Forces - SFU.ca
... NOTE: We will designate vectors with arrows in diagrams, and with boldface (r) or an arrow over the symbol (r ) in text. We will use italics (r) when referring to only the magnitude of a vector quantity. ...
... NOTE: We will designate vectors with arrows in diagrams, and with boldface (r) or an arrow over the symbol (r ) in text. We will use italics (r) when referring to only the magnitude of a vector quantity. ...
M-8 - University of Iowa Physics
... their PE decreases. The cars then use their KE to bring them up the next hill. As the cars rise their KE decreases and PE increases. ...
... their PE decreases. The cars then use their KE to bring them up the next hill. As the cars rise their KE decreases and PE increases. ...
Dynamicsrev
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion States that: for every action (force) there is an equal but opposite reaction (force). For an example - a book is placed on a table. The book exerts a force (due to gravity) on the table. An equal force is also exerted from the table to the book. Both forces cancel o ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion States that: for every action (force) there is an equal but opposite reaction (force). For an example - a book is placed on a table. The book exerts a force (due to gravity) on the table. An equal force is also exerted from the table to the book. Both forces cancel o ...
Chapter 12
... The elastic limit is the maximum stress that can be applied to the substance before it becomes permanently deformed When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed ...
... The elastic limit is the maximum stress that can be applied to the substance before it becomes permanently deformed When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed ...
Chapter 12
... The torque due to the gravitational force on an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravi ...
... The torque due to the gravitational force on an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravi ...
Chapter 4-5 Review Ideas and Concepts You Are Responsible For
... Development of Force Concept Understand the definition of force. Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System Define net force, external force, and system. Understand Newton’s second law of ...
... Development of Force Concept Understand the definition of force. Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System Define net force, external force, and system. Understand Newton’s second law of ...
Newton`s First Law
... • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
... • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
Spring Scales - Bryn Mawr College
... The individual forces balance. The object does not accelerate. The object’s translational velocity does not change. An object in equilibrium experiences zero net torque. The individual torques balance. The object does not experience an angular acceleration. The object’s angular velocity remains cons ...
... The individual forces balance. The object does not accelerate. The object’s translational velocity does not change. An object in equilibrium experiences zero net torque. The individual torques balance. The object does not experience an angular acceleration. The object’s angular velocity remains cons ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
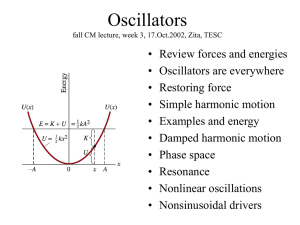
... Second-order diffeq needs two linearly independent solutions: x = x1 + x2. Unknown coefficients to be determined by BC. Sub in your solution and solve for angular frequency w 2 f ...
... Second-order diffeq needs two linearly independent solutions: x = x1 + x2. Unknown coefficients to be determined by BC. Sub in your solution and solve for angular frequency w 2 f ...
The conservation laws in the field theoretical representation of
... vector could be interpreted as a “probability flux” (“Wahrscheinlichkeitsfluss”), then an analog interpretation for a tensor of second-order, here replacing the Dirac vector, would hardly have any meaning. Therefore, I think that at this stage no compromise is any longer possible between the “reacti ...
... vector could be interpreted as a “probability flux” (“Wahrscheinlichkeitsfluss”), then an analog interpretation for a tensor of second-order, here replacing the Dirac vector, would hardly have any meaning. Therefore, I think that at this stage no compromise is any longer possible between the “reacti ...
Chapter 8
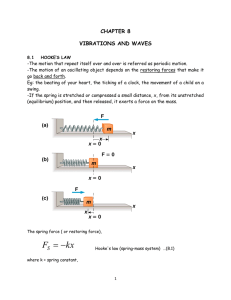
... -The motion that repeat itself over and over is referred as periodic motion. -The motion of an oscillating object depends on the restoring forces that make it go back and forth. Eg: the beating of your heart, the ticking of a clock, the movement of a child on a swing. -If the spring is stretched or ...
... -The motion that repeat itself over and over is referred as periodic motion. -The motion of an oscillating object depends on the restoring forces that make it go back and forth. Eg: the beating of your heart, the ticking of a clock, the movement of a child on a swing. -If the spring is stretched or ...