Thermochemistry
... Key terms: Hess’ Law- states that in going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or a series of steps. Hess’ Law allows scientists to determine the enthalpy of formation in a reaction they a ...
... Key terms: Hess’ Law- states that in going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or a series of steps. Hess’ Law allows scientists to determine the enthalpy of formation in a reaction they a ...
forms of energy
... work. People have learned how to change energy from one form to another so that we can do work more easily and live more comfortably. Energy is neither created nor destroyed, only converted to another form, i.e. the total energy present at every stage in a chain of energy conversions is the same. ...
... work. People have learned how to change energy from one form to another so that we can do work more easily and live more comfortably. Energy is neither created nor destroyed, only converted to another form, i.e. the total energy present at every stage in a chain of energy conversions is the same. ...
Ideal Mechanical Advantage
... the square of the speed. Kinetic Energy = ½ mass x (velocity)2 and the SI unit of KE is also Joules, which is the same unit used for work. When work is done on an object, energy is transformed from one form to another. The sum of the changes in potential, kinetic and heat energy is equal to the work ...
... the square of the speed. Kinetic Energy = ½ mass x (velocity)2 and the SI unit of KE is also Joules, which is the same unit used for work. When work is done on an object, energy is transformed from one form to another. The sum of the changes in potential, kinetic and heat energy is equal to the work ...
Energy Flow
... • “Energy” is the ability to do work, such as causing motion, or interaction between molecules. This is the idea of “energy” used in your textbook. • “Energy” is used in an everyday sense to mean “alertness,” “strength,” or “vitality.” ...
... • “Energy” is the ability to do work, such as causing motion, or interaction between molecules. This is the idea of “energy” used in your textbook. • “Energy” is used in an everyday sense to mean “alertness,” “strength,” or “vitality.” ...
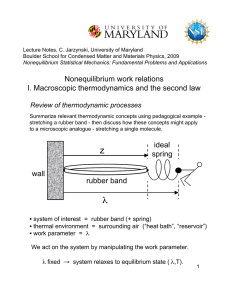
W - Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
CBSE Class 9 Work Energy and Power Solved test paper-06
... Ans: (a) Law of conservation of energy: Total energy of this universe is conserved (is constant). Energy cannot be created nor be destroyed. But can be transformed from one form to another. b) A stretched slinky and stretched rubber band possesses elastic potential energy. Flowing water and speeding ...
... Ans: (a) Law of conservation of energy: Total energy of this universe is conserved (is constant). Energy cannot be created nor be destroyed. But can be transformed from one form to another. b) A stretched slinky and stretched rubber band possesses elastic potential energy. Flowing water and speeding ...
(Thermochemistry-Chapter 5) - Fall 2015
... State Functions • State function: depends only on the initial and final states of system, not on how the internal energy is used. ...
... State Functions • State function: depends only on the initial and final states of system, not on how the internal energy is used. ...
Chapter 12
... while doing 2000 J of work on the environment during a constant pressure process. (a) Compute the change in internal energy of the gas. (b) If the internal energy drops by 4500 J and 2000 J is expelled from the system, find the change in volume assuming a constant pressure at 1.01 X 105 Pa. ...
... while doing 2000 J of work on the environment during a constant pressure process. (a) Compute the change in internal energy of the gas. (b) If the internal energy drops by 4500 J and 2000 J is expelled from the system, find the change in volume assuming a constant pressure at 1.01 X 105 Pa. ...
Announcements
... l The volume decreases by a fraction 1/273 for every degree decrease in temperature l This implied that if a gas were cooled to -273o C, it would decrease to zero volume ◆ of course, by this point the gas would have turned into a liquid, but it brings up the idea that, while there is no upper l ...
... l The volume decreases by a fraction 1/273 for every degree decrease in temperature l This implied that if a gas were cooled to -273o C, it would decrease to zero volume ◆ of course, by this point the gas would have turned into a liquid, but it brings up the idea that, while there is no upper l ...
ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice – Torque
... max location all of that gravitational potential will become spring potential when it reaches its lowest position. When the box oscillates back up it will return to its original location converting all of its energy back to gravitational potential and will oscillate back and forth between these two ...
... max location all of that gravitational potential will become spring potential when it reaches its lowest position. When the box oscillates back up it will return to its original location converting all of its energy back to gravitational potential and will oscillate back and forth between these two ...
Internal Energy, Heat, Enthalpy, and Calorimetry
... State Functions Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system Finding that value is simply too complex a problem However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state Called a state function A state ...
... State Functions Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system Finding that value is simply too complex a problem However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state Called a state function A state ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Physics 8.286: The Early Universe
... where k = −2E/c2 . In this form the equation looks more like a conservation of energy relation, although the constant E does not have the dimensions of energy. There are two ways, however, in which the quantity E can be connected to the conservation of energy. It is related the energy of a test part ...
... where k = −2E/c2 . In this form the equation looks more like a conservation of energy relation, although the constant E does not have the dimensions of energy. There are two ways, however, in which the quantity E can be connected to the conservation of energy. It is related the energy of a test part ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Calculating Mechanical Energy pg. 297 • An object’s mechanical energy is a combination of its potential energy and its kinetic energy. How do you find an object’s mechanical energy ?? You can find an object’s mechanical energy by adding the object’s kinetic energy and potential energy. (Mechanical ...
... Calculating Mechanical Energy pg. 297 • An object’s mechanical energy is a combination of its potential energy and its kinetic energy. How do you find an object’s mechanical energy ?? You can find an object’s mechanical energy by adding the object’s kinetic energy and potential energy. (Mechanical ...
Energy Forms Notes
... All matter has this energy regardless if work is being done or not SO IS ALSO CALLED REST ENERGY because we don’t tap into it for most processes & practical purposes Is determined by Einstein’s famous equation ...
... All matter has this energy regardless if work is being done or not SO IS ALSO CALLED REST ENERGY because we don’t tap into it for most processes & practical purposes Is determined by Einstein’s famous equation ...
chapter 4 - Celina City Schools
... D) The effect of ____________ on energy: (using the example of a swing) 1) Friction and air resistance cause some of the mechanical energy to change to ____________ energy. 2) The total amount of energy always stays the ____________. E) Nuclear ____________ and ____________ 1) Nuclear fusion – a rea ...
... D) The effect of ____________ on energy: (using the example of a swing) 1) Friction and air resistance cause some of the mechanical energy to change to ____________ energy. 2) The total amount of energy always stays the ____________. E) Nuclear ____________ and ____________ 1) Nuclear fusion – a rea ...
PINEWOOD DERBY RACE Conservation of Energy Conservation of
... •Therefore, car A loses more gravitational potential energy. •Therefore, it gains more kinetic energy and is faster at the bottom. ...
... •Therefore, car A loses more gravitational potential energy. •Therefore, it gains more kinetic energy and is faster at the bottom. ...