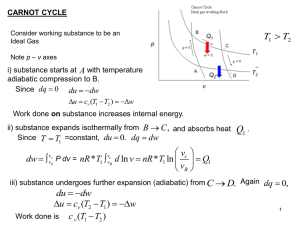
Chapter 23 Energy is conserved, so the change in potential energy
... 30. By energy conservation, all of the initial potential energy of the charges will change to kinetic energy when the charges are very far away from each other. By momentum conservation, since the initial momentum is zero and the charges have identical masses, the charges will have equal speeds in o ...
... 30. By energy conservation, all of the initial potential energy of the charges will change to kinetic energy when the charges are very far away from each other. By momentum conservation, since the initial momentum is zero and the charges have identical masses, the charges will have equal speeds in o ...
MODELLI MATEMATICI PER IL TRASPORTO DI CARICHE NEI
... thermal vibrations of the ions off their positions in the lattice, which destroy the periodicity of the interaction potential. These effects are described by the collision operator C(f) and leads to the ...
... thermal vibrations of the ions off their positions in the lattice, which destroy the periodicity of the interaction potential. These effects are described by the collision operator C(f) and leads to the ...
Lecture 2: Adiabatic Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium
... Adiabatic Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium ...
... Adiabatic Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium ...
PPT
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
ME 7280 Statistical Thermodynamics
... Once the basic theory is compete, we will look at cases of particular interest; ideal and non ideal gases, thermal radiation (an ideal gas of photons), lattice vibrations in a solid (an ideal gas of phonons) and the free electron theory of metals. Relevance: Because statistical thermodynamics result ...
... Once the basic theory is compete, we will look at cases of particular interest; ideal and non ideal gases, thermal radiation (an ideal gas of photons), lattice vibrations in a solid (an ideal gas of phonons) and the free electron theory of metals. Relevance: Because statistical thermodynamics result ...
What is Work?
... In order for work to be done: • A force must be applied to an object and the object must move a distance. This woman is pushing on the cart (exerting a force) and the cart is moving a distance, so this woman is doing work on the cart. If the woman pushed the cart and the cart did not move, then the ...
... In order for work to be done: • A force must be applied to an object and the object must move a distance. This woman is pushing on the cart (exerting a force) and the cart is moving a distance, so this woman is doing work on the cart. If the woman pushed the cart and the cart did not move, then the ...
presentation source
... IV In our example the only external parameter was the volume In general, gravitational, electric or magnetic fields, elastic energy etc. could all change The definition of temperature only holds if all of these are held fixed ...
... IV In our example the only external parameter was the volume In general, gravitational, electric or magnetic fields, elastic energy etc. could all change The definition of temperature only holds if all of these are held fixed ...
Sect. 5.2 (IA)
... Surface Distribution: (thin shell; M = ∫ρs(r)da) Φ = -G ∫[ρs(r)da/r] Integral over surface S Line Distribution: (one d; M = ∫ρ(r)ds) Φ = - G ∫[ρ(r)ds/r] Integral over line Γ ...
... Surface Distribution: (thin shell; M = ∫ρs(r)da) Φ = -G ∫[ρs(r)da/r] Integral over surface S Line Distribution: (one d; M = ∫ρ(r)ds) Φ = - G ∫[ρ(r)ds/r] Integral over line Γ ...
Energy Transfer & First Law of
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
4 - WordPress.com
... A 200 grams bullet move through the air with a velocity of 150 m/s at 250 m height. Calculate the total Potential energy and Kinetic Energy of the bullet. Calculate in Joule the work done in each of the following cases: ...
... A 200 grams bullet move through the air with a velocity of 150 m/s at 250 m height. Calculate the total Potential energy and Kinetic Energy of the bullet. Calculate in Joule the work done in each of the following cases: ...
ch 2 matter and energy
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
ConcepTest
... being whirled around at a constant speed in a circle. What can you say about the work done by tension? ...
... being whirled around at a constant speed in a circle. What can you say about the work done by tension? ...
ch 2 matter and energy
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
... Science Has Some Limitations 1. Particular hypotheses, theories, or laws have a high probability of being true while not being absolute 2. Bias can be minimized by scientists ...
PPT
... potential on each plate. Assume you are far from the edges of the plates. • What is the electric field between the plates in each case? • What (and where) is the charge density on the plates in case (1)? • What happens to an electron released midway between the plates in case (1)? ...
... potential on each plate. Assume you are far from the edges of the plates. • What is the electric field between the plates in each case? • What (and where) is the charge density on the plates in case (1)? • What happens to an electron released midway between the plates in case (1)? ...