Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously ...
... Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously ...
Chapter 7
... Conservation of Momentum – Collide & Stick together A bullet whose mass, m, is 50.0g is fired horizontally with a speed, v, of 1,100 m/s into a large wooden block of mass, M = 6.0 kg that is initially at rest on a horizontal table. If the block is free to slide without friction across the table, wha ...
... Conservation of Momentum – Collide & Stick together A bullet whose mass, m, is 50.0g is fired horizontally with a speed, v, of 1,100 m/s into a large wooden block of mass, M = 6.0 kg that is initially at rest on a horizontal table. If the block is free to slide without friction across the table, wha ...
05.TE.Newton`s Second Law
... figure 5.1 From this, you can see that y is directly proportional to x; that is, any increase in x (the manipulated variable) will result in a proportional increase in y (the responding variable). Figure 5.2 shows three different relationships between three different sets of x and y variables. Each ...
... figure 5.1 From this, you can see that y is directly proportional to x; that is, any increase in x (the manipulated variable) will result in a proportional increase in y (the responding variable). Figure 5.2 shows three different relationships between three different sets of x and y variables. Each ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In this part of the experiment you will investigate Hooke’s Law, which quantitatively describes the behavior of a spring as a force is applied to either stretch or compress the spring. 1. To do this, use the provided clamp to suspend the spring from the ring stand on your table. Hang the mass hanger ...
... In this part of the experiment you will investigate Hooke’s Law, which quantitatively describes the behavior of a spring as a force is applied to either stretch or compress the spring. 1. To do this, use the provided clamp to suspend the spring from the ring stand on your table. Hang the mass hanger ...
Class notes
... F = ma. (We’ll get to F~ = m~a later this week.) Physicists refer to this as the “equation of motion” for a particle moving through time in one dimension of space. Let x(t) be the position x of a particle at time t. Then the velocity is v(t) = dx/dt ≡ ẋ. (Have you all seen this notation before??) A ...
... F = ma. (We’ll get to F~ = m~a later this week.) Physicists refer to this as the “equation of motion” for a particle moving through time in one dimension of space. Let x(t) be the position x of a particle at time t. Then the velocity is v(t) = dx/dt ≡ ẋ. (Have you all seen this notation before??) A ...
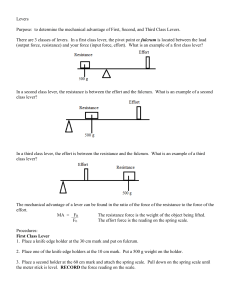
Levers Lab
... Second Class Lever 1. Move the fulcrum and knife edge holder to the 0 cm mark on the meter stick. Move the 500 g mass and holder to the 30 cm mark. 2. Turn the other holder upside down and place at the 60 cm mark on the meter stick. Pull up on the spring scale until the lever is level. Record the fo ...
... Second Class Lever 1. Move the fulcrum and knife edge holder to the 0 cm mark on the meter stick. Move the 500 g mass and holder to the 30 cm mark. 2. Turn the other holder upside down and place at the 60 cm mark on the meter stick. Pull up on the spring scale until the lever is level. Record the fo ...
Momentum and Impulse MC practice problems
... (A) It reduces the kinetic energy loss of the stunt person. (B) It reduces the momentum change of the stunt person. (C) It increases the momentum change of the stunt person. (D) It shortens the stopping time of the stunt person and increases the force applied during the landing. (E) It lengthens the ...
... (A) It reduces the kinetic energy loss of the stunt person. (B) It reduces the momentum change of the stunt person. (C) It increases the momentum change of the stunt person. (D) It shortens the stopping time of the stunt person and increases the force applied during the landing. (E) It lengthens the ...