The Big Bang Theory:
... Newton’s Static Universe • Universe is static and composed of an infinite number of stars that are scattered randomly throughout an infinite space. • Universe is infinitely old and will exist forever without any major changes. • Time and Space are steady and independent of one another and any objec ...
... Newton’s Static Universe • Universe is static and composed of an infinite number of stars that are scattered randomly throughout an infinite space. • Universe is infinitely old and will exist forever without any major changes. • Time and Space are steady and independent of one another and any objec ...
HW#5a Page 1 of 4 For circular motion, we know that the total force
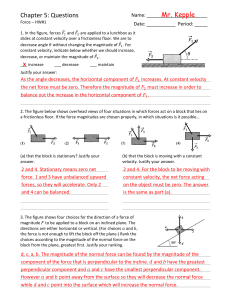
... (Please use the x and y directions shown to answer the questions below.) a.) Find the acceleration of each mass, and the size of the tension in the rope: (Note: Make sure to find the general expressions first; this is an extremely important skill. Only after that, plug in the numerical values.) m1: ...
... (Please use the x and y directions shown to answer the questions below.) a.) Find the acceleration of each mass, and the size of the tension in the rope: (Note: Make sure to find the general expressions first; this is an extremely important skill. Only after that, plug in the numerical values.) m1: ...
D109-08x
... in X-ray, radio, and visible wavelengths as well as the green light of oxygen gas. Astronomers studied the galaxy across several wavelengths to trace how stars, gas, and dust are being tossed around and torn from the fragile galaxy. The composite image at left shows long streamers of gas flowing fro ...
... in X-ray, radio, and visible wavelengths as well as the green light of oxygen gas. Astronomers studied the galaxy across several wavelengths to trace how stars, gas, and dust are being tossed around and torn from the fragile galaxy. The composite image at left shows long streamers of gas flowing fro ...
Practice exam 2, Mechanics ch. 0-9
... rest relative to the ocean. (This entire problem deals only with motion in the horizontal plane.) Find the direction and speed at which the cigarettes, P, are moving relative to the cart, C. Give the direction as an angle, and include a diagram showing how the direction is defined. Hint: Since P is ...
... rest relative to the ocean. (This entire problem deals only with motion in the horizontal plane.) Find the direction and speed at which the cigarettes, P, are moving relative to the cart, C. Give the direction as an angle, and include a diagram showing how the direction is defined. Hint: Since P is ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... acceleration vector can be calculated. B) If the acceleration vector and mass of an object are known, then the Net Force acting on the object can be calculated. It may surprise you! C) If the acceleration vector and mass of an object are known, but the calculated Net Force and the identified forces ...
... acceleration vector can be calculated. B) If the acceleration vector and mass of an object are known, then the Net Force acting on the object can be calculated. It may surprise you! C) If the acceleration vector and mass of an object are known, but the calculated Net Force and the identified forces ...
patterns of motion and equilibrium - SCIENCE
... • Linear motion: motion along a straight line. • It can be uniform, with constant speed or non uniform with a variable speed • An example of linear motion is that of a ball thrown straight up and falling back straight down. • objects not subjected to forces will continue to move uniformly in a strai ...
... • Linear motion: motion along a straight line. • It can be uniform, with constant speed or non uniform with a variable speed • An example of linear motion is that of a ball thrown straight up and falling back straight down. • objects not subjected to forces will continue to move uniformly in a strai ...
Definitions Topic 2
... form into another, but the total amount of energy of a system never changes. 18. The work- energy theorem applies to changes in kinetic and potential energy that can also be used to explain changes in thermal, mechanical , electrical and nuclear energy as well. It is important to understand how ener ...
... form into another, but the total amount of energy of a system never changes. 18. The work- energy theorem applies to changes in kinetic and potential energy that can also be used to explain changes in thermal, mechanical , electrical and nuclear energy as well. It is important to understand how ener ...
Lecture 23 (Mar 18) - West Virginia University
... radius 16.0 cm. The mass of a red blood cell is 3.0 10-16 kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 10-11 N. At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? ...
... radius 16.0 cm. The mass of a red blood cell is 3.0 10-16 kg, and the magnitude of the force acting on it as it settles out of the plasma is 4.0 10-11 N. At how many revolutions per second should the centrifuge be operated? ...
Galaxies
... Based on rotation curves, use Kepler’s 3rd law to infer masses of galaxies Adding ―visible‖ mass in stars, interstellar gas, dust, etc., we find that most of the mass is ―invisible,‖ just as we did for the Milky Way. Dark Matter ...
... Based on rotation curves, use Kepler’s 3rd law to infer masses of galaxies Adding ―visible‖ mass in stars, interstellar gas, dust, etc., we find that most of the mass is ―invisible,‖ just as we did for the Milky Way. Dark Matter ...
State the universal law of gravitation
... 10. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why? According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other w ...
... 10. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why? According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other w ...
Grade Level 8
... statements made by people outside the area of their particular expertise. b. Identify the flaws of reasoning in arguments that are based on poorly designed research (e.g., facts intermingled with opinion, conclusions based on insufficient evidence c. Question the value of arguments based on small sa ...
... statements made by people outside the area of their particular expertise. b. Identify the flaws of reasoning in arguments that are based on poorly designed research (e.g., facts intermingled with opinion, conclusions based on insufficient evidence c. Question the value of arguments based on small sa ...
Force_Motion - World of Teaching
... Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 1 kilogram 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms ...
... Four pairs of objects have the masses shown below. If the objects in each pair are the same distance apart, the gravitational force between the objects in which pair is greatest? 1 kilogram and 1 kilogram 1 kilogram and 2 kilograms 2 kilograms and 1 kilogram 2 kilograms and 2 kilograms ...
Conceptual Physics
... 19.What is the ideal angle of projection for maximum horizontal range? 45 degrees C. Forces and Newton’s Laws 20. Definitions and formulas a) Mass- amount of matter, measure of inertia b) Inertia- resistance to acceleration, mass c) Force- push or pull d) Newton’s first law- If net force = 0 then bo ...
... 19.What is the ideal angle of projection for maximum horizontal range? 45 degrees C. Forces and Newton’s Laws 20. Definitions and formulas a) Mass- amount of matter, measure of inertia b) Inertia- resistance to acceleration, mass c) Force- push or pull d) Newton’s first law- If net force = 0 then bo ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.