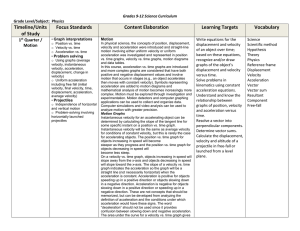
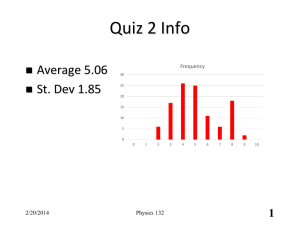
Homework week 6.
... Note that the electric field enclosed in the area within Electrode A is zero and the electric field outside the outer electrode is also zero. So all points within the red square are at the same potential (VA) and all points outside the blue square are at the same electric potential (VB). Figure 1 be ...
... Note that the electric field enclosed in the area within Electrode A is zero and the electric field outside the outer electrode is also zero. So all points within the red square are at the same potential (VA) and all points outside the blue square are at the same electric potential (VB). Figure 1 be ...
C - Tapp Middle School
... 1. What type of energy comes from a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged? a. kinetic energy c. thermal energy b. chemical energy d. light energy 2. Which of the following is due to the random motion of particles? a. kinetic energy c. thermal energy b. nuclear energy d. sound energy 3. W ...
... 1. What type of energy comes from a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged? a. kinetic energy c. thermal energy b. chemical energy d. light energy 2. Which of the following is due to the random motion of particles? a. kinetic energy c. thermal energy b. nuclear energy d. sound energy 3. W ...
the problem book
... c. In the sodium atom the single valence electron sees the core as a spherically symmetric distribution of charge. Every sodium energy-level for nonzero angular momentum has a fine structure associated with it due to spin-orbit interaction of the valence electron. Using central-field model, write do ...
... c. In the sodium atom the single valence electron sees the core as a spherically symmetric distribution of charge. Every sodium energy-level for nonzero angular momentum has a fine structure associated with it due to spin-orbit interaction of the valence electron. Using central-field model, write do ...
Conservation of Energy
... to measure how much energy you get from various foods1 C is equivalent to about 4,184 J. Every gram of fat a person consumes can supply 9 C of energy. ...
... to measure how much energy you get from various foods1 C is equivalent to about 4,184 J. Every gram of fat a person consumes can supply 9 C of energy. ...
Energy - USU physics
... position, and (2) the work done is independent of the path taken between two given points, we say the force is conservative. Gravity is a conservative force (I will prove this shortly). Friction is not a conservative force it depends upon velocity and it fails condition (2) (just proved above). Cons ...
... position, and (2) the work done is independent of the path taken between two given points, we say the force is conservative. Gravity is a conservative force (I will prove this shortly). Friction is not a conservative force it depends upon velocity and it fails condition (2) (just proved above). Cons ...
Slide 1
... Conceptual Example 23-1: A negative charge. Suppose a negative charge, such as an electron, is placed near the negative plate at point b, as shown here. If the electron is free to move, will its electric potential energy increase or decrease? How will the electric potential change? ...
... Conceptual Example 23-1: A negative charge. Suppose a negative charge, such as an electron, is placed near the negative plate at point b, as shown here. If the electron is free to move, will its electric potential energy increase or decrease? How will the electric potential change? ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... The Law of Conservation of Energy says that energy cannot be created nor ___________________, but it can be transformed from one form to another. In other words, all of the energy available at the start of a transformation still exists in some form of energy after the change is complete. Energy isn’ ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy says that energy cannot be created nor ___________________, but it can be transformed from one form to another. In other words, all of the energy available at the start of a transformation still exists in some form of energy after the change is complete. Energy isn’ ...
Lecture 6 : Potential - University of Central Florida
... When we have an arbitrary charge distribution, we can use uE to calculate the stored energy U dU = uE d(Vol) = (1/2) 0 E2 d(Vol) U = (1/2) 0 E2 d(Vol) [The integral covers the entire region in which the field E exists] ...
... When we have an arbitrary charge distribution, we can use uE to calculate the stored energy U dU = uE d(Vol) = (1/2) 0 E2 d(Vol) U = (1/2) 0 E2 d(Vol) [The integral covers the entire region in which the field E exists] ...