Lecture Notes PHY 321 - Classical Mechanics I Instructor: Scott Pratt,
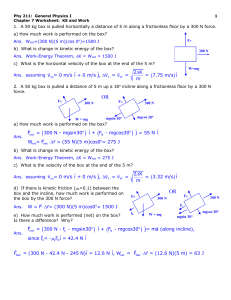
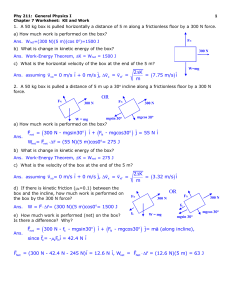
... The arbitrary constants for equations of motion are usually determined by the initial conditions, or more generally boundary conditions. By inspection A = v0x , the initial x component of the velocity. The differential equation for vy is a bit more complicated due to the presence of g. Differential ...
... The arbitrary constants for equations of motion are usually determined by the initial conditions, or more generally boundary conditions. By inspection A = v0x , the initial x component of the velocity. The differential equation for vy is a bit more complicated due to the presence of g. Differential ...
(a) Calculate the speed of electrons which have a de Broglie
... using the arrangement in the diagram above. The lamp is replaced by a source of electrons and the system is evacuated. The student accelerates the electrons to a velocity of 1.4 × 106 m s–1. The beam of electrons is then incident on the double slits. The electrons produce light when incident on the ...
... using the arrangement in the diagram above. The lamp is replaced by a source of electrons and the system is evacuated. The student accelerates the electrons to a velocity of 1.4 × 106 m s–1. The beam of electrons is then incident on the double slits. The electrons produce light when incident on the ...
Paradoxes about Light Phenomena: Photo
... space and time with lines of demarcation between matter, energy, time and space. As these quantities remain distinct and absolute, the speed of light changes. Einstein, however, perceived a Universe with no fixed lines between matter, energy, time, and space but with an absolute speed of light. He f ...
... space and time with lines of demarcation between matter, energy, time and space. As these quantities remain distinct and absolute, the speed of light changes. Einstein, however, perceived a Universe with no fixed lines between matter, energy, time, and space but with an absolute speed of light. He f ...

















![[10] AL Kholmetskii, T. Yarman, OV Missevitch, Kündig`s Experiment](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010773015_1-b3d732fc642ab38b293e58aff252fdab-300x300.png)



