Germ-line modification
... identity of the future person. Therefore, any conclusion regarding the moral acceptability of modifying the mtDNA applies mutatis mutandis to modification of the nuclear genome. This means that modification of the nuclear genome is equally acceptable as long as, other things being equal, this does n ...
... identity of the future person. Therefore, any conclusion regarding the moral acceptability of modifying the mtDNA applies mutatis mutandis to modification of the nuclear genome. This means that modification of the nuclear genome is equally acceptable as long as, other things being equal, this does n ...
Evolution of the Y-Chromosome in Primates
... than others (Skaletsky et al., 2003). These more recent additions are at an earlier stage of degeneration than other parts of the chromosome in which less DNA has yet to be removed, which as a result, has created a mosaic of genes on the Y-chromosome that are at different stages of degeneration. Thi ...
... than others (Skaletsky et al., 2003). These more recent additions are at an earlier stage of degeneration than other parts of the chromosome in which less DNA has yet to be removed, which as a result, has created a mosaic of genes on the Y-chromosome that are at different stages of degeneration. Thi ...
News from the west: Ancient DNA from a French megalithic burial
... of significant post-Neolithic migrations, they proposed a Paleolithic ancestry for modern Europeans. Nonetheless, two recent publications (Bramanti et al., 2009; Malmström et al., 2009) reported sequences from late European hunter-gatherers that demonstrated genetic differentiation between ancient h ...
... of significant post-Neolithic migrations, they proposed a Paleolithic ancestry for modern Europeans. Nonetheless, two recent publications (Bramanti et al., 2009; Malmström et al., 2009) reported sequences from late European hunter-gatherers that demonstrated genetic differentiation between ancient h ...
Genetic Diversity in an Andean Population from Peru and Regional
... level of gene flow among equilibrium and nonequilibrium populations with different geographic locations, from both DNA RFLP and sequence data and classic protein markers [39–44]. The gene flow as measured by the product Nm can be estimated from FST (GST) values on the basis of the island model of po ...
... level of gene flow among equilibrium and nonequilibrium populations with different geographic locations, from both DNA RFLP and sequence data and classic protein markers [39–44]. The gene flow as measured by the product Nm can be estimated from FST (GST) values on the basis of the island model of po ...
Advanced Topics in STR DNA Analysis
... Role of Y-STRs and mtDNA Compared to Autosomal STRs Autosomal STRs provide a higher power of • discrimination and are the preferred method whenever possible Due to capabilities for male-specific amplification, • Y-chromosome STRs (Y-STRs) can be useful in extreme female-male mixtures (e.g., when di ...
... Role of Y-STRs and mtDNA Compared to Autosomal STRs Autosomal STRs provide a higher power of • discrimination and are the preferred method whenever possible Due to capabilities for male-specific amplification, • Y-chromosome STRs (Y-STRs) can be useful in extreme female-male mixtures (e.g., when di ...
Y-Chromosome Marker S28 / U152 Haplogroup
... ”Of interest is the fact that while R-U152 has a clear French-Italian center of weight, the locations exhibiting highest STR variance are Germany and Slovakia, i.e., Central Europe. My guess is that R-U152 originated in Central Europe spreading to the west and south, perhaps with Italo-Celtic speak ...
... ”Of interest is the fact that while R-U152 has a clear French-Italian center of weight, the locations exhibiting highest STR variance are Germany and Slovakia, i.e., Central Europe. My guess is that R-U152 originated in Central Europe spreading to the west and south, perhaps with Italo-Celtic speak ...
Lecture 31 (4-25-11)
... • An enigma! Not only was Neandertal DNA in the European, it was in the individuals from China and New Guinea as well. • Therefore, Chinese and Papuans are as closely related to Neandertals as Europeans. • Neandertal fossils have never been found in either eastern Asia or New Guinea. • Therefore, i ...
... • An enigma! Not only was Neandertal DNA in the European, it was in the individuals from China and New Guinea as well. • Therefore, Chinese and Papuans are as closely related to Neandertals as Europeans. • Neandertal fossils have never been found in either eastern Asia or New Guinea. • Therefore, i ...
Y Chromosome Markers
... – Evidence is positive for semen but no male DNA is found in genotypes – Male/Female mixture is known to exist – Large number of semen stains need to be separated and ID’d – Evidence of more than one male perpetrator ...
... – Evidence is positive for semen but no male DNA is found in genotypes – Male/Female mixture is known to exist – Large number of semen stains need to be separated and ID’d – Evidence of more than one male perpetrator ...
Comparison between the Polish population and European
... haplogroup composition of the Finnish population are observed between the results obtained by Finnilä et al. (2001) and Niemi et al. (2003). This phenomenon may be possibly explained by different selection criteria of the subjects in each analyzed sample. The other possible explanation is that the s ...
... haplogroup composition of the Finnish population are observed between the results obtained by Finnilä et al. (2001) and Niemi et al. (2003). This phenomenon may be possibly explained by different selection criteria of the subjects in each analyzed sample. The other possible explanation is that the s ...
New clues to the evolutionary history of the main European paternal
... (Galicia, Asturias, 8%) and NE (Barcelona, Alicante, 6%), and the minimum lies in the Basque region (2%). In Europe, haplogroup U152 has its maximum in the Alpine region, and thus perhaps its frequency pattern could be explained by a migration from the Alpine region of origin to the Iberian Peninsul ...
... (Galicia, Asturias, 8%) and NE (Barcelona, Alicante, 6%), and the minimum lies in the Basque region (2%). In Europe, haplogroup U152 has its maximum in the Alpine region, and thus perhaps its frequency pattern could be explained by a migration from the Alpine region of origin to the Iberian Peninsul ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
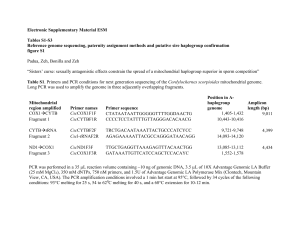
... amplification conditions involved a 1 min hot start at 95°C, followed by 34 cycles of the following conditions: 93°C melting for 25 s, and 68°C annealing/extension for 8 min For each replication, PCR products from the mother, the two putative sires and an average of 22 offspring were run on a 1.5% a ...
... amplification conditions involved a 1 min hot start at 95°C, followed by 34 cycles of the following conditions: 93°C melting for 25 s, and 68°C annealing/extension for 8 min For each replication, PCR products from the mother, the two putative sires and an average of 22 offspring were run on a 1.5% a ...
Past History of the Retson Family based on DNA evidence Written
... The Retson male family line (Y-DNA) is an ancient one and is defined as I1 (eye one). It is thought that it represents part of the first wave of modern humans out of the Middle East which migrated out through present-day Greece and the Balkans2. The initial group was formed by Haplogroup IJ3. These ...
... The Retson male family line (Y-DNA) is an ancient one and is defined as I1 (eye one). It is thought that it represents part of the first wave of modern humans out of the Middle East which migrated out through present-day Greece and the Balkans2. The initial group was formed by Haplogroup IJ3. These ...
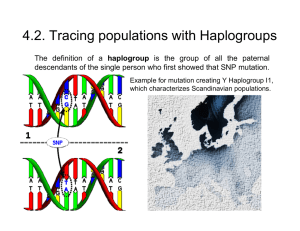
4.2. Tracing populations with Haplogroups
... Chronological development of mtDNA haplogroups U => 50,000 to 60,000 years ago (arose in Western Asia) H => 30,000 to 50,000 years ago (in the Near East - associated with Cro-Magnon in Europe) J => 45,000 years ago (in the Near East) X => over 30,000 years ago (in Caucasus) (Neanderthal???) I => 30 ...
... Chronological development of mtDNA haplogroups U => 50,000 to 60,000 years ago (arose in Western Asia) H => 30,000 to 50,000 years ago (in the Near East - associated with Cro-Magnon in Europe) J => 45,000 years ago (in the Near East) X => over 30,000 years ago (in Caucasus) (Neanderthal???) I => 30 ...
Analysis of Y chromosome lineages in native South American
... shows that most of the variation is found within populations and not among populations. Furthermore the P value ( P = 0.09971) associated to the latter variation is non-significant, suggesting this value is not real. However at the Y-STRs level we found a small percentage of variation among populati ...
... shows that most of the variation is found within populations and not among populations. Furthermore the P value ( P = 0.09971) associated to the latter variation is non-significant, suggesting this value is not real. However at the Y-STRs level we found a small percentage of variation among populati ...
Purpose of Y-chromosome Analysis - College of Letters, Arts, and
... Over 60% of the Bedouin belong to Haplogroup J1. The Arabs have two distinct cultures, sedentary and nomadic. The latter is what the world refers to as the Bedouin. The sedentary Arabs took advantage of oases throughout the Middle East and the Bedouin took advantage of the scarce resources by becomi ...
... Over 60% of the Bedouin belong to Haplogroup J1. The Arabs have two distinct cultures, sedentary and nomadic. The latter is what the world refers to as the Bedouin. The sedentary Arabs took advantage of oases throughout the Middle East and the Bedouin took advantage of the scarce resources by becomi ...