Newton`s Second Law.
... The alteration of motion is ever proportional to the motive force impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed. This is of course, the famous “F = ma”, once we interpret “alteration of motion” as “acceleration” and combine “motive force” and “direction o ...
... The alteration of motion is ever proportional to the motive force impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed. This is of course, the famous “F = ma”, once we interpret “alteration of motion” as “acceleration” and combine “motive force” and “direction o ...
Thu Mar 22
... 1) “For a conservative force, the magnitude of the force is related to potential energy. The larger the potential energy, the larger the magnitude of the force.” 2) “For a conservative force, the magnitude of the force is related to potential energy. For any equipotential contour line, the magnitude ...
... 1) “For a conservative force, the magnitude of the force is related to potential energy. The larger the potential energy, the larger the magnitude of the force.” 2) “For a conservative force, the magnitude of the force is related to potential energy. For any equipotential contour line, the magnitude ...
Document
... • For the mass in the problem above, what is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the block by the hoop when the block reaches the bottom of the hoop? F⊥ supports weight and provides centripetal force for circular motion. ...
... • For the mass in the problem above, what is the magnitude of the normal force exerted on the block by the hoop when the block reaches the bottom of the hoop? F⊥ supports weight and provides centripetal force for circular motion. ...
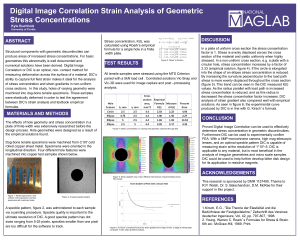
Digital Image Correlation Strain Analysis of Geometric Stress
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
M5.1 Fall 2004 Lab M5: Hooke`s Law and the Simple Harmonic
... Part 1: Measurement of the spring constant k Begin by weighing the spring (you will need the weight in part 2). You might want to check the reliability of the digital balances by weighing the spring on two different balances. Use the digital balances with 0.1g resolution. The spring used in this lab ...
... Part 1: Measurement of the spring constant k Begin by weighing the spring (you will need the weight in part 2). You might want to check the reliability of the digital balances by weighing the spring on two different balances. Use the digital balances with 0.1g resolution. The spring used in this lab ...
Chapter 1 - Dr. ZM Nizam
... derived: • Consider a homogenous rod BC of length L and uniform cross section of area A subjected to a centric axial load P (Figure). If the resulting axial stress σ = P/A does not exceed the proportional limit of the material, the Hooke’s law can be apply and write as follow: ...
... derived: • Consider a homogenous rod BC of length L and uniform cross section of area A subjected to a centric axial load P (Figure). If the resulting axial stress σ = P/A does not exceed the proportional limit of the material, the Hooke’s law can be apply and write as follow: ...
Hooke`s Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Name
... Theory: Think about stretching a spring. The more stretching force you apply, the more stretch you get. Robert Hooke (1635-1703), a British physicist, discovered this empirical relationship between the stretching force and the stretch (x), known as Hooke’s law. ...
... Theory: Think about stretching a spring. The more stretching force you apply, the more stretch you get. Robert Hooke (1635-1703), a British physicist, discovered this empirical relationship between the stretching force and the stretch (x), known as Hooke’s law. ...
Ch 7 Kinetic Energy and Work
... Ideal, or linear springs follow a rule called: Hooke’s Law: Fs = - k x Also an ideal spring will have negligible mass. • k is called the spring constant. This determines how stiff the spring is. • x is the distance the spring is deformed (stretched or compressed) from the equilibrium length. • The m ...
... Ideal, or linear springs follow a rule called: Hooke’s Law: Fs = - k x Also an ideal spring will have negligible mass. • k is called the spring constant. This determines how stiff the spring is. • x is the distance the spring is deformed (stretched or compressed) from the equilibrium length. • The m ...