SCHOOL ...
... Their surface antigens are seen as “foreign” by the body’s white blood cells which make antibodies. Antibodies are specific – eg when flu virus mutates the body has to make new antibodies for it which is why we can get flu time and time again. WANGANUI HIGH SCHOOL ...
Editable Lecture PPT - Science Prof Online
... (ScienceProfSPO) for updates. • Many SPO PowerPoints are available in a variety of formats, such as fully editable PowerPoint files, as well as uneditable versions in smaller file sizes, such as PowerPoint Shows and Portable Document Format (.pdf), for ease of printing. • Images used on this resourc ...
... (ScienceProfSPO) for updates. • Many SPO PowerPoints are available in a variety of formats, such as fully editable PowerPoint files, as well as uneditable versions in smaller file sizes, such as PowerPoint Shows and Portable Document Format (.pdf), for ease of printing. • Images used on this resourc ...
Invertebrates - Cloudfront.net
... • These peculiar fossils puzzled paleontologists for years because they seemed quite different from any modern invertebrates • More recently, paleontologists have identified beautifully preserved, microscopic fossils, between 610 and 570 million years old, that seem to be the developing embryos of e ...
... • These peculiar fossils puzzled paleontologists for years because they seemed quite different from any modern invertebrates • More recently, paleontologists have identified beautifully preserved, microscopic fossils, between 610 and 570 million years old, that seem to be the developing embryos of e ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... § All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions that code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work of cells. (HSLS1-1) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea is also addressed by HS-LS3- 1.) § Multice ...
... § All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions that code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work of cells. (HSLS1-1) (Note: This Disciplinary Core Idea is also addressed by HS-LS3- 1.) § Multice ...
body systems1
... systems to maintain homeostasis and other hormones work with many organ systems to help you grow. ...
... systems to maintain homeostasis and other hormones work with many organ systems to help you grow. ...
connective tissue
... 3. Bone tissue—Bones are living structures that grow and are able to repair ...
... 3. Bone tissue—Bones are living structures that grow and are able to repair ...
BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY OF AQUA-SPHERE
... the Earth came from space, it is commonly believed that earliest life was born in Primordial Ocean on the Earth 4 billion years ago. Living organisms are defined as the ones with a cell membrane, metabolic system and function of self reproduction. It still remains a issue as to how these necessary c ...
... the Earth came from space, it is commonly believed that earliest life was born in Primordial Ocean on the Earth 4 billion years ago. Living organisms are defined as the ones with a cell membrane, metabolic system and function of self reproduction. It still remains a issue as to how these necessary c ...
BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY OF AQUA
... the Earth came from space, it is commonly believed that earliest life was born in Primordial Ocean on the Earth 4 billion years ago. Living organisms are defined as the ones with a cell membrane, metabolic system and function of self reproduction. It still remains a issue as to how these necessary c ...
... the Earth came from space, it is commonly believed that earliest life was born in Primordial Ocean on the Earth 4 billion years ago. Living organisms are defined as the ones with a cell membrane, metabolic system and function of self reproduction. It still remains a issue as to how these necessary c ...
Chapter 42.
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
On Your Own” Questions - Kingdom Builders Coop
... 1.3 A biologist studies an organism and then two of its offspring. They are all identical in every possible way. Do these organisms reproduce sexually or asexually? _____________________ 1.4 When trying to convince you of something, people will often insert “Science has proven...” at the beginning o ...
... 1.3 A biologist studies an organism and then two of its offspring. They are all identical in every possible way. Do these organisms reproduce sexually or asexually? _____________________ 1.4 When trying to convince you of something, people will often insert “Science has proven...” at the beginning o ...
ch_42 gas exchange - Valhalla High School
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
... O2 & CO2 diffuse much faster through air respiratory surfaces exposed to air do not have to be ventilated as thoroughly as gills ...
GCSE Biology Specification (For teaching from 2016
... future prosperity, and all learners should be taught essential aspects of the knowledge, methods, processes and uses of science. They should be helped to appreciate how the complex and diverse phenomena of the natural world can be described in terms of a small number of key ideas relating to the sci ...
... future prosperity, and all learners should be taught essential aspects of the knowledge, methods, processes and uses of science. They should be helped to appreciate how the complex and diverse phenomena of the natural world can be described in terms of a small number of key ideas relating to the sci ...
36 classification a
... This leaves us on the brink of Chordata and the vertebrates. IB holds you to no more details here. The AP only teachers have pushed more of these chapters. (We hit the last two text sections under human evolution.) ...
... This leaves us on the brink of Chordata and the vertebrates. IB holds you to no more details here. The AP only teachers have pushed more of these chapters. (We hit the last two text sections under human evolution.) ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.