Notes for Newton
... 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of ...
... 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of ...
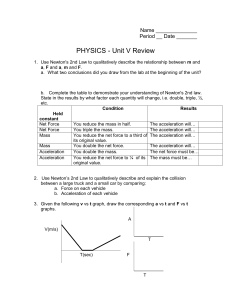
Unit V review
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
Newtons Laws of Motion Review WS
... c. Using aluminum instead of steel makes it possible to trim 477 lbs. off a typical 3500 lb. car. The less weight (or mass) of a car, the less fuel it takes to make it ...
... c. Using aluminum instead of steel makes it possible to trim 477 lbs. off a typical 3500 lb. car. The less weight (or mass) of a car, the less fuel it takes to make it ...
Circular Motion
... gravitational field can be explained by gravitational field strength, g. The value of g is equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on a unit mass at that point, or g=Fg/m. Gravitational filed strength is equal to free fall acceleration, however, they are not the same thing. E.g. ob ...
... gravitational field can be explained by gravitational field strength, g. The value of g is equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on a unit mass at that point, or g=Fg/m. Gravitational filed strength is equal to free fall acceleration, however, they are not the same thing. E.g. ob ...
No Slide Title
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. He wondered whether the same force attrac ...
... Newton knew that at the surface of the earth bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. He wondered whether the same force attrac ...
Universal Laws of Motion - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... direction, e.g. “10 m/s moving east” acceleration – a change in an object’s velocity, i.e. a change in either speed or direction is an acceleration [m/s2] ...
... direction, e.g. “10 m/s moving east” acceleration – a change in an object’s velocity, i.e. a change in either speed or direction is an acceleration [m/s2] ...
Force and Newton Laws
... • A 400-newton girl standing on a dock exerts a force of 100 Newton's on a 10,000-newton sailboat as she pushes it away from the dock. How much force does the sailboat exert on the girl? • Mass of Earth= 5.98 x 10^24 kg • Mass of moon= 7.35 x 10 ^22 kg • Distance= 3.84 x 10 ^8 m ...
... • A 400-newton girl standing on a dock exerts a force of 100 Newton's on a 10,000-newton sailboat as she pushes it away from the dock. How much force does the sailboat exert on the girl? • Mass of Earth= 5.98 x 10^24 kg • Mass of moon= 7.35 x 10 ^22 kg • Distance= 3.84 x 10 ^8 m ...
Chapter 2: Forces and the Momentum Principle
... to maintain its velocity - forces act to change motion, not to sustain the motion (e.g., the speed of the space shuttle) - seems contrary to everyday experience ❑ Inertia – tendency for an object to remain at rest, or to remain in motion with a constant velocity ...
... to maintain its velocity - forces act to change motion, not to sustain the motion (e.g., the speed of the space shuttle) - seems contrary to everyday experience ❑ Inertia – tendency for an object to remain at rest, or to remain in motion with a constant velocity ...
natsciGR
... Newton vs. Einstein -both make essentially identical predictions as long as the strength of the gravitational field is weak. Some divergence: 1. The orientation of Mercury's orbit is found to precess in space over time.This is commonly called the "precession of the perihelion", because it causes th ...
... Newton vs. Einstein -both make essentially identical predictions as long as the strength of the gravitational field is weak. Some divergence: 1. The orientation of Mercury's orbit is found to precess in space over time.This is commonly called the "precession of the perihelion", because it causes th ...
Forces
... The gravitational force on a sky diver with a mass of 60 kg would be F = mg = (60kg) (9.8 m/s2) = 588 N ...
... The gravitational force on a sky diver with a mass of 60 kg would be F = mg = (60kg) (9.8 m/s2) = 588 N ...
Physical Science
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... What does F mean? This is the (vector) sum of all of the forces that on the particle in question. To do this sum it is very important to be clear about what you are calling the system under study. The laws imply the effect of a force is to cause acceleration. ...
... What does F mean? This is the (vector) sum of all of the forces that on the particle in question. To do this sum it is very important to be clear about what you are calling the system under study. The laws imply the effect of a force is to cause acceleration. ...
Forces in One Direction
... • Despite the fact that this equation is almost 500 years old, it is still one of the most powerful equations we know. • A force is a push or a pull. It may be gravitational, electrical/magnetic, nuclear or simple muscular effort. ...
... • Despite the fact that this equation is almost 500 years old, it is still one of the most powerful equations we know. • A force is a push or a pull. It may be gravitational, electrical/magnetic, nuclear or simple muscular effort. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.