7Unit-4Ch.11-C.Drift-amp-Plate-T.Slideshow
... Geologists found rocks that were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
... Geologists found rocks that were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
Unit 5 Test Plate Tectonics
... a. divergent boundary b. convergent continental-continental boundary c. convergent oceanic-continental boundary d. convergent oceanic-oceanic boundary 5. Which of the following factors helps determine whether a volcanic eruption will be violent or relatively quiet? a. amount of dissolved gases in th ...
... a. divergent boundary b. convergent continental-continental boundary c. convergent oceanic-continental boundary d. convergent oceanic-oceanic boundary 5. Which of the following factors helps determine whether a volcanic eruption will be violent or relatively quiet? a. amount of dissolved gases in th ...
Volcanoes - Comal ISD
... From deep in the earth reaches the surface of the crust!!! The basic process of an eruption is listed here: 3. When it breaks through the surface, we get a Vent volcanic eruption! ...
... From deep in the earth reaches the surface of the crust!!! The basic process of an eruption is listed here: 3. When it breaks through the surface, we get a Vent volcanic eruption! ...
Volcanic Landforms
... volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent. More layers of such lava harden on top of previous layers. The layers gradually build a wide, gently sloping mountain called a shield volcano. If a vol ...
... volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent. More layers of such lava harden on top of previous layers. The layers gradually build a wide, gently sloping mountain called a shield volcano. If a vol ...
Volcano Review sheet - new for 2016-17
... A. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly B. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly C. This is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly D. This in an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly E. This is a metamorphic rock that cooled quickly AB. This is a metamorphi ...
... A. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly B. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly C. This is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly D. This in an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly E. This is a metamorphic rock that cooled quickly AB. This is a metamorphi ...
HotspotActivity_forSERC.v2
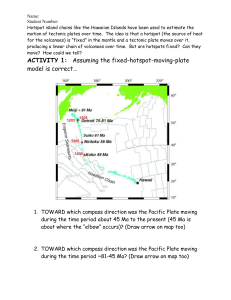
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
Plate Tectonics
... In a divergent plate boundary, molten rock rises to the surface and cools to become new crust. This newly formed crust is continually being replaced by new molten rock. Older crust diverges and is forced to move away from the area where new molten rock will form into new crust. ...
... In a divergent plate boundary, molten rock rises to the surface and cools to become new crust. This newly formed crust is continually being replaced by new molten rock. Older crust diverges and is forced to move away from the area where new molten rock will form into new crust. ...
28.1 Understanding Earth
... Theory of plate tectonics, started in 1965, and explains the movement of continents and other geological events, like earthquakes and volcanoes through the movement of giant plates of rock called tectonic plates. ...
... Theory of plate tectonics, started in 1965, and explains the movement of continents and other geological events, like earthquakes and volcanoes through the movement of giant plates of rock called tectonic plates. ...
Alper Midterm 1 Solution (1)
... c) Slide against 5) Divergent boundaries are also known as (2pt) a) Subduction zones b) Spreading ridges c) Reverse faults 6) Mantle is............... (2pt) a) Partially molten b) Solid c) Molten 7) Trenches are formed at subduction zones. (2pt) a) True b) False 8) Volcanoes are formed by subduction ...
... c) Slide against 5) Divergent boundaries are also known as (2pt) a) Subduction zones b) Spreading ridges c) Reverse faults 6) Mantle is............... (2pt) a) Partially molten b) Solid c) Molten 7) Trenches are formed at subduction zones. (2pt) a) True b) False 8) Volcanoes are formed by subduction ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... As magma rises toward the surface, the dissolved gas begins to expand as pressure decreases and this exerts an enormous upward force on the magma. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
... As magma rises toward the surface, the dissolved gas begins to expand as pressure decreases and this exerts an enormous upward force on the magma. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
Volcanic Activity
... the plates separate, known as rift zones. Rift volcanism mainly occurs under water along ocean ridges. This can be seen above sea level in Iceland Some volcanoes are located far from plate boundaries. These volcanoes form as the result of hot spots, which are unusually hot regions of Earth’s man ...
... the plates separate, known as rift zones. Rift volcanism mainly occurs under water along ocean ridges. This can be seen above sea level in Iceland Some volcanoes are located far from plate boundaries. These volcanoes form as the result of hot spots, which are unusually hot regions of Earth’s man ...
Unit 4
... upon which we live.The theory states that the earth`s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more plates of various sizes that are moving relative to one another as they ride on top of hotter, more mobile material. F The theory has provided explanations to questions that scientists had specul ...
... upon which we live.The theory states that the earth`s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more plates of various sizes that are moving relative to one another as they ride on top of hotter, more mobile material. F The theory has provided explanations to questions that scientists had specul ...
Igneous Rocks
... Granite is an example of an intrusive rock (Igneous Rock) because it is formed very slowly and deep in the Earth’s Crust. ...
... Granite is an example of an intrusive rock (Igneous Rock) because it is formed very slowly and deep in the Earth’s Crust. ...
Unit Six Notes
... • What evidence do we have that supports the idea of one giant supercontinent (Pangaea)? Cite evidence from Alfred Wegner’s findings. • What force is causing the Earth’s plates to move? ...
... • What evidence do we have that supports the idea of one giant supercontinent (Pangaea)? Cite evidence from Alfred Wegner’s findings. • What force is causing the Earth’s plates to move? ...
Geologic Time
... • Uniformitarianism - processes we observe today are most likely the same processes that occurred millions of years ago. When in Earth’s history does this painting show? Triassic ~200 mya Today (2015) ...
... • Uniformitarianism - processes we observe today are most likely the same processes that occurred millions of years ago. When in Earth’s history does this painting show? Triassic ~200 mya Today (2015) ...
Unit 1 Revision
... • For 4 marks need 4 points (or 2 points each explained) • In Japan, buildings are made to withstand earthquakes such as being built with shockabsorbers in their foundations. Also, people are taught what to do if an earthquake strikes such as taking cover under a table or standing in a doorway. In H ...
... • For 4 marks need 4 points (or 2 points each explained) • In Japan, buildings are made to withstand earthquakes such as being built with shockabsorbers in their foundations. Also, people are taught what to do if an earthquake strikes such as taking cover under a table or standing in a doorway. In H ...
Physical Processes STEW
... Material is moved by the action of WIND, WATER, or ICE WATER: Motion of water picks up soil – river Abrasive action of waves – grind down rock, carries soil away. ...
... Material is moved by the action of WIND, WATER, or ICE WATER: Motion of water picks up soil – river Abrasive action of waves – grind down rock, carries soil away. ...
Dynamic_Planet_CyFalls_
... D. Volcanoe eruptions are inversely proportional to local atomospheric pressure 24. Volcanic activity located away from plate boundaries is associated with A. B. C. D. ...
... D. Volcanoe eruptions are inversely proportional to local atomospheric pressure 24. Volcanic activity located away from plate boundaries is associated with A. B. C. D. ...
George Cuvier (1769 – 1832) Introduced the concept of
... Published geological text Promoted uniformitarianism, helped establish it as a fundamental principle of geology #6 principle of relative dating Inclusion: if a rock is includes pieces of another rock, the pieces are older. ...
... Published geological text Promoted uniformitarianism, helped establish it as a fundamental principle of geology #6 principle of relative dating Inclusion: if a rock is includes pieces of another rock, the pieces are older. ...
Introduction to geology
... Milestones in the history of geology Key ideas and the people behind them The geological time scale Relative and absolute dating (‘clocks in rocks’) Reading history in the rocks Inside the earth Journey to the centre of the Earth The changing earth Plate tectonics; earthquakes and volcanoes Minerals ...
... Milestones in the history of geology Key ideas and the people behind them The geological time scale Relative and absolute dating (‘clocks in rocks’) Reading history in the rocks Inside the earth Journey to the centre of the Earth The changing earth Plate tectonics; earthquakes and volcanoes Minerals ...
GY111 Introductory Geology - University of South Alabama
... • Folded and thrust-faulted by the Alleghenian orogeny at the end of the Paleozoic. • Alleghenian orogeny was the result of the collision between Laurentia and Godwana to form Pangea. • The folding of erosionally resistant and non-resistant rocks produces the valley & ridge topography. • Much of the ...
... • Folded and thrust-faulted by the Alleghenian orogeny at the end of the Paleozoic. • Alleghenian orogeny was the result of the collision between Laurentia and Godwana to form Pangea. • The folding of erosionally resistant and non-resistant rocks produces the valley & ridge topography. • Much of the ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.