Document
... Ex: Baby gender. The probability of having a boy is 50%. My sister-in-law just had a girl (and is expecting another!). The probability works when applied to the whole population (large number of trials), not when applied to my sister-in-law (a single experiment). ...
... Ex: Baby gender. The probability of having a boy is 50%. My sister-in-law just had a girl (and is expecting another!). The probability works when applied to the whole population (large number of trials), not when applied to my sister-in-law (a single experiment). ...
Examples for Chapter 6
... 1. Students who have completed a speed reading course have reading speeds that are normally distributed with a mean of 950 words per minute and a standard deviation equal to 220 words per minute. Based on this information, a. what is the probability of a student reading at more than 1400 words per m ...
... 1. Students who have completed a speed reading course have reading speeds that are normally distributed with a mean of 950 words per minute and a standard deviation equal to 220 words per minute. Based on this information, a. what is the probability of a student reading at more than 1400 words per m ...
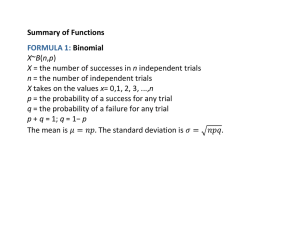
27. DIFFERENTIATING CONTINUOUS VS DISCRETE RANDOM
... Flip a coin three times; X = the total number of heads.The values o X are . X= 0, 1, 2, 3 Throw two dice; X = the sum of the numbers facing up.The values of X are . ...
... Flip a coin three times; X = the total number of heads.The values o X are . X= 0, 1, 2, 3 Throw two dice; X = the sum of the numbers facing up.The values of X are . ...
Prep for Exam 1 Thursday 8-14-06 (36 Kb ) STT 315 Fall 2006
... a. Closed book, no notes, no notes/papers, no electronics/headphones/phones of any kind, even in view (put every such thing away, out of sight). b. The seating will be assigned by your instructor. c. Some few formulas will be given on the exam as described below. d. You are responsible for the mater ...
... a. Closed book, no notes, no notes/papers, no electronics/headphones/phones of any kind, even in view (put every such thing away, out of sight). b. The seating will be assigned by your instructor. c. Some few formulas will be given on the exam as described below. d. You are responsible for the mater ...
Additional Problems (Ch. 2)
... together. Some of them may also be done as examples in class. 1. (Feller, An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, Vol I) Each of the 50 states has two senators. A committee of 50 senators is to be selected at random. Let A = {Florida is represented on the committee} B = {all stat ...
... together. Some of them may also be done as examples in class. 1. (Feller, An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, Vol I) Each of the 50 states has two senators. A committee of 50 senators is to be selected at random. Let A = {Florida is represented on the committee} B = {all stat ...