The Effective Mass of a Ball in the Air
... where W = mg is the weight of the ball in vacuum, m is the mass of the ball in vacuum, g is the acceleration of gravity, B = mair g is the buoyant force, mair is the mass of the air displaced by the ball, D is the drag force (a function of the ball's velocity), a is the downward acceleration and ma ...
... where W = mg is the weight of the ball in vacuum, m is the mass of the ball in vacuum, g is the acceleration of gravity, B = mair g is the buoyant force, mair is the mass of the air displaced by the ball, D is the drag force (a function of the ball's velocity), a is the downward acceleration and ma ...
Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Why do our plants stay in the sun’s orbit? Why does the moon stay in orbit around the Earth? Gravitational force (field force) is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. It is a field force that always exists between any two masses, regardles ...
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Why do our plants stay in the sun’s orbit? Why does the moon stay in orbit around the Earth? Gravitational force (field force) is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. It is a field force that always exists between any two masses, regardles ...
PH100-2D Preparatory Physics I Dr. Brian Geislinger
... for these later courses, the student will obtain the basic skills necessary to allow them to focus on the conceptual material presented later in either PH201 or PH221. Attendance Policy: Roll will not be taken, but your attendance in class is expected. Cell phone Policy: Please respect me as well as ...
... for these later courses, the student will obtain the basic skills necessary to allow them to focus on the conceptual material presented later in either PH201 or PH221. Attendance Policy: Roll will not be taken, but your attendance in class is expected. Cell phone Policy: Please respect me as well as ...
AM #1-35 - Edublogs
... 1. Compare a dependent and an independent variable. 2. Differentiate between a theory to a law. 3. Compare quantitative and qualitative data. 4. 6783.49 cl = ? dkl AM #6 1. An object has a density of 1.8 g/ml. Will the object sink or float? 2. What tools do you need to calculate density? 3. Give an ...
... 1. Compare a dependent and an independent variable. 2. Differentiate between a theory to a law. 3. Compare quantitative and qualitative data. 4. 6783.49 cl = ? dkl AM #6 1. An object has a density of 1.8 g/ml. Will the object sink or float? 2. What tools do you need to calculate density? 3. Give an ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The car has more mass and therefore more inertia. The more inertia an object has, the more force is needed to change its state of motion (like making ...
... The car has more mass and therefore more inertia. The more inertia an object has, the more force is needed to change its state of motion (like making ...
Forces Introduction Powerpoint
... Kinematics: The study of how objects move (velocity, acceleration) ...
... Kinematics: The study of how objects move (velocity, acceleration) ...
PH607lec08
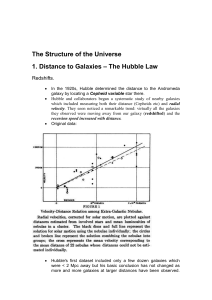
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
Grade 10 Force PowerPoint II
... Name all the forces acting upon these systems. Which systems have zero net force? Remember when Fnet = 0 then a = 0, but it can still have v. • A book sitting on a table. ...
... Name all the forces acting upon these systems. Which systems have zero net force? Remember when Fnet = 0 then a = 0, but it can still have v. • A book sitting on a table. ...
Dynamics
... A 2.00 kg mass resting on a plane inclined at an angle of 40.0o with the horizontal is attached to a hanging mass by means of a frictionless pulley as shown. The hanging mass takes 1.62 seconds to fall through a distance of 1.52 meters starting from rest. What is the mass of the hanging mass if (a) ...
... A 2.00 kg mass resting on a plane inclined at an angle of 40.0o with the horizontal is attached to a hanging mass by means of a frictionless pulley as shown. The hanging mass takes 1.62 seconds to fall through a distance of 1.52 meters starting from rest. What is the mass of the hanging mass if (a) ...
Cosmology, galaxies, stars and the sun
... pressure and temperature to increase, until the star finally stabilizes. •A star can exist anywhere from 1 Million to 30 Billion years! (depending on size) ...
... pressure and temperature to increase, until the star finally stabilizes. •A star can exist anywhere from 1 Million to 30 Billion years! (depending on size) ...
DV_Matter-Teacher
... Acceleration Due to Gravity • There is a force exerted on an object as the result of the mass of the Earth – Therefore, the object is accelerated (I.e. the speed increases) when released At time = 0 seconds, an object is released with no velocity ...
... Acceleration Due to Gravity • There is a force exerted on an object as the result of the mass of the Earth – Therefore, the object is accelerated (I.e. the speed increases) when released At time = 0 seconds, an object is released with no velocity ...
Topic 4.1 Formative
... 2. ____In picture_____ 3. In the picture place an “A” at all the points where the acceleration of the mass will be at its maximum. 3. ____In picture_____ 4. What is the proportionality constant for this particular system that relates a to –x in the proportion a -x that defines SHM? 4. ____________ ...
... 2. ____In picture_____ 3. In the picture place an “A” at all the points where the acceleration of the mass will be at its maximum. 3. ____In picture_____ 4. What is the proportionality constant for this particular system that relates a to –x in the proportion a -x that defines SHM? 4. ____________ ...
m 1
... • Most planets in the Solar System are very close to a perfect circle – Eccentricity, e ~ 0 for a circle ...
... • Most planets in the Solar System are very close to a perfect circle – Eccentricity, e ~ 0 for a circle ...
Which of the following lists of elements contains an alkaline earth
... 2. Water at the top of Niagara Falls can be said to have energy that can be used to do work as it “falls”. This is an example of a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Water at the top of Niagara Falls can be said to have energy that can be used to do work as it “falls”. This is an example of a. b. c. d. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.