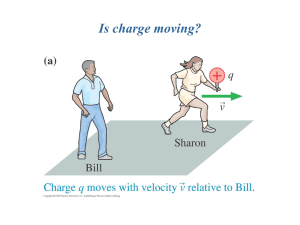
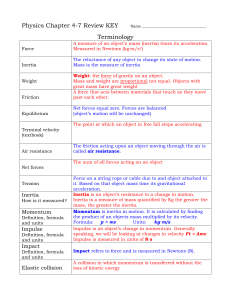
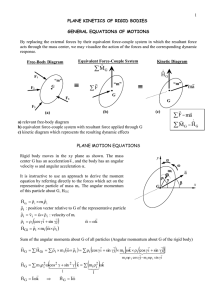
Theoretical questions
... 10. Explain the terms of inertial and no inertial coordinate systems. 11. Define the force impulse and momentum of the mass point. Derive the relation between the force impulse acting to the mass point and its momentum. Derive the law of conservation of momentum of the mass point. 12. Define work ac ...
... 10. Explain the terms of inertial and no inertial coordinate systems. 11. Define the force impulse and momentum of the mass point. Derive the relation between the force impulse acting to the mass point and its momentum. Derive the law of conservation of momentum of the mass point. 12. Define work ac ...
9th grade standards SPS1. Students will investigate our current
... d. Explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram. SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration. b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia Relationship ...
... d. Explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram. SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration. b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia Relationship ...
GPS Content Standards
... d. Explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram. SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration. b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia Relationship ...
... d. Explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram. SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration. b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia Relationship ...
Part VI
... Force (Torque) F τ Mass (moment of inertia) m I Newton’s 2nd Law ∑F = ma ∑τ = Iα Kinetic Energy (KE) (½)mv2 (½)Iω2 CONNECTIONS: v = rω, atan= rα aR = (v2/r) = ω2r , τ = rF , I = ∑(mr2) ...
... Force (Torque) F τ Mass (moment of inertia) m I Newton’s 2nd Law ∑F = ma ∑τ = Iα Kinetic Energy (KE) (½)mv2 (½)Iω2 CONNECTIONS: v = rω, atan= rα aR = (v2/r) = ω2r , τ = rF , I = ∑(mr2) ...