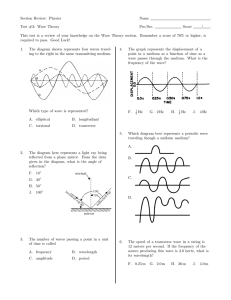
Section Review: Physics Name Test #3: Wave Theory Per/Sec
... A, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 30 meters per second due east from a height of 20 meters above level ground. At the same instant, a 20-kilogram sphere, B, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 10 meters per second due west from a height of 80 meters above ...
... A, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 30 meters per second due east from a height of 20 meters above level ground. At the same instant, a 20-kilogram sphere, B, is projected horizontally with a velocity of 10 meters per second due west from a height of 80 meters above ...
SECTION7.2 Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
empirical correlation between the shear
... estimated. Two different approaches (low vs. high strain) were compared, and the results were found to be in good agreement when the relative difference between the velocities is small and smooth. Dynamic probing tests are good for studying a discrete point of interest in a large field area based on ...
... estimated. Two different approaches (low vs. high strain) were compared, and the results were found to be in good agreement when the relative difference between the velocities is small and smooth. Dynamic probing tests are good for studying a discrete point of interest in a large field area based on ...
Continental hyperextension, mantle exhumation and thin oceanic
... recorded by the earliest oceanic crust. However, the late stages of continental extension and the eventual breakup of the continent, at the Iberia-Newfoundland margin, occurred during the Cretaceous constant polarity interval (121–83 Ma), resulting in a lack of strong magnetic reversals which would ...
... recorded by the earliest oceanic crust. However, the late stages of continental extension and the eventual breakup of the continent, at the Iberia-Newfoundland margin, occurred during the Cretaceous constant polarity interval (121–83 Ma), resulting in a lack of strong magnetic reversals which would ...
Chapter 5 - CPO Science
... gymnast. The acceleration must be zero if he is not moving. The net force must also be zero because of the second law. The only way the net force can be zero is if the ropes pull upward with a force exactly equal and opposite the force of gravity pulling downward. If the weight of the gymnast is –70 ...
... gymnast. The acceleration must be zero if he is not moving. The net force must also be zero because of the second law. The only way the net force can be zero is if the ropes pull upward with a force exactly equal and opposite the force of gravity pulling downward. If the weight of the gymnast is –70 ...
Simulating migrated seismic data by filtering an earth model A
... In this paper a forward modeling and migration scheme is proposed for calculating spatial resolution filters in a velocity model. For this purpose, we first show an example to illustrate how we simulate a migration image by filtering an earth model with a spatial resolution filter. This is followed by a ...
... In this paper a forward modeling and migration scheme is proposed for calculating spatial resolution filters in a velocity model. For this purpose, we first show an example to illustrate how we simulate a migration image by filtering an earth model with a spatial resolution filter. This is followed by a ...
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1
... Both rocks undergo 1D motion with a=-g=-9.81 m/s2 Use 2) for rock 1 (upward) and realize that y(t)=0 when the rock lands: 0 = 100 + 15t-0.5x9.81t2 t=6.27 s (quadratic equation, disregard negative answer) Use 2 for rock 2 (dropped) to find the time it takes to reach the ground 0=100 +0t -0.5x9.81t2 t ...
... Both rocks undergo 1D motion with a=-g=-9.81 m/s2 Use 2) for rock 1 (upward) and realize that y(t)=0 when the rock lands: 0 = 100 + 15t-0.5x9.81t2 t=6.27 s (quadratic equation, disregard negative answer) Use 2 for rock 2 (dropped) to find the time it takes to reach the ground 0=100 +0t -0.5x9.81t2 t ...
Multi-Objective Optimization of LQR Control Quarter Car Suspension System using Genetic Algorithm
... lumped parameter 2 DoF quarter car model is used for control application with objective to minimize sprung mass response. The weight matrix, Q, is chosen for LQR control application. Sam et al. [8] presented a model of a quarter car in state space form for control application. LQR controller is used ...
... lumped parameter 2 DoF quarter car model is used for control application with objective to minimize sprung mass response. The weight matrix, Q, is chosen for LQR control application. Sam et al. [8] presented a model of a quarter car in state space form for control application. LQR controller is used ...
Projectile Orbital Motion 2012 - EarthScienceNHS
... • 1. An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion maintains its velocity unless it experiences an unbalanced force. • 2. The unbalanced force acting on an object equals the object’s mass times its acceleration. (Force = mass x acceleration) • 3. For every action force, there is an equal ...
... • 1. An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion maintains its velocity unless it experiences an unbalanced force. • 2. The unbalanced force acting on an object equals the object’s mass times its acceleration. (Force = mass x acceleration) • 3. For every action force, there is an equal ...
Earthquake-generated tsunamis in the Mediterranean Sea
... size of its associated Typical Fault. We then let the Typical Fault float along strike of its parent source zone and simulated all tsunamis it could trigger. Simulations are based on the solution of the nonlinear shallow water equations through a finite difference technique. For each run we calculat ...
... size of its associated Typical Fault. We then let the Typical Fault float along strike of its parent source zone and simulated all tsunamis it could trigger. Simulations are based on the solution of the nonlinear shallow water equations through a finite difference technique. For each run we calculat ...
Test Review Problems
... 1. When an object is moving with uniform circular motion, the object’s tangential speed a. is circular. b. is perpendicular to the plane of motion. c. is constant. d. is directed toward the center of motion. 2. When an object is moving with uniform circular motion, the centripetal acceleration of th ...
... 1. When an object is moving with uniform circular motion, the object’s tangential speed a. is circular. b. is perpendicular to the plane of motion. c. is constant. d. is directed toward the center of motion. 2. When an object is moving with uniform circular motion, the centripetal acceleration of th ...