Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy
... SG A 0.5 kg mass is attached to a spring on a horizontal frictionless table. The mass is pulled to stretch the spring 5.0 cm and is released from rest. When the mass crosses the point at which the spring is not stretched, x = 0, its speed is 20 cm/s. If the experiment is repeated with a 10.0 cm init ...
... SG A 0.5 kg mass is attached to a spring on a horizontal frictionless table. The mass is pulled to stretch the spring 5.0 cm and is released from rest. When the mass crosses the point at which the spring is not stretched, x = 0, its speed is 20 cm/s. If the experiment is repeated with a 10.0 cm init ...
Kinetic energy - GZ @ Science Class Online
... equal, but opposite, push/pull effects on an object. Unbalanced forces can change the speed and/or direction of an object ...
... equal, but opposite, push/pull effects on an object. Unbalanced forces can change the speed and/or direction of an object ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint
... of the sled is about -1 m/s2 and the time it takes the sled to stop is about 2 s. Thus, the distance the sled traveled in the given amount of time should be less than the distance it would have traveled in the absence of friction. 2.5 m < (2.2 m/s)(2 s) = 4.4 m ...
... of the sled is about -1 m/s2 and the time it takes the sled to stop is about 2 s. Thus, the distance the sled traveled in the given amount of time should be less than the distance it would have traveled in the absence of friction. 2.5 m < (2.2 m/s)(2 s) = 4.4 m ...
Energy:
... •Roller coasters work because of the energy that is built into the system. •Cars are pulled mechanically up the tallest hill, giving them a great deal of potential energy. •Conversions between potential and kinetic energy power the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
... •Roller coasters work because of the energy that is built into the system. •Cars are pulled mechanically up the tallest hill, giving them a great deal of potential energy. •Conversions between potential and kinetic energy power the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
Energy:
... deal of potential energy. From that point, the conversion between potential and kinetic energy powers the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
... deal of potential energy. From that point, the conversion between potential and kinetic energy powers the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
Chapter 5 Problems
... 41. A 2.1 x 103-kg car starts from rest at the top of a 5.0m-long driveway that is sloped at 20° with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 4.0 x 103 N impedes the motion, find the speed of the car at the bottom of the driveway. 42. A 25.0-kg child on a 2.00-m-long swing is released from r ...
... 41. A 2.1 x 103-kg car starts from rest at the top of a 5.0m-long driveway that is sloped at 20° with the horizontal. If an average friction force of 4.0 x 103 N impedes the motion, find the speed of the car at the bottom of the driveway. 42. A 25.0-kg child on a 2.00-m-long swing is released from r ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... A ball is thrown upward with an initial speed v from the roof of a building. An identical ball is thrown downward with the same initial speed v. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? Ignore air resistance effects. a) The kinetic energies of the two ba ...
... A ball is thrown upward with an initial speed v from the roof of a building. An identical ball is thrown downward with the same initial speed v. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? Ignore air resistance effects. a) The kinetic energies of the two ba ...
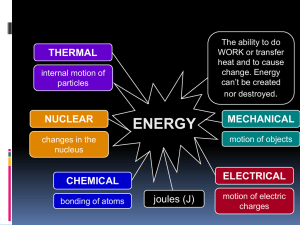
TYPES AND FORMS OF ENERGY
... What is Mechanical Energy? Energy due to a object’s motion (kinetic) or position (potential). The bowling ball has mechanical energy. When the ball strikes the pins, mechanical energy is transferred to the pins! ...
... What is Mechanical Energy? Energy due to a object’s motion (kinetic) or position (potential). The bowling ball has mechanical energy. When the ball strikes the pins, mechanical energy is transferred to the pins! ...