File
... An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cau ...
... An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cau ...
... An earthquake is caused by a sudden slip on a fault. The tectonic plates are always slowly moving, but they get stuck at their edges due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the earth's crust and cau ...
PowerPoint (Winter) - Faculty Server Contact
... structural basin. The scale is not the same for these two plutons, a lopolith is generally much larger. © John Winter and Prentice Hall. ...
... structural basin. The scale is not the same for these two plutons, a lopolith is generally much larger. © John Winter and Prentice Hall. ...
Testing Your Knowledge
... 2. What would the present-day environmental effects be for an eruption such as that which created Crater Lake? 3. Why are there no active volcanoes in the eastern parts of the United States and Canada? 4. Why are continental igneous rocks richer in silica than oceanic igneous rocks? 5. In parts of m ...
... 2. What would the present-day environmental effects be for an eruption such as that which created Crater Lake? 3. Why are there no active volcanoes in the eastern parts of the United States and Canada? 4. Why are continental igneous rocks richer in silica than oceanic igneous rocks? 5. In parts of m ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Associated with very thick sedimentary strata – Required depth varies from one location to another depending on the prevailing geothermal gradient ...
... – Associated with very thick sedimentary strata – Required depth varies from one location to another depending on the prevailing geothermal gradient ...
General geohydrology of the Pajarito Plateau
... INTRODUCTION The Pajarito Plateau, twenty miles northwest of Santa Fe in north-central New Mexico, forms an apron of volcanic and sedimentary rocks around the eastern flanks of the Jemez Mountains (Fig. 1). The plateau slopes gently eastward from the mountains toward the Rio Grande where it terminat ...
... INTRODUCTION The Pajarito Plateau, twenty miles northwest of Santa Fe in north-central New Mexico, forms an apron of volcanic and sedimentary rocks around the eastern flanks of the Jemez Mountains (Fig. 1). The plateau slopes gently eastward from the mountains toward the Rio Grande where it terminat ...
A Sea Change in Ocean Drilling
... spreads outward toward deep-sea trench subduction zones. Crustal drilling also showed how great upwellings of hot rock, called plumes, could create chains of islands and seamounts such as Hawaii. These discoveries have raised new questions about solid earth cycles and geodynamics, one of three broad ...
... spreads outward toward deep-sea trench subduction zones. Crustal drilling also showed how great upwellings of hot rock, called plumes, could create chains of islands and seamounts such as Hawaii. These discoveries have raised new questions about solid earth cycles and geodynamics, one of three broad ...
Volcanoes - Kativik School Board
... Shield Volcanoes Although Shield Volcanoes are also formed by the solidification of the lava that flows on the surface they are _______ in height. This is because the eruptions are _______ and ___________ but relatively steady and the lava is more runny. ...
... Shield Volcanoes Although Shield Volcanoes are also formed by the solidification of the lava that flows on the surface they are _______ in height. This is because the eruptions are _______ and ___________ but relatively steady and the lava is more runny. ...
MS Volcanoes
... the middle of a tectonic plate. Hot spots lie directly above a column of hot rock called a mantle plume. Mantle plumes continuously bring magma up from the mantle towards the crust ( Figure 1.3). As the tectonic plates move above a hot spot, they form a chain of volcanoes. The islands of Hawaii form ...
... the middle of a tectonic plate. Hot spots lie directly above a column of hot rock called a mantle plume. Mantle plumes continuously bring magma up from the mantle towards the crust ( Figure 1.3). As the tectonic plates move above a hot spot, they form a chain of volcanoes. The islands of Hawaii form ...
Living Things - Mountain View Middle School
... •Thickest under mountains; thinnest under the ocean •Continental (land) mostly granite •Oceanic (ocean floor) mostly basalt ...
... •Thickest under mountains; thinnest under the ocean •Continental (land) mostly granite •Oceanic (ocean floor) mostly basalt ...
foot of the slope determined as the the point of maximum change of
... • The identification of the region defined as the base of the continental slope ...
... • The identification of the region defined as the base of the continental slope ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Ring of Fire Science
... Contact metamorphism occurs when hot magma rising up through the crust of the Earth heats the country rocks (local rocks in the area) through which it moves. Where there is a crack or joint in the rock the hot magma will flow into it. Dikes and sills form in the rocks as these small intrusions of ma ...
... Contact metamorphism occurs when hot magma rising up through the crust of the Earth heats the country rocks (local rocks in the area) through which it moves. Where there is a crack or joint in the rock the hot magma will flow into it. Dikes and sills form in the rocks as these small intrusions of ma ...
CRCT Earth Science Review 6
... B Rock slips along a fault, releases energy as seismic waves, and returns to its original shape. C Rock changes shape, but does not release significant amounts of energy. D Rock becomes compacted under pressure and realigns its mineral grains. ...
... B Rock slips along a fault, releases energy as seismic waves, and returns to its original shape. C Rock changes shape, but does not release significant amounts of energy. D Rock becomes compacted under pressure and realigns its mineral grains. ...
A climate induced transition in the tectonic style of a terrestrial planet
... of a two-way connection between volcanic and climatic history (Phillips et al., 2001). Phillips et al. (2001) explored the implications of this connection through a coupled model of climate and volcanic history. Although Venus shows no signs of geologically recent plate tectonic activity, it has bee ...
... of a two-way connection between volcanic and climatic history (Phillips et al., 2001). Phillips et al. (2001) explored the implications of this connection through a coupled model of climate and volcanic history. Although Venus shows no signs of geologically recent plate tectonic activity, it has bee ...
Lecture Notes - Feldspars
... destroy the center of symmetry and the mineral will become triclinic microcline. Maximum microcline would be a fully ordered mineral with all of the Al on one of the two sites t1a or t1b. • The solid solution between Or and Ab is complete at high temperatures, but is limited at lower temperatures. T ...
... destroy the center of symmetry and the mineral will become triclinic microcline. Maximum microcline would be a fully ordered mineral with all of the Al on one of the two sites t1a or t1b. • The solid solution between Or and Ab is complete at high temperatures, but is limited at lower temperatures. T ...
7. Early Evolution of the South Atlantic Ocean: Role of the Rifting
... trends are parallel except in a few areas where ancient lines of weakness were reactivated (Figs. 3, 4). Within the T-to-R unit, the presence of seismic reflectors having a slope intermediate between those of T and R records episodes of tectonic activity during the tilting of blocks (Fig. 4). Basic ...
... trends are parallel except in a few areas where ancient lines of weakness were reactivated (Figs. 3, 4). Within the T-to-R unit, the presence of seismic reflectors having a slope intermediate between those of T and R records episodes of tectonic activity during the tilting of blocks (Fig. 4). Basic ...
Changes in the Earth and its Atmosphere
... because there is only a difference of 3°C in their boiling points accept because they have boiling points that are almost the ...
... because there is only a difference of 3°C in their boiling points accept because they have boiling points that are almost the ...
ES Chapter 18
... • When magma reaches Earth’s surface it is called lava. • A vent is where lava erupts through an opening in the crust. • As lava flows out onto the surface, it cools and solidifies around the vent, eventually accumulating to form a mountain known as a volcano. • A crater is a bowl-shaped depression ...
... • When magma reaches Earth’s surface it is called lava. • A vent is where lava erupts through an opening in the crust. • As lava flows out onto the surface, it cools and solidifies around the vent, eventually accumulating to form a mountain known as a volcano. • A crater is a bowl-shaped depression ...
Why study fault lines - opotikicollegeearthscience
... • The Alpine Fault is called a strike slip or transform fault. The Australian plate is sliding horizontally towards the north-east, at the same time as the Pacific plate is pushing up, forming the Southern Alps. The mountains are rising at 7 millimetres a year, but erosion wears them down at a simil ...
... • The Alpine Fault is called a strike slip or transform fault. The Australian plate is sliding horizontally towards the north-east, at the same time as the Pacific plate is pushing up, forming the Southern Alps. The mountains are rising at 7 millimetres a year, but erosion wears them down at a simil ...
Chapter 18 PowerPoint
... • The three major types of magma are: basaltic magma, andesitic magma, and rhyolitic magma. – Basaltic magma has the same composition as basalt and fuels the volcanoes that make up the Hawaiian Islands and Surtsey, which is south of Iceland. – Andesitic magma has the same composition as andesite and ...
... • The three major types of magma are: basaltic magma, andesitic magma, and rhyolitic magma. – Basaltic magma has the same composition as basalt and fuels the volcanoes that make up the Hawaiian Islands and Surtsey, which is south of Iceland. – Andesitic magma has the same composition as andesite and ...
Word - New Haven Science
... science. Students will be introduced to qualitative relationships among mass and force as well as speed and distance. Some forces can only act on objects when they touch. Other forces, such as gravity, affect objects from a distance. Students will apply those relationships to explore what happens to ...
... science. Students will be introduced to qualitative relationships among mass and force as well as speed and distance. Some forces can only act on objects when they touch. Other forces, such as gravity, affect objects from a distance. Students will apply those relationships to explore what happens to ...
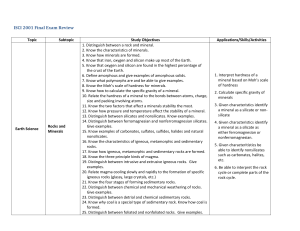
ISCI 2001 Final Exam Review
... minerals they are made of (basalt vs granitic) 2. Distinguish between the lithosphere and asthenosphere parts of the mantle. 3. Distinguish between the outer and inner core and the elements and minerals are made of. 4. Know that there are 8 plates and know what the plates are made of. 5. Know that t ...
... minerals they are made of (basalt vs granitic) 2. Distinguish between the lithosphere and asthenosphere parts of the mantle. 3. Distinguish between the outer and inner core and the elements and minerals are made of. 4. Know that there are 8 plates and know what the plates are made of. 5. Know that t ...
ESS 305 Mt. St. Helens National Volcanic Monument Spring 2015
... constructed by lava flows and the accumulation of pyroclastic debris, and they are quickly torn down by erosion and later eruptions. Several such episodes of growth and destruction may occur in the life of one of these volcanoes before the underlying igneous activity shifts to a different outlet. In ...
... constructed by lava flows and the accumulation of pyroclastic debris, and they are quickly torn down by erosion and later eruptions. Several such episodes of growth and destruction may occur in the life of one of these volcanoes before the underlying igneous activity shifts to a different outlet. In ...
FREE Sample Here
... 11) During the geologic past, the magnetic field poles have generally been very close to Earth's geographical poles. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 12) Seafloor spreading rates can be estimated if the geologic ages of the magnetic field reversals are independently known. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 13) The volcanoes ...
... 11) During the geologic past, the magnetic field poles have generally been very close to Earth's geographical poles. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 12) Seafloor spreading rates can be estimated if the geologic ages of the magnetic field reversals are independently known. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 13) The volcanoes ...
Geochemistry and petrogenesis of extrusive rocks, dykes and high
... The geochemical study is based on major- and trace element analyses of the extrusive rocks, the transition zone dykes, the sheeted dykes and the FMG (collectively referred to as metabasalts). A total of 193 samples (54, 18, 102 and 19 from the volcanic zone, the transition zone, the dyke complex an ...
... The geochemical study is based on major- and trace element analyses of the extrusive rocks, the transition zone dykes, the sheeted dykes and the FMG (collectively referred to as metabasalts). A total of 193 samples (54, 18, 102 and 19 from the volcanic zone, the transition zone, the dyke complex an ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.