Lab 7 Ballistic Pendulum! !
... Calculate the initial speed from this data. Include the uncertainty. Analysis Here is a case where two measurements of the same value are done two different ways without an expected value. How do we know if the two experiments agree? We now have two pdf’s, one for each experiment. One question we wa ...
... Calculate the initial speed from this data. Include the uncertainty. Analysis Here is a case where two measurements of the same value are done two different ways without an expected value. How do we know if the two experiments agree? We now have two pdf’s, one for each experiment. One question we wa ...
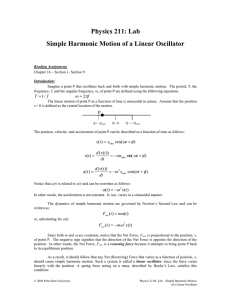
Lab #11: Simple Harmonic Motion of a Linear Oscillator
... Fnet (t ) m 2 x(t ) Since both m and are constants, notice that the Net Force, Fnet, is proportional to the position, x, of point P. The negative sign signifies that the direction of the Net Force is opposite the direction of the position. In other words, the Net Force, Fnet, is a restoring fo ...
... Fnet (t ) m 2 x(t ) Since both m and are constants, notice that the Net Force, Fnet, is proportional to the position, x, of point P. The negative sign signifies that the direction of the Net Force is opposite the direction of the position. In other words, the Net Force, Fnet, is a restoring fo ...
Seismic Waves
... secondary waves. The third waves are called L-waves or Love waves, named after the scientist who first discovered it. ...
... secondary waves. The third waves are called L-waves or Love waves, named after the scientist who first discovered it. ...
Seismic Waves - Earth Science with Mrs. Wilson
... secondary waves. The third waves are called L-waves or Love waves, named after the scientist who first discovered it. ...
... secondary waves. The third waves are called L-waves or Love waves, named after the scientist who first discovered it. ...
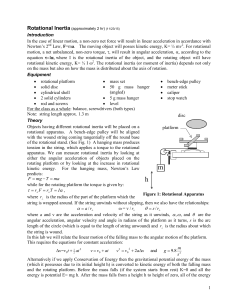
Rotational Dynamics
... inertia than long legs. An animal with shorter legs has a quicker stride than one with long legs (same is true for pendulums). When running, we bend our legs to reduce the rotational inertia so that we can rotate them back and forth more quickly. ...
... inertia than long legs. An animal with shorter legs has a quicker stride than one with long legs (same is true for pendulums). When running, we bend our legs to reduce the rotational inertia so that we can rotate them back and forth more quickly. ...
Section 2.10: Apparent Weight
... hit the water. In reality, a gravitational force is acting on you during your fall. What is missing is the upward reaction force provided by whatever supports your weight at other times—the seat of a chair, the floor of a room, the diving board, the water. It is useful to distinguish between the act ...
... hit the water. In reality, a gravitational force is acting on you during your fall. What is missing is the upward reaction force provided by whatever supports your weight at other times—the seat of a chair, the floor of a room, the diving board, the water. It is useful to distinguish between the act ...
lectures 2015
... cancel before the last line. An exception to this rule arises where some terms are dimensionless factors which are simple fractions. 4. Check the dimensions Think about the dimensions of every quantity even as you write it down. You will find this a discipline which helps enormously to avoid errors ...
... cancel before the last line. An exception to this rule arises where some terms are dimensionless factors which are simple fractions. 4. Check the dimensions Think about the dimensions of every quantity even as you write it down. You will find this a discipline which helps enormously to avoid errors ...
Circular Motion
... To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration (such as tension on a string). Then you can apply Newton’s second law for the component in the direction of the acceleration in the following way. Newton’s Second Law for ...
... To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration (such as tension on a string). Then you can apply Newton’s second law for the component in the direction of the acceleration in the following way. Newton’s Second Law for ...
Experiment 4 The Simple Pendulum Reading:
... given initial angle. If Eq B3 holds, and the higher terms are negligible, the plot should be close to linear. Perform a linear least squares fit of the data to T()/T* vs. (and find A from this fit). Compare your slope with the theoretical value of 1/16. It is not necessary to find the uncertaint ...
... given initial angle. If Eq B3 holds, and the higher terms are negligible, the plot should be close to linear. Perform a linear least squares fit of the data to T()/T* vs. (and find A from this fit). Compare your slope with the theoretical value of 1/16. It is not necessary to find the uncertaint ...