Seismic waves - opotikicollegeearthscience
... • Surface waves are similar in nature to water waves and travel just under the Earth’s surface. They are typically generated when the source of the earthquake is close to the Earth’s surface. Although surface waves travel more slowly than S-waves, they can be much larger in amplitude and can be the ...
... • Surface waves are similar in nature to water waves and travel just under the Earth’s surface. They are typically generated when the source of the earthquake is close to the Earth’s surface. Although surface waves travel more slowly than S-waves, they can be much larger in amplitude and can be the ...
13. Time to Accumulate Chloride Ions in the World`s Oceans, More
... would have had deep roots.That is, the relatively low densities of the rocks in the mountains would have caused them to float like icebergs atop the underlying denser mantle with most of their volume below sea level, extending to deep roots. Through a long period of geologic time and after periods o ...
... would have had deep roots.That is, the relatively low densities of the rocks in the mountains would have caused them to float like icebergs atop the underlying denser mantle with most of their volume below sea level, extending to deep roots. Through a long period of geologic time and after periods o ...
Frimmel_Chameis subterrane_Gariep
... places, such as 5 km north of Bakers Bay and just south of the above-mentioned old mining camp, the greenschist is followed by a sequence of dolomite up to 50 m thick with intercalated pelite which contains tourmalinite layers, lenses and boudins, and albitite. The dolomite is brecciated with white, ...
... places, such as 5 km north of Bakers Bay and just south of the above-mentioned old mining camp, the greenschist is followed by a sequence of dolomite up to 50 m thick with intercalated pelite which contains tourmalinite layers, lenses and boudins, and albitite. The dolomite is brecciated with white, ...
Ignimbrite flare-up and deformation in the southern Sierra Madre
... of this volcanic province was built in two episodes of ignimbrite flare-up in Oligocene (31.5–28 Ma) and early Miocene (23.5 – 20 Ma) time, and that extensional deformation occurred mostly before the transfer of Baja California to the Pacific plate. Extensive ignimbrite successions, with 40Ar/39Ar a ...
... of this volcanic province was built in two episodes of ignimbrite flare-up in Oligocene (31.5–28 Ma) and early Miocene (23.5 – 20 Ma) time, and that extensional deformation occurred mostly before the transfer of Baja California to the Pacific plate. Extensive ignimbrite successions, with 40Ar/39Ar a ...
The Tolbachik volcanic massif: A review of the petrology
... Quaternary arc volcanism in Kamchatka comprises three zones parallel to the Kurile–Kamchatka trench that consistently shift relative each other slightly to the north from east to west (Fig. 1a): the Eastern Volcanic Front (EVF), the graben-like Central Kamchatka Depression (CKD) with the active Klyu ...
... Quaternary arc volcanism in Kamchatka comprises three zones parallel to the Kurile–Kamchatka trench that consistently shift relative each other slightly to the north from east to west (Fig. 1a): the Eastern Volcanic Front (EVF), the graben-like Central Kamchatka Depression (CKD) with the active Klyu ...
Earthquakes
... At least a dozen major landslides on volcanoes have taken place over the past several million years along the Canary Islands. From: Ward, S.N. and Day, S.,2002, Cumbre Vieja Volcano—Potential collapse and tsunami at La Palma, Canary Islands. ...
... At least a dozen major landslides on volcanoes have taken place over the past several million years along the Canary Islands. From: Ward, S.N. and Day, S.,2002, Cumbre Vieja Volcano—Potential collapse and tsunami at La Palma, Canary Islands. ...
Seismic Waves File
... smaller bits, called plates, which float on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. ...
... smaller bits, called plates, which float on a dense mantle. Parts of the mantle are molten liquid and movements in this liquid cause the plates to drift into one another. It is the meeting of the plates that causes the earthquakes. The density of the material forming the Earth increases with depth. ...
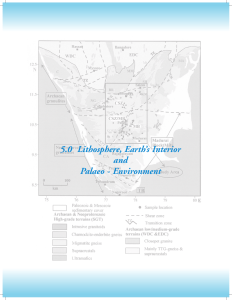
Lithosphere, Earth`s Interior and Paleo-Environment
... of the granite-greenstone Dharwar Craton (DC) and the Southern Granulite Terrain (SGT). The SGT is dominantly composed of late-Archaean granulites in the northern part whilst Proterozoic granulites in the southern part. These two major geological blocks, i.e. DC and SGT, are separated by orthopyroxe ...
... of the granite-greenstone Dharwar Craton (DC) and the Southern Granulite Terrain (SGT). The SGT is dominantly composed of late-Archaean granulites in the northern part whilst Proterozoic granulites in the southern part. These two major geological blocks, i.e. DC and SGT, are separated by orthopyroxe ...
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 76, No. 2, pp
... Both station delays and slowness distribution are quite similar to those computed earlier by Hearn (1984b). The major differences between the two sets of delays occur primarily in the Los Angeles and the Ventura basins. Differences of up to 0.4 sec exist. As tests of the tomographic method on the sa ...
... Both station delays and slowness distribution are quite similar to those computed earlier by Hearn (1984b). The major differences between the two sets of delays occur primarily in the Los Angeles and the Ventura basins. Differences of up to 0.4 sec exist. As tests of the tomographic method on the sa ...
Effects of Hydrothermal Cooling and Magma Injection on Mid
... develop in response to the rheology and boundary conditions and are not imposed a priori. Comparing our numerical experiments with observed faulting at the center and ends of several segments along the slow-spreading Mid-Atlantic Ridge, we find that temperatures near the segment end must be warmer t ...
... develop in response to the rheology and boundary conditions and are not imposed a priori. Comparing our numerical experiments with observed faulting at the center and ends of several segments along the slow-spreading Mid-Atlantic Ridge, we find that temperatures near the segment end must be warmer t ...
Gervais_Chapter 14 Geohazards
... Volcanoes shape Earth’s crust. They can pour cubic kilometers of lava onto Earth’s surface to build new islands and landmasses. They form beautiful snowcapped peaks that have inspired humans for generations, and they provide nutrient-rich soils that plants thrive in. Volcanoes can also be extremely ...
... Volcanoes shape Earth’s crust. They can pour cubic kilometers of lava onto Earth’s surface to build new islands and landmasses. They form beautiful snowcapped peaks that have inspired humans for generations, and they provide nutrient-rich soils that plants thrive in. Volcanoes can also be extremely ...
Shaking Ground
... took so many lives in the recent earthquake that shook Central America. In this case, in fact, mudslides were the most significant destructive force, claiming hundreds of lives. ...
... took so many lives in the recent earthquake that shook Central America. In this case, in fact, mudslides were the most significant destructive force, claiming hundreds of lives. ...
Tectonics, Dynamics, and Seismic Hazard in the Canada–Alaska
... balance between plate boundary forces and topography-related gravitational forces. In particular, the strong compression and gravitational forces associated with the Yakutat collision zone are the primary driver of the complex tectonics from eastern Yukon to central Alaska, resulting in crustal extr ...
... balance between plate boundary forces and topography-related gravitational forces. In particular, the strong compression and gravitational forces associated with the Yakutat collision zone are the primary driver of the complex tectonics from eastern Yukon to central Alaska, resulting in crustal extr ...
MAJOR-ELEMENT CHEMISTRY OF PLUTONIC ROCK SUITES
... of volcanic rock suites has been well d o c u m e n t e d (Christiansen and Lipman, 1972; Martin and Piwinskii, 1972; Pearce et al., 1977). Plutonic suites have also been compared with volcanic suites of known tectonic setting, which allow indirect inferences to be made about the tectonic setting of ...
... of volcanic rock suites has been well d o c u m e n t e d (Christiansen and Lipman, 1972; Martin and Piwinskii, 1972; Pearce et al., 1977). Plutonic suites have also been compared with volcanic suites of known tectonic setting, which allow indirect inferences to be made about the tectonic setting of ...
0_primary_structures
... Bulbous protrusions of denser sand into less dense mud layers Forms due to density instability when sediment is still soft (i.e., still unlithified) The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sin ...
... Bulbous protrusions of denser sand into less dense mud layers Forms due to density instability when sediment is still soft (i.e., still unlithified) The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sin ...
Microbes and volcanoes: A tale from the oceans, ophiolites, and
... Alt and Mata (2000) inferred an incongruent dissolution process from the major element geochemistry of bioalteration cavities, even though any of these local geochemical effects may have occurred during or after bioalteration. Storrie-Lombardi and Fisk (2003) showed through principal component analy ...
... Alt and Mata (2000) inferred an incongruent dissolution process from the major element geochemistry of bioalteration cavities, even though any of these local geochemical effects may have occurred during or after bioalteration. Storrie-Lombardi and Fisk (2003) showed through principal component analy ...
Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
... • Glacial ages and other climate evidence • Evidence of glaciation in now tropical regions • Direction of glacial flow and rock scouring • Plant and animal fossils indicate different climate than today © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Glacial ages and other climate evidence • Evidence of glaciation in now tropical regions • Direction of glacial flow and rock scouring • Plant and animal fossils indicate different climate than today © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The evolving nature of terrestrial crust from the Hadean, through the
... Archaean mantle lost heat – through modern style plate tectonics with fully established spreading and subduction or some form of heat transfer through longer-lived ‘oceanic’ lithosphere – we find ourselves also confronted with the question of whether Archaean plumes existed and how they might have op ...
... Archaean mantle lost heat – through modern style plate tectonics with fully established spreading and subduction or some form of heat transfer through longer-lived ‘oceanic’ lithosphere – we find ourselves also confronted with the question of whether Archaean plumes existed and how they might have op ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Powerpoint.
... • Glacial ages and other climate evidence • Evidence of glaciation in now tropical regions • Direction of glacial flow and rock scouring • Plant and animal fossils indicate different climate than today © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Glacial ages and other climate evidence • Evidence of glaciation in now tropical regions • Direction of glacial flow and rock scouring • Plant and animal fossils indicate different climate than today © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
How the Earth Was Made: The Deepest Place on Earth
... 14. Why is the Challenger Deep deeper than the Marianas Trench? (39:00) 15. Why is the idea that magma welling up at mid ocean ridges causing the plates to separate now considered to be wrong? (40:00) ...
... 14. Why is the Challenger Deep deeper than the Marianas Trench? (39:00) 15. Why is the idea that magma welling up at mid ocean ridges causing the plates to separate now considered to be wrong? (40:00) ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.