09 Newtons Second Law
... so that both small and large forces are applied. Make sure that your hand is only touching the hook on the Force Sensor and not the Force Sensor or cart body. 6. Note the shape of the force vs. time and acceleration vs. time graphs. If the force values exceed ±10N, redo the data collection. Click th ...
... so that both small and large forces are applied. Make sure that your hand is only touching the hook on the Force Sensor and not the Force Sensor or cart body. 6. Note the shape of the force vs. time and acceleration vs. time graphs. If the force values exceed ±10N, redo the data collection. Click th ...
How High Can You Jump On Mars?
... It only depends on the mass of the Earth and how far you are from the center of the Earth. Well, if you are falling near the surface of the Earth, then the value of the distance d between you and the center of the Earth is essentially the radius of the Earth, which is about 4, 000 miles. If you look ...
... It only depends on the mass of the Earth and how far you are from the center of the Earth. Well, if you are falling near the surface of the Earth, then the value of the distance d between you and the center of the Earth is essentially the radius of the Earth, which is about 4, 000 miles. If you look ...
hw4
... east. Find the magnitude and direction (relative to due east) of the displacement that the duck undergoes in 3.0 s while the forces are acting. *44 Refer to Multiple-Concept Example 10 for help in solving problems like this one. An ice skater is gliding horizontally across the ice with an initial ve ...
... east. Find the magnitude and direction (relative to due east) of the displacement that the duck undergoes in 3.0 s while the forces are acting. *44 Refer to Multiple-Concept Example 10 for help in solving problems like this one. An ice skater is gliding horizontally across the ice with an initial ve ...
Kinetics of particles Newton`s Second Law
... In step 2 the FBD and MAD are drawn. This just means drawing the object of interest twice. Note that the coordinate system is shown too. There are several ways to draw an MAD, the simplest being to draw the vectors both in the positive coordinate directions, as is done above. Doing this in ...
... In step 2 the FBD and MAD are drawn. This just means drawing the object of interest twice. Note that the coordinate system is shown too. There are several ways to draw an MAD, the simplest being to draw the vectors both in the positive coordinate directions, as is done above. Doing this in ...
Slide 1
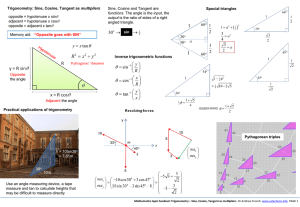
... For an object in motion the concept of velocity is important. There are two types of velocity that can be defined. Suppose an object moves from one point to another in a certain time interval. The average velocity during that time interval is defined as: Average Velocity = Change in position divided ...
... For an object in motion the concept of velocity is important. There are two types of velocity that can be defined. Suppose an object moves from one point to another in a certain time interval. The average velocity during that time interval is defined as: Average Velocity = Change in position divided ...
Monday, Sept. 16, 2002 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... either at rest or moving at a constant velocity. 3. Objects would like to keep its current state of motion, as long as there is no force that interferes with the motion. This tendency is called the Inertia. A frame of reference that is moving at constant velocity is called an Inertial Frame Monday, ...
... either at rest or moving at a constant velocity. 3. Objects would like to keep its current state of motion, as long as there is no force that interferes with the motion. This tendency is called the Inertia. A frame of reference that is moving at constant velocity is called an Inertial Frame Monday, ...
Force of Friction
... A 35.0 kg lawn mower is pushed across a level lawn in a direction of 0.0. The force exerted on the handle is 100 N @ 310.0. Assume friction is negligible. (a) Determine the acceleration of the mower. (b) Determine the normal force acting on the lawn mower. ...
... A 35.0 kg lawn mower is pushed across a level lawn in a direction of 0.0. The force exerted on the handle is 100 N @ 310.0. Assume friction is negligible. (a) Determine the acceleration of the mower. (b) Determine the normal force acting on the lawn mower. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion power point
... The more massive an object is, the more force that is required to accelerate it OR the more force used, the farther an object will go • 2nd: Mrs. Massey throws a ball as hard as she can, and it lands on the roof! Then, she throws the same ball as gently as she can, and it lands only one foot in fron ...
... The more massive an object is, the more force that is required to accelerate it OR the more force used, the farther an object will go • 2nd: Mrs. Massey throws a ball as hard as she can, and it lands on the roof! Then, she throws the same ball as gently as she can, and it lands only one foot in fron ...
National 4/5 Physics Dynamics and Space Summary Notes
... very short time interval as the vehicle passes that point. Average speed and instantaneous speed are often very different e.g. the average speed for a car over an entire journey from Glasgow to Edinburgh could be 40 mph, but at any point in the journey, the instantaneous speed of the car could be 30 ...
... very short time interval as the vehicle passes that point. Average speed and instantaneous speed are often very different e.g. the average speed for a car over an entire journey from Glasgow to Edinburgh could be 40 mph, but at any point in the journey, the instantaneous speed of the car could be 30 ...
Gravitational Force and Orbits
... of water in the hanging mass. We are making the string MIMIC Gravity. Numbers that are easy to use in lab have been provided. You will have one trial where you hang 0.500 kg mass from the string, and measure the time period with the radius set at 1.00m. Then you will reduce the mass to 0.250kg. This ...
... of water in the hanging mass. We are making the string MIMIC Gravity. Numbers that are easy to use in lab have been provided. You will have one trial where you hang 0.500 kg mass from the string, and measure the time period with the radius set at 1.00m. Then you will reduce the mass to 0.250kg. This ...
10 Dyn and Space N 1and 2 Theory
... unbalanced force, mass and acceleration for situations where more than one force is acting. Apply of Newton’s second law to space travel, including rocket launch, landing and terminal velocity. ...
... unbalanced force, mass and acceleration for situations where more than one force is acting. Apply of Newton’s second law to space travel, including rocket launch, landing and terminal velocity. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... because they act on different objects only one force from the pair acts on a particular object to determine if the forces on an object are balanced, you need to examine all the forces from different action-reaction force pairs. ...
... because they act on different objects only one force from the pair acts on a particular object to determine if the forces on an object are balanced, you need to examine all the forces from different action-reaction force pairs. ...
Chapter 15
... A Particle in Simple Harmonic Motion, 2 A function that satisfies the equation is needed. Need a function x(t) whose second derivative is the same as the original function with a negative sign and multiplied by w2. The sine and cosine functions meet these requirements. ...
... A Particle in Simple Harmonic Motion, 2 A function that satisfies the equation is needed. Need a function x(t) whose second derivative is the same as the original function with a negative sign and multiplied by w2. The sine and cosine functions meet these requirements. ...
What is time to top?
... Mass and weight Newtons second law enables us to measure relative mass. If we apply the same force to two objects and measure the accelerations then. F = m1a1 and F = m2a2 so m1/m2 = a2/a1 We then need to have one mass as a calibration and a kilogram is the mass of a piece of platinum held in Paris ...
... Mass and weight Newtons second law enables us to measure relative mass. If we apply the same force to two objects and measure the accelerations then. F = m1a1 and F = m2a2 so m1/m2 = a2/a1 We then need to have one mass as a calibration and a kilogram is the mass of a piece of platinum held in Paris ...
Topic 2.1 ppt
... If you are stationary and watching things come towards you or away from you, then determining relative velocities is straightforward since your frame of reference is at rest. If, however, you are in motion, either towards or away from an object in motion, then your frame of reference is moving and r ...
... If you are stationary and watching things come towards you or away from you, then determining relative velocities is straightforward since your frame of reference is at rest. If, however, you are in motion, either towards or away from an object in motion, then your frame of reference is moving and r ...
Chapter 12 Section 1
... Seismic Waves and Earth’s Interior • By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists can learn more about the makeup and structure of Earth’s interior. Earth’s Internal Layers • In 1909, Andrija Mohorovičić discovered that the speed of seismic waves increases abruptly at about 30 km ...
... Seismic Waves and Earth’s Interior • By studying the speed and direction of seismic waves, scientists can learn more about the makeup and structure of Earth’s interior. Earth’s Internal Layers • In 1909, Andrija Mohorovičić discovered that the speed of seismic waves increases abruptly at about 30 km ...