The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
File
... that signal nearby neurons. Neurosecretory cells perform both functions by secreting their chemical signals into the blood In vertebrates two classes of molecules function as hormones. Amino acid derived ho ...
... that signal nearby neurons. Neurosecretory cells perform both functions by secreting their chemical signals into the blood In vertebrates two classes of molecules function as hormones. Amino acid derived ho ...
The Endocrine System
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
... • These hormones increase heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate • Increase efficiency of muscle contractions and blood sugar ...
The Endocrine System
... “Circular situation in which information about the status of something is continually reported (fed back) to a central control region.” ...
... “Circular situation in which information about the status of something is continually reported (fed back) to a central control region.” ...
Endocrine System
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
... gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. ...
Central Nervous System Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the
... What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? Receptors ...
... What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? Receptors ...
The Endocrine System and Homeostasis
... These are specific DNA sequences in the promoter of genes that will be turned on (sometimes off) by the interaction. ...
... These are specific DNA sequences in the promoter of genes that will be turned on (sometimes off) by the interaction. ...
Drugs Unit 2 - Cat`s TCM Notes
... ACh released from the presynaptic nerve accumulates, stimulating the ACh receptors Bind reversibly to acetylcholinesterase, so effects will pass with time Myasthenia Gravis Definition Chronic muscular disease caused by a defect in neuromuscular transmission Autoimmune disease; patients make ant ...
... ACh released from the presynaptic nerve accumulates, stimulating the ACh receptors Bind reversibly to acetylcholinesterase, so effects will pass with time Myasthenia Gravis Definition Chronic muscular disease caused by a defect in neuromuscular transmission Autoimmune disease; patients make ant ...
Neurotransmitters, Endocrine System, Synapses
... ❖ The synaptic structures can be blocked or moved out of place by a genetic defect, causing dysfunction. ❖ The dendrite receptor can also not process the signal of a neurotransmitter, causing the signal to not pass on. ❖ Dysfunctional synapses are main culprits of anxiety disorders, depression, deme ...
... ❖ The synaptic structures can be blocked or moved out of place by a genetic defect, causing dysfunction. ❖ The dendrite receptor can also not process the signal of a neurotransmitter, causing the signal to not pass on. ❖ Dysfunctional synapses are main culprits of anxiety disorders, depression, deme ...
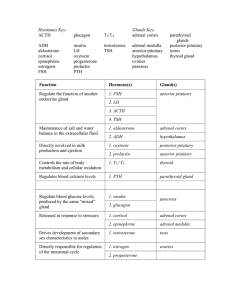
Hormones Key: Glands Key: ACTH glucagon T3/T4 adrenal cortex
... adrenal cortex adrenal medulla anterior pituitary hypothalamus ovaries pancreas ...
... adrenal cortex adrenal medulla anterior pituitary hypothalamus ovaries pancreas ...
Document
... B. located near the pituitary gland C. clusters of endocrine tissue found throughout the pancreas D. paired glands, one of which is located above each kidney ...
... B. located near the pituitary gland C. clusters of endocrine tissue found throughout the pancreas D. paired glands, one of which is located above each kidney ...
Human Sexual Response A. Signs of arousal Divisions of the
... “sympathetic adrenal hormones” produced and secreted by adrenal glands norepinephrine Divisions of the Nervous System released as neurotransmitter I. CNS (central nervous system) from neurons in II. PNS (peripherial nervous system) sympathetic A. Somatic nervous system nervous system voluntary/skele ...
... “sympathetic adrenal hormones” produced and secreted by adrenal glands norepinephrine Divisions of the Nervous System released as neurotransmitter I. CNS (central nervous system) from neurons in II. PNS (peripherial nervous system) sympathetic A. Somatic nervous system nervous system voluntary/skele ...
Document
... 3. Typical secretions: hormones which affect distant targets and/or many tissues a. peptide hormones - proteins, glycoproteins, or peptides which bind to receptors on cell surfaces; work via second messengers, water soluble; e.g. insulin, glucagon, follicle stimulating hormone b. steroid hormones - ...
... 3. Typical secretions: hormones which affect distant targets and/or many tissues a. peptide hormones - proteins, glycoproteins, or peptides which bind to receptors on cell surfaces; work via second messengers, water soluble; e.g. insulin, glucagon, follicle stimulating hormone b. steroid hormones - ...
Dr. Ghassan The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): After studying
... Changes in organ and tissue function throughout the body are coordinated so that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both heart rate and myocardial contractility are increased so that the heart pumps more blood per minute. Sym ...
... Changes in organ and tissue function throughout the body are coordinated so that there is an increase in the delivery of well-oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the working skeletal muscles. Both heart rate and myocardial contractility are increased so that the heart pumps more blood per minute. Sym ...
The endocrine system (overview) The endocrine system (overview)
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
... The endocrine system: a system of endocrine (ductless) glands or specialised cells which can secrete hormones directly into local capillaries for distribution around the body. ...
Lect 6 hormones 2
... • Produced in parafollicle cells of the thyroid gland (C-cells) • High Blood Ca++ stimulates release of calcitonin (also by a calcium-sensing receptor) • Act to decrease blood Ca++ by ...
... • Produced in parafollicle cells of the thyroid gland (C-cells) • High Blood Ca++ stimulates release of calcitonin (also by a calcium-sensing receptor) • Act to decrease blood Ca++ by ...
The autonomic nervous system (ANS)
... Nicotinic Receptors are located on: Motor end plates of skeletal muscles (somatic targets) All ganglionic neurons (sypathetic and parasympathetic) The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ACh always produces a stimulatory effect when it binds with nicotinic receptors Muscarine Recept ...
... Nicotinic Receptors are located on: Motor end plates of skeletal muscles (somatic targets) All ganglionic neurons (sypathetic and parasympathetic) The hormone-producing cells of the adrenal medulla ACh always produces a stimulatory effect when it binds with nicotinic receptors Muscarine Recept ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Stroke – cerebral hemorrhage (blood clot) in vessels - can result in brain damage Polio – viral disease of CNS; may result in paralysis; preventable through immunization ...
... Stroke – cerebral hemorrhage (blood clot) in vessels - can result in brain damage Polio – viral disease of CNS; may result in paralysis; preventable through immunization ...
key - Scioly.org
... be used as a tiebreaker. If there is still a tie, the other questions in this assessment will be considered tie breakers as well are denoted with a * next to them ...
... be used as a tiebreaker. If there is still a tie, the other questions in this assessment will be considered tie breakers as well are denoted with a * next to them ...
Regulation: Endocrine System II
... • Insulin (70%, beta cells) – secreted during/immediately after a meal when blood glucose and amino acid levels rise – stimulates glucose and amino acid uptake – nutrient storage effect blood glucose level • Glucagon (20%, alpha cells) – secreted between meals when blood glucose levels fall – st ...
... • Insulin (70%, beta cells) – secreted during/immediately after a meal when blood glucose and amino acid levels rise – stimulates glucose and amino acid uptake – nutrient storage effect blood glucose level • Glucagon (20%, alpha cells) – secreted between meals when blood glucose levels fall – st ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... These cells respond to the arrival of impulses down the preganglionic fibers, by secreting the catecholamine hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream. The preganglionic fibers, like those of the parasympathetic division, release the neurotransmitter, ACh, which binds to nicotini ...
... These cells respond to the arrival of impulses down the preganglionic fibers, by secreting the catecholamine hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream. The preganglionic fibers, like those of the parasympathetic division, release the neurotransmitter, ACh, which binds to nicotini ...
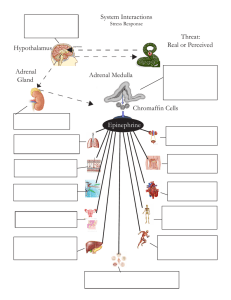
Adrenal Medulla Chromaffin Cells Epinephrine Threat: Real or
... in the body as the body prepares to fight or run away in order to survive. The hypothalamus is connected to the adrenal glands sitting on top of the kidneys by a set of neurons. The adrenal medulla releases adrenalin known as epinephrine. This response is recognized as the first stage of a general a ...
... in the body as the body prepares to fight or run away in order to survive. The hypothalamus is connected to the adrenal glands sitting on top of the kidneys by a set of neurons. The adrenal medulla releases adrenalin known as epinephrine. This response is recognized as the first stage of a general a ...
History of catecholamine research

The catecholamines comprise the endogenous substances dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and adrenaline (epinephrine) as well as numerous artificially synthesized compounds such as isoprenaline. Their investigation constitutes a prominent chapter in the history of physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology. Adrenaline was the first hormone extracted from its endocrine gland and obtained in pure form, before the word hormone was coined. It was also the first hormone the structure and biosynthesis of which were clarified. Apart from acetylcholine, adrenaline and noradrenaline were the first neurotransmitters to be discovered and the first intercellular biochemical signals to be found in intracellular vesicles. The β-adrenoceptor was the first G protein-coupled receptor the gene of which was cloned.Goal-directed catecholamine research began with the preparation by George Oliver and Edward Albert Sharpey-Schafer of a pharmacologically active extract from the adrenal glands.