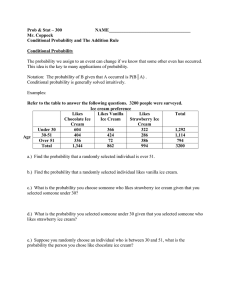
Probability Worksheet
... A bag contains 10 marbles. There is 1 green marble, 3 blue marbles, 4 yellow marbles and 2 red marbles. Thomas pulls out a marble from the bag without looking. Give answers in fractions. a) What is the probability of him pulling out a red marble? ………………………………………... b) What is the probability of him ...
... A bag contains 10 marbles. There is 1 green marble, 3 blue marbles, 4 yellow marbles and 2 red marbles. Thomas pulls out a marble from the bag without looking. Give answers in fractions. a) What is the probability of him pulling out a red marble? ………………………………………... b) What is the probability of him ...
Exam 2 (doc Version)
... 3. A cut piece of pitch pine is going to be used as a support beam. The density of the wood is not uniform throughout its interior, having a mean value of 0.674 g/cm3 and a standard deviation of 0.027 g/cm3. Density measurements are made at 40 randomly chosen core samples of the piece. a) Calculate ...
... 3. A cut piece of pitch pine is going to be used as a support beam. The density of the wood is not uniform throughout its interior, having a mean value of 0.674 g/cm3 and a standard deviation of 0.027 g/cm3. Density measurements are made at 40 randomly chosen core samples of the piece. a) Calculate ...
4-1 Notes (answers)
... TTF FTF TFF FFF (b) What is the probability that all three items will be false. P(All F) = 1 ...
... TTF FTF TFF FFF (b) What is the probability that all three items will be false. P(All F) = 1 ...
Probability: What Chance Do You Have?
... Complex Probability You have a class with 5 boys and 8 girls. You draw a student at random, and then pick a different student at random next. The probability of choosing two girls in a row would be found by multiplying the probability of picking a girl the first time by the probability of picking ...
... Complex Probability You have a class with 5 boys and 8 girls. You draw a student at random, and then pick a different student at random next. The probability of choosing two girls in a row would be found by multiplying the probability of picking a girl the first time by the probability of picking ...
Name
... Suppose you are given a standard 6-sided die and told that the die is “loaded” in such a way that while the numbers 1, 3, 4, and 6 are equally likely to turn up, the numbers 2 and 5 are three times as likely to turn up as any of the other numbers. 20.) The die is rolled once and the number turning ...
... Suppose you are given a standard 6-sided die and told that the die is “loaded” in such a way that while the numbers 1, 3, 4, and 6 are equally likely to turn up, the numbers 2 and 5 are three times as likely to turn up as any of the other numbers. 20.) The die is rolled once and the number turning ...
Probability - missburkerocks
... In many situations we can assume outcomes are equally likely. When events are equally likely: Equally likely outcomes may come from, for example: experiments with coins, dice, spinners and packs of cards ...
... In many situations we can assume outcomes are equally likely. When events are equally likely: Equally likely outcomes may come from, for example: experiments with coins, dice, spinners and packs of cards ...