Chapter 9 Test Study Guide - Motion and Energy
... 4. The ability to do work is called __________________ 5. A centimeter is equal to ___________________ meters 6. The metric unit for time is the _____________________ 7. A vector is an arrow that shows both _______________________and ___________________________ 8. The rate at which the velocity of a ...
... 4. The ability to do work is called __________________ 5. A centimeter is equal to ___________________ meters 6. The metric unit for time is the _____________________ 7. A vector is an arrow that shows both _______________________and ___________________________ 8. The rate at which the velocity of a ...
2 2(9.80 )(20.4 ) 20.0 vgym = ∆ = = 92 12 7.6 JFN m
... 1. A 65 kg diver is poised at the edge of a platform 10.0 m above the water. a. Calculate the diver’s gravitational potential energy relative to the water’s surface. PEg = (65 kg)(9.80 m/s2)(10.0 m) = 6400 J b. The pool is 4.5 m deep. Calculate the diver’s gravitational potential energy relative to ...
... 1. A 65 kg diver is poised at the edge of a platform 10.0 m above the water. a. Calculate the diver’s gravitational potential energy relative to the water’s surface. PEg = (65 kg)(9.80 m/s2)(10.0 m) = 6400 J b. The pool is 4.5 m deep. Calculate the diver’s gravitational potential energy relative to ...
SCCS Physics Chapter 11 Study Guide Name
... 10. Describe an object that has rotational KE but no translational KE. 11. Describe an object that has translational KE but no rotational KE. 12. At what point in a pendulum’s swing are the the following quantities at maximum values? a) velocity b) potential energy c)kinetic energy PROBLEMS: (Draw a ...
... 10. Describe an object that has rotational KE but no translational KE. 11. Describe an object that has translational KE but no rotational KE. 12. At what point in a pendulum’s swing are the the following quantities at maximum values? a) velocity b) potential energy c)kinetic energy PROBLEMS: (Draw a ...
Energy
... • Also Travels in waves but are much slower than light • Is produced by vibrating air molecules which in turn vibrate our ear drums. ...
... • Also Travels in waves but are much slower than light • Is produced by vibrating air molecules which in turn vibrate our ear drums. ...
A box is sitting on the floor
... 1) Kinetic energy is being converted into gravitational potential energy. 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg ...
... 1) Kinetic energy is being converted into gravitational potential energy. 2) The normal force does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg ...
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... Formulas S= D/T Speed = Distance/ Time ; Momentum= mv; a= Vf - Vi / t (acceleration) ...
... Formulas S= D/T Speed = Distance/ Time ; Momentum= mv; a= Vf - Vi / t (acceleration) ...
work and energy - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... 9) Seema tried to push a heavy rock of mass 100 kg for 200 s, but could not move it. Find the work done by Seema at the end of 200s.Find out the power delivered by her. Give reason to justify the answer. 10) Distinguish between positive work and negative work. When you lift an object up, two forces ...
... 9) Seema tried to push a heavy rock of mass 100 kg for 200 s, but could not move it. Find the work done by Seema at the end of 200s.Find out the power delivered by her. Give reason to justify the answer. 10) Distinguish between positive work and negative work. When you lift an object up, two forces ...
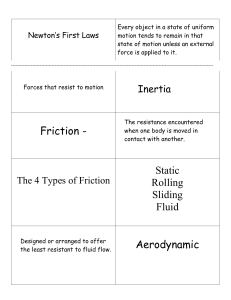
Cut squares along dotted line then fold in half to make flashcard
... The resistance encountered when one body is moved in contact with another. ...
... The resistance encountered when one body is moved in contact with another. ...
Slide 1
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
Conservation of Energy
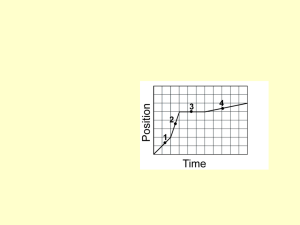
... Use the meter stick taped to the right door frame in the video for scaling purposes. Translate the origin to the lowest position marked in any frame so that the floor will be the zero reference point for potential energy. Plots of position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time are useful. ...
... Use the meter stick taped to the right door frame in the video for scaling purposes. Translate the origin to the lowest position marked in any frame so that the floor will be the zero reference point for potential energy. Plots of position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time are useful. ...
T3 F2013 9 30
... is in meters and t is in seconds). I. Find an expression as a function of time for a) the velocity b) the linear momentum c) the acceleration d) the force, of the particle relative to the origin. II. About the origin, at t = 1s, determine d) the torque and e) the angular momentum of the particle in ...
... is in meters and t is in seconds). I. Find an expression as a function of time for a) the velocity b) the linear momentum c) the acceleration d) the force, of the particle relative to the origin. II. About the origin, at t = 1s, determine d) the torque and e) the angular momentum of the particle in ...
PEKE - Science
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
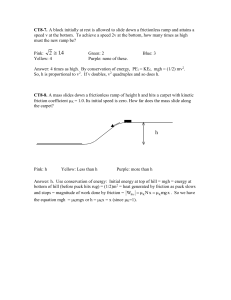
CT8b
... Answer: The acceleration is negative. In 1D, F = - dU/dx. The slope of the curve dU/dx is positive at x=A, so F = ma = -dU/dx is negative there. The force F and the acceleration a = F/m are negative at x=A (meaning their directions are to the left, toward negative x.) The kinetic energy might be zer ...
... Answer: The acceleration is negative. In 1D, F = - dU/dx. The slope of the curve dU/dx is positive at x=A, so F = ma = -dU/dx is negative there. The force F and the acceleration a = F/m are negative at x=A (meaning their directions are to the left, toward negative x.) The kinetic energy might be zer ...
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
... f) By comparing your answers from parts (c) and (d), do you see a term that could represent kinetic energy and that depends on the characteristics that you think kinetic energy should depend on? g) Show that the units of this quantity are equal to the units for energy, joules. ...
... f) By comparing your answers from parts (c) and (d), do you see a term that could represent kinetic energy and that depends on the characteristics that you think kinetic energy should depend on? g) Show that the units of this quantity are equal to the units for energy, joules. ...
P2 Forces and energy Revision Sheet
... 11.State the energy changes of a falling ball from when it drops, to when it lands on the floor [5] ...
... 11.State the energy changes of a falling ball from when it drops, to when it lands on the floor [5] ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
... Energy: Ability to do work Different Types of Energy The Ninja, a roller coaster at Six Flags over Georgia, has a height of 122 ft and a speed of 52 mi/h. The potential energy due to its height changes into kinetic energy of motion. ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitting on a desk that is 2 meters off the ground, what is th ...
... 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcase. The height of each shelf is 1.0 meters, 1.5 meters, and 2.0 meters. 4) If you had a book that had a mass of 2.7 kg and it is sitting on a desk that is 2 meters off the ground, what is th ...