final project template
... at the crossroads of three great regions: the Cascades range to the north, the Sierra Nevada Mountains to the south and the Great Basin desert to the east. ...
... at the crossroads of three great regions: the Cascades range to the north, the Sierra Nevada Mountains to the south and the Great Basin desert to the east. ...
Tectonics of the Java Trench – Sumatra, Philippines
... Plate is rotating clockwise and moving eastward, that relative to the Eurasian Plate. The volcanism in the area is divided into four sections based on magmatic composition. There are three components contributing to this anomaly, characterized by high or low K content and high or low 87Sr/86Sr value ...
... Plate is rotating clockwise and moving eastward, that relative to the Eurasian Plate. The volcanism in the area is divided into four sections based on magmatic composition. There are three components contributing to this anomaly, characterized by high or low K content and high or low 87Sr/86Sr value ...
Chapter 15
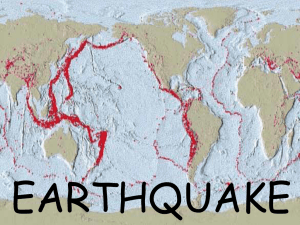
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
Plate Tectonics: Earthquake Epicenter
... moving plates. The discoveries of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the mirrored striping of magnetic fields across the Ridge led to a re-thinking of the continental drift theory and efforts to actually measure relative movements of the plates. The later discoveries of this movement and evidence for mantle ...
... moving plates. The discoveries of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the mirrored striping of magnetic fields across the Ridge led to a re-thinking of the continental drift theory and efforts to actually measure relative movements of the plates. The later discoveries of this movement and evidence for mantle ...
Scientific Reasoning 2016 - Indiana University Northwest
... floor of the Red Sea. While the entire sea floor is young, some parts of the Red Sea floor are younger than others. Predict where you would expect to find the youngest ocean crust. a. Along the shores of the Arabian Peninsula and northeastern Africa b. There is likely a random pattern of younger and ...
... floor of the Red Sea. While the entire sea floor is young, some parts of the Red Sea floor are younger than others. Predict where you would expect to find the youngest ocean crust. a. Along the shores of the Arabian Peninsula and northeastern Africa b. There is likely a random pattern of younger and ...
Slide 1
... Controls of rigidity Oceanic lithosphere Continental lithosphere Flexural Buckling Theory In nature and in experiments Dynamics of Orogenic Wedges Critical taper Theory Analog models Numerical Models Modeling Foreland Basin Moving tectonic load Erosion and deposition of bivergent margins ...
... Controls of rigidity Oceanic lithosphere Continental lithosphere Flexural Buckling Theory In nature and in experiments Dynamics of Orogenic Wedges Critical taper Theory Analog models Numerical Models Modeling Foreland Basin Moving tectonic load Erosion and deposition of bivergent margins ...
Page - Lab #10 - Rock Identification A rock is a substance made up
... within a given rock sample. This is often described as the rock’s mineralogy. Another important component in rock identification is to correctly interpret the rock texture. Technically, texture is the size, shape, and grain-to-grain relationships between minerals in a rock. For the purposes of this ...
... within a given rock sample. This is often described as the rock’s mineralogy. Another important component in rock identification is to correctly interpret the rock texture. Technically, texture is the size, shape, and grain-to-grain relationships between minerals in a rock. For the purposes of this ...
Geology 13/14 (RTF 44kB)
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
Word - LEARNZ
... continental drift; that there was one super continent, Pangaea, ( meaning all lands ), and that this broke up, forming the continents of today. Originally his ideas were thought to be incorrect as no one could explain how the continents could have moved over time. By the 1960s with increasing scient ...
... continental drift; that there was one super continent, Pangaea, ( meaning all lands ), and that this broke up, forming the continents of today. Originally his ideas were thought to be incorrect as no one could explain how the continents could have moved over time. By the 1960s with increasing scient ...
Volcanic ash - Cloudfront.net
... • The magma inside a shield volcano is rich in iron and magnesium and is very fluid. • Since the magma is very fluid, the lava coming out of the volcano tends to flow great distances. • When shield volcanoes erupt, the flowing lava gives the volcano the shape of a gently sloping ...
... • The magma inside a shield volcano is rich in iron and magnesium and is very fluid. • Since the magma is very fluid, the lava coming out of the volcano tends to flow great distances. • When shield volcanoes erupt, the flowing lava gives the volcano the shape of a gently sloping ...
Entire 8th grade earth science curriculum
... size and shape and classified into three types of landforms. Their form is controlled by magma chemistry and the plate tectonic context. NONE ...
... size and shape and classified into three types of landforms. Their form is controlled by magma chemistry and the plate tectonic context. NONE ...
Physical Geology 14e Plummer TB
... Chapter 01 - Introducing Geology, the Essentials of Plate Tectonics, and Other Important Concepts ...
... Chapter 01 - Introducing Geology, the Essentials of Plate Tectonics, and Other Important Concepts ...
Folds and Faults, Earthquakes Rock Deformation 1. 2. 3
... on the North American Plate. Besides the short term effects of being an earthquake ‘hot zone’, western California will, in about one million years, be part of Alaska, as the Pacific Plate continues its north-westerly trek. Much crushing and grinding takes place as these two enormous plates move past ...
... on the North American Plate. Besides the short term effects of being an earthquake ‘hot zone’, western California will, in about one million years, be part of Alaska, as the Pacific Plate continues its north-westerly trek. Much crushing and grinding takes place as these two enormous plates move past ...
Space-time patterns of Late Cretaceous to present magmatism
... Cenozoic volcanic and plutonic rocks are used to evaluate the evolution of magmatism in New Mexico. Several tectonomagmatic subdivisions can be seen in the data. These are: (1) Late Cretaceous to middle Eocene (75–45 Ma) magmatism occurred along and to the south of the northeasttrendi ...
... Cenozoic volcanic and plutonic rocks are used to evaluate the evolution of magmatism in New Mexico. Several tectonomagmatic subdivisions can be seen in the data. These are: (1) Late Cretaceous to middle Eocene (75–45 Ma) magmatism occurred along and to the south of the northeasttrendi ...
Heart of Fire
... Andesite can arise in a variety of ways, but most is produced by the partial melting of wet basalt. This often occurs where oceanic crust dives beneath another plate. Andesitic magma ...
... Andesite can arise in a variety of ways, but most is produced by the partial melting of wet basalt. This often occurs where oceanic crust dives beneath another plate. Andesitic magma ...
ppt
... Imagine a strike-slip fault within a flat earth and stations A through E distributed on the ground surface at different distances from the fault trace. The first P-wave arrival at each of the stations will be either compressional or dilatational. In this example the distribution of the compressional ...
... Imagine a strike-slip fault within a flat earth and stations A through E distributed on the ground surface at different distances from the fault trace. The first P-wave arrival at each of the stations will be either compressional or dilatational. In this example the distribution of the compressional ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Knowledge of the Earth’s interior is essential for the understanding of processes observed at the surface such as volcanism, seismicity, plate movements, vertical movements or variations of the geomagnetic field. But as direct probing of the deep interior remains impossible, indirect observations ha ...
... Knowledge of the Earth’s interior is essential for the understanding of processes observed at the surface such as volcanism, seismicity, plate movements, vertical movements or variations of the geomagnetic field. But as direct probing of the deep interior remains impossible, indirect observations ha ...
Subduction Zones of the World: Comparison to the Cascadia
... release areas. The larger asperity was located near the epicenter, and a second, smaller one was within the second half of the rupture zone near Kodiak Island. ...
... release areas. The larger asperity was located near the epicenter, and a second, smaller one was within the second half of the rupture zone near Kodiak Island. ...
Seismological Analysis and the Effect of Earthquakes in the New
... When this stressor pressure exceeds the strength of the rocks, the crust breaks and can snap into a new position. Vibrations from this are called seismic waves, which travel through and along the earth’s surface. These seismic waves are called earthquakes (Bolt 1993). Earthquakes often occur at faul ...
... When this stressor pressure exceeds the strength of the rocks, the crust breaks and can snap into a new position. Vibrations from this are called seismic waves, which travel through and along the earth’s surface. These seismic waves are called earthquakes (Bolt 1993). Earthquakes often occur at faul ...
Rocks, Minerals & the Rock Cycle
... Granite – Slow cooling below the earth’s surface Rhyolite – Quick cooling on the earth’s surface ...
... Granite – Slow cooling below the earth’s surface Rhyolite – Quick cooling on the earth’s surface ...
Volcanic Activity
... How does magma rise through the lithosphere? • Liquid magma in the asthenosphere is less dense than the rock in the lithosphere above it, so it flows upward through cracks in the rock – The magma is stored in the magma chamber ...
... How does magma rise through the lithosphere? • Liquid magma in the asthenosphere is less dense than the rock in the lithosphere above it, so it flows upward through cracks in the rock – The magma is stored in the magma chamber ...
Plate Tectonics - North Coast Distance Education
... represent younger rock, much of which has been deformed by mountain building. Most of the deformation occurred from 450 million to 650 million years ago. Several fragments of the African shield are stranded along the northern coast of Brazil. Green dots represent rocks that are more than 2 billion y ...
... represent younger rock, much of which has been deformed by mountain building. Most of the deformation occurred from 450 million to 650 million years ago. Several fragments of the African shield are stranded along the northern coast of Brazil. Green dots represent rocks that are more than 2 billion y ...
Could Iceland be a modern analogue for the Earth`s early
... differentiation and source composition. Martin and Sigmarsson (2007b) showed that in basalt flows, the composition (i.e. K2O ⁄ Na2O) of felsic melts in segregation veins is mainly controlled by the composition of the parental magma. In mantle plume environments, the basaltic precursors are already alk ...
... differentiation and source composition. Martin and Sigmarsson (2007b) showed that in basalt flows, the composition (i.e. K2O ⁄ Na2O) of felsic melts in segregation veins is mainly controlled by the composition of the parental magma. In mantle plume environments, the basaltic precursors are already alk ...
The earth dynamic system: the earth rotation vs mantle convection
... shape of the plates. In the models like Figure 7 and Figure 8, if the Coriolis force and some other force relating to the earth rotation are accounted, the mantle movement situation will be more complex. For example, when a mantle plume, which has considerable impact on tectonic evolution of plates ...
... shape of the plates. In the models like Figure 7 and Figure 8, if the Coriolis force and some other force relating to the earth rotation are accounted, the mantle movement situation will be more complex. For example, when a mantle plume, which has considerable impact on tectonic evolution of plates ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.