Secondary_4
... Sc 4.1.1 State the properties of magnets; Sc 4.1.2 Explain how magnets can be made or induced; Sc 4.1.3 Describe the electrical methods of magnetisation and demagnetisation; Sc 4.1.4 Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet and also between the poles of two magnets; Sc 4.1.5 Distinguish bet ...
... Sc 4.1.1 State the properties of magnets; Sc 4.1.2 Explain how magnets can be made or induced; Sc 4.1.3 Describe the electrical methods of magnetisation and demagnetisation; Sc 4.1.4 Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet and also between the poles of two magnets; Sc 4.1.5 Distinguish bet ...
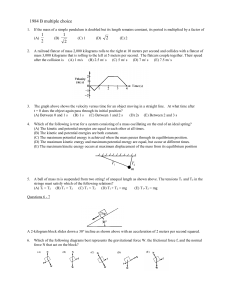
ap physics ii exam -2015
... 3. Monochromatic Light - a light which has only one wavelength (or frequency) is called monochromatic light. Ex. - laser is a monochromatic but sunlight is not monochromatic. Coherent Light – Two wave sources are coherent if they have a constant phase difference and the same frequency. All the waves ...
... 3. Monochromatic Light - a light which has only one wavelength (or frequency) is called monochromatic light. Ex. - laser is a monochromatic but sunlight is not monochromatic. Coherent Light – Two wave sources are coherent if they have a constant phase difference and the same frequency. All the waves ...
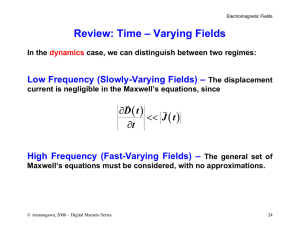
Review: Time – Varying Fields
... G G ∇ × ( v × B ( t )) = G G G G G G G G G G v∇ ⋅ B − B∇ ⋅ v + ( B ⋅ ∇ ) v − ( v ⋅ ∇ ) B = − ( v ⋅ ∇ ) B ...
... G G ∇ × ( v × B ( t )) = G G G G G G G G G G v∇ ⋅ B − B∇ ⋅ v + ( B ⋅ ∇ ) v − ( v ⋅ ∇ ) B = − ( v ⋅ ∇ ) B ...
Semiconductors
... such as angle-resolved photoemission or, most directly, the de Haasvan Alphen effect. Effective masses can also be estimated using the coefficient g of the ...
... such as angle-resolved photoemission or, most directly, the de Haasvan Alphen effect. Effective masses can also be estimated using the coefficient g of the ...
2 Kinetic energy
... The result of the 16 J of work done on the 2 kg object is that it has acquired a speed of 4 m S-' (Figure 8). Now if I try to stop the object, I shall have to apply a force against its motion, i.e. do negative work on it. To look at this another way, the object will do positive work on me, or anythi ...
... The result of the 16 J of work done on the 2 kg object is that it has acquired a speed of 4 m S-' (Figure 8). Now if I try to stop the object, I shall have to apply a force against its motion, i.e. do negative work on it. To look at this another way, the object will do positive work on me, or anythi ...
On the physical structure of radiant energy: waves and
... ether, like transmissive medium, never appears because whether in the wave theory of electromagnetic field or in the corpuscular theory of light the ether isn’ t necessary to explain phenomena of propagation and diffraction likewise it isn’ t necessary to explain the issue of relativity[2]. All the ...
... ether, like transmissive medium, never appears because whether in the wave theory of electromagnetic field or in the corpuscular theory of light the ether isn’ t necessary to explain phenomena of propagation and diffraction likewise it isn’ t necessary to explain the issue of relativity[2]. All the ...
Chapter 2 The Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
... Field is a physics term for a region that is under the influence of some force that can act on matter within that region. For example, the Sun produces a gravitational field that attracts the planets in the solar system and thus influences their orbits. Stationary electric charges produce electric f ...
... Field is a physics term for a region that is under the influence of some force that can act on matter within that region. For example, the Sun produces a gravitational field that attracts the planets in the solar system and thus influences their orbits. Stationary electric charges produce electric f ...
Ch_07
... the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical or nuclear energy. A completely inelastic collision is one where the objects stick together afterwards, so there is only one final velocity. ...
... the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical or nuclear energy. A completely inelastic collision is one where the objects stick together afterwards, so there is only one final velocity. ...