504 Advanced Placement Physics C Course Description Students
... Students are expected to complete rigorous course and lab work consistent with college level Physics and to complete 5-8 hours per week of independent practice such as homework, reading, and projects. This course will follow the curriculum prescribed for an AP Physics C – Mechanics class. Students w ...
... Students are expected to complete rigorous course and lab work consistent with college level Physics and to complete 5-8 hours per week of independent practice such as homework, reading, and projects. This course will follow the curriculum prescribed for an AP Physics C – Mechanics class. Students w ...
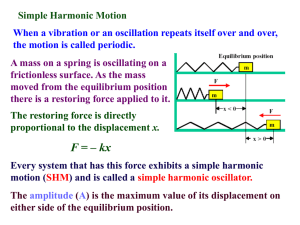
The Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
... a. Find the momentum of an automobile of mass 1350 kg travelling at 20 m/s b. Find the momentum of an automobile of mass 1350 kg travelling at 65 km/h c. A vehicle travelling at 30 m/s possesses 32,000 kg m/s of momentum. Find the mass of the vehicle. Question 2 (To be solved in class) Find the velo ...
... a. Find the momentum of an automobile of mass 1350 kg travelling at 20 m/s b. Find the momentum of an automobile of mass 1350 kg travelling at 65 km/h c. A vehicle travelling at 30 m/s possesses 32,000 kg m/s of momentum. Find the mass of the vehicle. Question 2 (To be solved in class) Find the velo ...
Aristotle on Motion
... with his horse and wagon. He is worried that the tattered bridge will not hold up his wagon full of many rare and exotic birds. He ponders for a moment about what he can do in his dilemma and comes up with a solution. He swiftly shakes the bird cage and safely crosses the bridge. – What did this do? ...
... with his horse and wagon. He is worried that the tattered bridge will not hold up his wagon full of many rare and exotic birds. He ponders for a moment about what he can do in his dilemma and comes up with a solution. He swiftly shakes the bird cage and safely crosses the bridge. – What did this do? ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12-N net force is applied to a 3-kg object? A 6-kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at the rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. An object is accelerating at 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass of the object is doubled, ...
... 1. What acceleration will result when a 12-N net force is applied to a 3-kg object? A 6-kg object? 2. A net force of 16 N causes a mass to accelerate at the rate of 5 m/s2. Determine the mass. 3. An object is accelerating at 2 m/s2. If the net force is tripled and the mass of the object is doubled, ...
Teachers Guide Second Law Simulation Lab
... Note: Timing and accelerations may vary some. Use the values that are calculated 5. Using graph paper, make a graph of acceleration (vertical axis) vs. mass (horizontal axis). Attach the graph to this lab report. ...
... Note: Timing and accelerations may vary some. Use the values that are calculated 5. Using graph paper, make a graph of acceleration (vertical axis) vs. mass (horizontal axis). Attach the graph to this lab report. ...
06 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion – Gravity The acceleration for any object moving under the sole influence of gravity on Earth is 9.8m/s2. Any moving object being acted upon ONLY by the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall” because these objects do not encounter air resistance. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion – Gravity The acceleration for any object moving under the sole influence of gravity on Earth is 9.8m/s2. Any moving object being acted upon ONLY by the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall” because these objects do not encounter air resistance. ...
Newton`s 2 nd Law of Motion
... It is static because there is no relative motion between the surfaces. ...
... It is static because there is no relative motion between the surfaces. ...
File
... string.When the string is plucked, many frequency waves will travel in both directions. Most will interfere randomly and die away. Only those with resonant frequencies will persist. Since the ends are fixed, they will be the nodes. The wavelengths of the standing waves have a simple relation to the ...
... string.When the string is plucked, many frequency waves will travel in both directions. Most will interfere randomly and die away. Only those with resonant frequencies will persist. Since the ends are fixed, they will be the nodes. The wavelengths of the standing waves have a simple relation to the ...
Chapter 5 - KFUPM Faculty List
... The acceleration along the x-axis is due to the net force along the x-axis. This holds for each axis individually. Important: the acceleration along a given axis is caused only by the sum of the force components along that same axis, and not by the force components along any other axis. To solve pro ...
... The acceleration along the x-axis is due to the net force along the x-axis. This holds for each axis individually. Important: the acceleration along a given axis is caused only by the sum of the force components along that same axis, and not by the force components along any other axis. To solve pro ...
Word - Structured Independent Learning
... table? Unlike the books, we only have to give the ball a small push to get it going. Assuming a smooth level surface, once the ball is moving no force is required to keep it moving. There is something strange going on here, why does the same applied force result in such different motions? Many years ...
... table? Unlike the books, we only have to give the ball a small push to get it going. Assuming a smooth level surface, once the ball is moving no force is required to keep it moving. There is something strange going on here, why does the same applied force result in such different motions? Many years ...
NEWTON`S LAWS
... then the object will fall with a constant velocity (terminal velocity) and an acceleration of zero. Drop the piece of paper and the metal disk side-by-side to see which one hits the floor first. Repeat, but place the piece of paper on top of the metal disk so it rides "piggy-back" on the disk. Make ...
... then the object will fall with a constant velocity (terminal velocity) and an acceleration of zero. Drop the piece of paper and the metal disk side-by-side to see which one hits the floor first. Repeat, but place the piece of paper on top of the metal disk so it rides "piggy-back" on the disk. Make ...
performance based analysis and modeling of a dual seismic force
... the link beams, brace members and columns are often located within the same vertical plane. Past EBF research has concentrated on short links, with limited information available on the real behaviour of those other than short links. This paper summarizes performance-based seismic analysis and modeli ...
... the link beams, brace members and columns are often located within the same vertical plane. Past EBF research has concentrated on short links, with limited information available on the real behaviour of those other than short links. This paper summarizes performance-based seismic analysis and modeli ...
Newton`sLaws - Redwood High School
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
... acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at the same rate of acceleration. ...
Example 2 - mrdsample
... high altitude. NOW consider the effect of air resistance (friction) during the fall. a) Initially at t=0, what forces act on the skydiver? b) Initially at t=0, what is the acceleration and velocity of the skydiver? c) As the skydiver begins to fall, what happens to the force of air resistance on sky ...
... high altitude. NOW consider the effect of air resistance (friction) during the fall. a) Initially at t=0, what forces act on the skydiver? b) Initially at t=0, what is the acceleration and velocity of the skydiver? c) As the skydiver begins to fall, what happens to the force of air resistance on sky ...