Slide 1
... 15.1 – Elastic Potential Energy • The potential energy of an object that is stretched or compressed is known as elastic potential energy. • Something is said to be elastic if it springs back to its original shape after it is stretched or compressed. ...
... 15.1 – Elastic Potential Energy • The potential energy of an object that is stretched or compressed is known as elastic potential energy. • Something is said to be elastic if it springs back to its original shape after it is stretched or compressed. ...
Electric Fields and Force
... The work done in moving a test charge of 2.0 mC from very far away to a point P is 1.50 x 10-8 J. What is the electric potential at point P? ...
... The work done in moving a test charge of 2.0 mC from very far away to a point P is 1.50 x 10-8 J. What is the electric potential at point P? ...
Electric Potential Difference
... electric field has an existence independent of the test charge, even though a test charge was (temporarily) introduced to define it. *Similarly, the existence of electric potential energy requires the existence of a test charge. However, it is assumed that the electric potential has an existence ind ...
... electric field has an existence independent of the test charge, even though a test charge was (temporarily) introduced to define it. *Similarly, the existence of electric potential energy requires the existence of a test charge. However, it is assumed that the electric potential has an existence ind ...
Document
... The proportionality constant (k) can only be used if the medium that separates the charges is a vacuum. If the region between the point charges is not a vacuum then the value of the proportionality constant to be used is determined by dividing k by the dielectric constant (K). For a vacuum K = 1, fo ...
... The proportionality constant (k) can only be used if the medium that separates the charges is a vacuum. If the region between the point charges is not a vacuum then the value of the proportionality constant to be used is determined by dividing k by the dielectric constant (K). For a vacuum K = 1, fo ...
Phy213_CH24_worksheet-s07
... 1 r qinner qinner 1 1 V = V - Vinner = - E(r)dr = - 2 dr = ...
... 1 r qinner qinner 1 1 V = V - Vinner = - E(r)dr = - 2 dr = ...
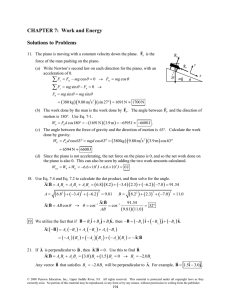
SolutionstoAssignedProblemsChapter7
... © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
Electric Potential - K
... An electron enters a uniform electric field of 145N/C pointed toward the right. The point of entry is 1.5m to the right of a given mark, and the point where the electron leaves the field is 4.6m to the right of that mark. (a) Determine the change in the electric potential energy of the electron (Ans ...
... An electron enters a uniform electric field of 145N/C pointed toward the right. The point of entry is 1.5m to the right of a given mark, and the point where the electron leaves the field is 4.6m to the right of that mark. (a) Determine the change in the electric potential energy of the electron (Ans ...
Lecture 7 - Capacitance
... Although we derived this expression for the uniform field of a parallel plate capacitor, this is a universal expression valid for ...
... Although we derived this expression for the uniform field of a parallel plate capacitor, this is a universal expression valid for ...