Title: Springs, Spring Constants, and Changes in Potential Energy
... Date: Partner(s): Background Information: The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant at all times. If there is no friction, this energy will remain mechanical energy. That is it can be exchanged between one form of potential energy and anoth ...
... Date: Partner(s): Background Information: The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant at all times. If there is no friction, this energy will remain mechanical energy. That is it can be exchanged between one form of potential energy and anoth ...
1.6 Work, Energy and Power
... possesses because of its position above the ground. Consider an object of mass m being lifted vertically for a height h from the ground. F mg F mg ...
... possesses because of its position above the ground. Consider an object of mass m being lifted vertically for a height h from the ground. F mg F mg ...
Lab M5: Hooke`s Law and the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
... Part 1: Measurement of the spring constant k Begin by weighing the spring (you will need the weight in part 2). You might want to check the reliability of the digital balances by weighing the spring on two different balances. Use the digital balances with 0.1g resolution. The spring used in this lab ...
... Part 1: Measurement of the spring constant k Begin by weighing the spring (you will need the weight in part 2). You might want to check the reliability of the digital balances by weighing the spring on two different balances. Use the digital balances with 0.1g resolution. The spring used in this lab ...
Impulse and Momentum - Mrs. Haug`s Website
... acting), the total momentum before collision is equal to the total momentum after collision. It is important to realize that the total linear momentum may be conserved even when the kinetic energies of the individual parts of the system ...
... acting), the total momentum before collision is equal to the total momentum after collision. It is important to realize that the total linear momentum may be conserved even when the kinetic energies of the individual parts of the system ...
(True ) or (False)?
... A man weighing 800 N is standing in an elevator moving with a constant velocity. The force exerted by the man on the floor of the elevator is: a) less than 80 N b) 800 N c) between 80 and 800 N d) more than 800 N ...
... A man weighing 800 N is standing in an elevator moving with a constant velocity. The force exerted by the man on the floor of the elevator is: a) less than 80 N b) 800 N c) between 80 and 800 N d) more than 800 N ...
$doc.title
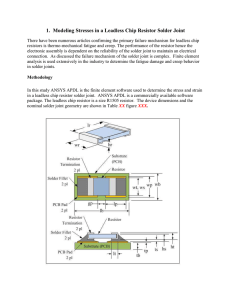
... To describe a problem in mathematical terms, one must make use of the basic laws that govern the elements of the problem. In continuum mechanics, these are the conser vation laws for mass and momentum. In addition, empirical constitutive laws are often needed to relate certain unknown variables; ex ...
... To describe a problem in mathematical terms, one must make use of the basic laws that govern the elements of the problem. In continuum mechanics, these are the conser vation laws for mass and momentum. In addition, empirical constitutive laws are often needed to relate certain unknown variables; ex ...
AS Unit G481: Mechanics
... describe examples of energy in different forms, its conversion and conservation, and apply the principle of energy conservation to simple examples; describe how deformation is caused by a force in one dimension and can be tensile or compressive; describe the behaviour of springs and wires in terms o ...
... describe examples of energy in different forms, its conversion and conservation, and apply the principle of energy conservation to simple examples; describe how deformation is caused by a force in one dimension and can be tensile or compressive; describe the behaviour of springs and wires in terms o ...
Lecture13
... by restoring forces and the system do not oscillate indefinitely. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
... by restoring forces and the system do not oscillate indefinitely. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
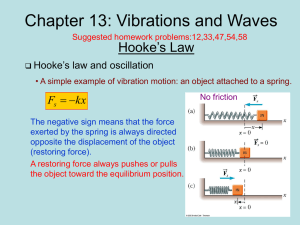
Chapter 13 Slide
... oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. (a) Find the period of oscillations. (b) Calculate the total energy of the system and maximum speed of the object if the amplitude of the motion is 3 cm. © What is the velocity of the object when the displacement is 2 cm. ...
... oscillates on a frictionless horizontal surface. (a) Find the period of oscillations. (b) Calculate the total energy of the system and maximum speed of the object if the amplitude of the motion is 3 cm. © What is the velocity of the object when the displacement is 2 cm. ...