Senior Science, Biology and Earth Science (125 questions) 1.) What
... 54.) What does spreading center volcanism produce? a. green smokers b. mid-oceanic ridges c. mid-continental ridges d. geysers 55.) What is a batholith? a. A massive pluton that cools slowly b. The first stage in the formation of metamorphic rocks c. Usually generates fine textured igneous rocks d. ...
... 54.) What does spreading center volcanism produce? a. green smokers b. mid-oceanic ridges c. mid-continental ridges d. geysers 55.) What is a batholith? a. A massive pluton that cools slowly b. The first stage in the formation of metamorphic rocks c. Usually generates fine textured igneous rocks d. ...
EARTHQUAKES: Origins and Predictions
... cated mostly in the ocean floor. An exception is the island of Iceland (see Figure 2), where the Mid-Atlantic ridge surfaces up and cuts the island in two. Divergent boundaries are associated with low seismic activity that occurs at shallow depths, because the lithosphere is weak and stresses canno ...
... cated mostly in the ocean floor. An exception is the island of Iceland (see Figure 2), where the Mid-Atlantic ridge surfaces up and cuts the island in two. Divergent boundaries are associated with low seismic activity that occurs at shallow depths, because the lithosphere is weak and stresses canno ...
ch08
... rock bodies welded along metamorphic zones called greenstone belts. The podlike bodies are mostly high-grade metaigneous rocks representing the felsic crust of Archean protocontinents, and the greenstones connecting them are metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks rich in chlorite, a green mineral fo ...
... rock bodies welded along metamorphic zones called greenstone belts. The podlike bodies are mostly high-grade metaigneous rocks representing the felsic crust of Archean protocontinents, and the greenstones connecting them are metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks rich in chlorite, a green mineral fo ...
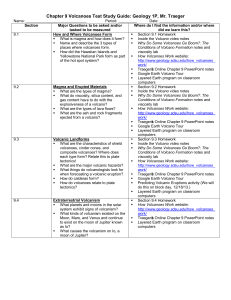
Chapter 9 Volcanoes Test Study Guide: Geology 1P, Mr. Traeger
... § Inside the Volcano video notes § What is magma and how does it form? § Why Do Some Volcanoes Go Boom?: The § Name and describe the 3 types of Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and places where volcanoes form. § How did the Hawaiian Islands and viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: Yellow ...
... § Inside the Volcano video notes § What is magma and how does it form? § Why Do Some Volcanoes Go Boom?: The § Name and describe the 3 types of Conditions of Volcano Formation notes and places where volcanoes form. § How did the Hawaiian Islands and viscosity lab § How Volcanoes Work website: Yellow ...
File - MrsBlochScience
... washcloth + water(wet cloth)= washcloth’s density increases Higher density of washcloth= washcloth heavier(denser)= sinks Read 3rd P. Changes in density ...
... washcloth + water(wet cloth)= washcloth’s density increases Higher density of washcloth= washcloth heavier(denser)= sinks Read 3rd P. Changes in density ...
Planet Earth - ScienceA2Z.com
... crust and mantle, not the core Meteors more similar to core Iron, silicated iron, stony iron, or stone, http://a52.g.akamaitech.net/f/52/827/1d/www.space.com/images/ig162_01.jpg ...
... crust and mantle, not the core Meteors more similar to core Iron, silicated iron, stony iron, or stone, http://a52.g.akamaitech.net/f/52/827/1d/www.space.com/images/ig162_01.jpg ...
Asthenospheric flow and origin of volcanism in the Baikal Rift area
... [21] (Fig. 1b). Estimates of the amount of total extension across the rift range from ≥10 km to 30–40 km [23,24]. The heat flow in the rift zone is only moderately elevated [25]. A hot, large-scale asthenospheric upwelling has been proposed to occur, eroding the lithosphere to crustal thickness belo ...
... [21] (Fig. 1b). Estimates of the amount of total extension across the rift range from ≥10 km to 30–40 km [23,24]. The heat flow in the rift zone is only moderately elevated [25]. A hot, large-scale asthenospheric upwelling has been proposed to occur, eroding the lithosphere to crustal thickness belo ...
Plate Tectonics as a Far- From- Equilibrium Self
... plates and plate boundaries can redefme themselves. Thus, the plate mosaic itself is a result of the global stress field, forces on the lithosphere, and history. In this respect an aggregation of plates differs from a granular material in which each grain is invariant. This perception of plate tecto ...
... plates and plate boundaries can redefme themselves. Thus, the plate mosaic itself is a result of the global stress field, forces on the lithosphere, and history. In this respect an aggregation of plates differs from a granular material in which each grain is invariant. This perception of plate tecto ...
File
... most spectacular metamorphosis of all the rocks. The reason is that the clay minerals form at Earth surface temperature (T) (030 C) and pressure (P) (1 bar) by weathering of pre-existing rocks. Thus, clay minerals are grossly out of equilibrium with the high temperature and pressure conditions found ...
... most spectacular metamorphosis of all the rocks. The reason is that the clay minerals form at Earth surface temperature (T) (030 C) and pressure (P) (1 bar) by weathering of pre-existing rocks. Thus, clay minerals are grossly out of equilibrium with the high temperature and pressure conditions found ...
Ocean Model Pre
... Amazingly enough, the ocean floor isn’t just flat. There are peaks, cones, ridges and cliffs that have formed beneath the sea. Many of these have been preserved largely unchanged because there is no wind, rain, and frost to wear away these features. On the Pacific floor, for example, there is a clif ...
... Amazingly enough, the ocean floor isn’t just flat. There are peaks, cones, ridges and cliffs that have formed beneath the sea. Many of these have been preserved largely unchanged because there is no wind, rain, and frost to wear away these features. On the Pacific floor, for example, there is a clif ...
Experiments With Portable Ocean Bottom - OBSIP
... plate bends. The largest potential reservoir, and uncertainty, is the degree to which faulting at the outer rise extends into the subducting plate lithosphere, and the degree of lithospheric serpentinization as a result. Recent work offshore of Nicaragua and Chile provides evidence for normal faulti ...
... plate bends. The largest potential reservoir, and uncertainty, is the degree to which faulting at the outer rise extends into the subducting plate lithosphere, and the degree of lithospheric serpentinization as a result. Recent work offshore of Nicaragua and Chile provides evidence for normal faulti ...
Investigation 1: Gathering Evidence and Modeling
... twice as fast as they do through water. How would this change the average travel time of the waves? Scientists cannot observe earthquake waves moving through the Earth in the same way you can observe waves moving through water. They can, however, record and study the energy from earthquake waves as ...
... twice as fast as they do through water. How would this change the average travel time of the waves? Scientists cannot observe earthquake waves moving through the Earth in the same way you can observe waves moving through water. They can, however, record and study the energy from earthquake waves as ...
convergent boundary
... currents created by heat trapped beneath the Earth's surface. Holmes hypothesized that convection currents welled up toward the surface and then drug continents across the surface. ...
... currents created by heat trapped beneath the Earth's surface. Holmes hypothesized that convection currents welled up toward the surface and then drug continents across the surface. ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... until they explode When they explode ash and pumice are blasted from the vent ...
... until they explode When they explode ash and pumice are blasted from the vent ...
Earthquakes - WordPress.com
... • Caused by volcanic or magmatic activity, • Caused by other sudden stress changes in the earth. ...
... • Caused by volcanic or magmatic activity, • Caused by other sudden stress changes in the earth. ...
Atlantic Conjugate Margins
... Global Plate Modelling: Objectives and Motivation • The construction of regional and global plate tectonic models is critical to understanding a wide range of geological processes such as basin dynamics, margin evolution and palaeo-environment development. • Plate models allow visualisation of regi ...
... Global Plate Modelling: Objectives and Motivation • The construction of regional and global plate tectonic models is critical to understanding a wide range of geological processes such as basin dynamics, margin evolution and palaeo-environment development. • Plate models allow visualisation of regi ...
File
... • Plates are sections of Earth's strong, rigid outer layer—the lithosphere. – They are up to 100 km thick. • Because plates are composed of lithosphere, they consist of the uppermost mantle and oceanic or continental crust. • Plates overlie the weaker asthenosphere. They ride along with the asthenos ...
... • Plates are sections of Earth's strong, rigid outer layer—the lithosphere. – They are up to 100 km thick. • Because plates are composed of lithosphere, they consist of the uppermost mantle and oceanic or continental crust. • Plates overlie the weaker asthenosphere. They ride along with the asthenos ...
Plate Tectonics through Time Treatise on Geophysics, N. H. Sleep
... Bleeker (2003), Sleep (2005), Condie and Benn (2006), and Polat and Kerrich (2006) review the rock record on continents. Moores (2002) reviews possible exposures of ancient oceanic crust. On the other hand, Stern (2005) argues that modern plate processes began in Neoproterozoic time. The author winn ...
... Bleeker (2003), Sleep (2005), Condie and Benn (2006), and Polat and Kerrich (2006) review the rock record on continents. Moores (2002) reviews possible exposures of ancient oceanic crust. On the other hand, Stern (2005) argues that modern plate processes began in Neoproterozoic time. The author winn ...
Earth`s History Lesson 3: Absolute Dating
... What is the best rock for radiometric dating? • Igneous rocks are the best types of rock samples to use for radiometric dating. • When they form, minerals in igneous rocks often contain only a parent isotope and none of the daughter isotope. • This makes the isotope percentage more accurate and easi ...
... What is the best rock for radiometric dating? • Igneous rocks are the best types of rock samples to use for radiometric dating. • When they form, minerals in igneous rocks often contain only a parent isotope and none of the daughter isotope. • This makes the isotope percentage more accurate and easi ...
Earth Changes
... But mostly we just get on out and take a look.” Geologists, seismologists, paleontologists too, Doing the rock science bugaloo! The igneous rock bubbles up from the ground, Sedimentary rock falls and settles on down. When it gets low enough, with some pressure and heat, A changed metamorphic rock yo ...
... But mostly we just get on out and take a look.” Geologists, seismologists, paleontologists too, Doing the rock science bugaloo! The igneous rock bubbles up from the ground, Sedimentary rock falls and settles on down. When it gets low enough, with some pressure and heat, A changed metamorphic rock yo ...
Lecture #6 Causes of Ice Ages & Glacial
... causing uplift of Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Drakes Passage opens ~30 Ma BP further enhancing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC). The ACC restricts warm tropical air from reaching Antarctica. Antarctic ice begins to develop (think about feedback mechanisms again with ice development, ocean ...
... causing uplift of Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Drakes Passage opens ~30 Ma BP further enhancing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC). The ACC restricts warm tropical air from reaching Antarctica. Antarctic ice begins to develop (think about feedback mechanisms again with ice development, ocean ...
Ancient Crete - Hodder Education
... The Hellenic Arc Crete lies in a subduction zone — the Hellenic Arc — where the African plate sinks below the Aegean microplate and the larger Eurasian plate behind it (Figure 1a). Plate motions create enormous stresses, so the crust in this area is riddled with active faults. Earthquakes, volcanic ...
... The Hellenic Arc Crete lies in a subduction zone — the Hellenic Arc — where the African plate sinks below the Aegean microplate and the larger Eurasian plate behind it (Figure 1a). Plate motions create enormous stresses, so the crust in this area is riddled with active faults. Earthquakes, volcanic ...
Environmental Science THE DYNAMIC EARTH Good overview with
... The Movement of Energy in the Atmosphere Air that is constantly moving upward, downward, or sideways causes the Earth’s __ weather. ___. In the troposphere, less dense air warmed by the Earth’s surface, rise into the atmosphere and currents of colder, more dense air sinks. As air current’s rise, th ...
... The Movement of Energy in the Atmosphere Air that is constantly moving upward, downward, or sideways causes the Earth’s __ weather. ___. In the troposphere, less dense air warmed by the Earth’s surface, rise into the atmosphere and currents of colder, more dense air sinks. As air current’s rise, th ...
Earthquakes - Library Video Company
... mantle — The largest layer of the Earth located directly under the crust, composed of very hot, dense, flowing rock. inner core — The solid center of the Earth made of extre m e ly hot metal under great pressure. outer core — The layer of the Earth surrounding the inner core made of (Continued) very ...
... mantle — The largest layer of the Earth located directly under the crust, composed of very hot, dense, flowing rock. inner core — The solid center of the Earth made of extre m e ly hot metal under great pressure. outer core — The layer of the Earth surrounding the inner core made of (Continued) very ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.