Science Final Study Guide - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Weathering and Erosion Difference between mechanical (physical) and chemical weathering What factors affect the rate of weathering Types of weathering (ice wedging, etc) Definition of weathering/erosion/deposition How soil is formed Mass Movement – types and how they’re caused River Er ...
... Weathering and Erosion Difference between mechanical (physical) and chemical weathering What factors affect the rate of weathering Types of weathering (ice wedging, etc) Definition of weathering/erosion/deposition How soil is formed Mass Movement – types and how they’re caused River Er ...
Plate Tectonics
... This type of plate boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other forming a zigzag plate margin. The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of a ______ boundary. ...
... This type of plate boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other forming a zigzag plate margin. The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of a ______ boundary. ...
chapter 14 - Kennedy APES
... C. Depletion time for a resource depends on how long it takes to use up a certain proportion (usually 80%) at a given rate of use. 1. Depletion time is extended by recycling, reusing and reducing consumption of a given resource. 2. New discoveries of a resource extend the depletion time also. 3. The ...
... C. Depletion time for a resource depends on how long it takes to use up a certain proportion (usually 80%) at a given rate of use. 1. Depletion time is extended by recycling, reusing and reducing consumption of a given resource. 2. New discoveries of a resource extend the depletion time also. 3. The ...
6th Grade Earth Science
... down rock into smaller pieces as a result of ice or water – MINERALS THAT MAKE UP THE ROCK DO NOT CHANGE! • ________________ - minerals that make up Chemical Weathering the rock change. • The cause of chemical weathering is a _________ with something in the reaction water or ________ oxygen environm ...
... down rock into smaller pieces as a result of ice or water – MINERALS THAT MAKE UP THE ROCK DO NOT CHANGE! • ________________ - minerals that make up Chemical Weathering the rock change. • The cause of chemical weathering is a _________ with something in the reaction water or ________ oxygen environm ...
Earth`s Layers
... currents. • Convection currents are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, then cooling and sinking again • The cycle repeats over and over. • The molten rock below Earth’s surface is known as magma ...
... currents. • Convection currents are caused by the very hot material at the deepest part of the mantle rising, then cooling and sinking again • The cycle repeats over and over. • The molten rock below Earth’s surface is known as magma ...
Untitled - Triumph Learning
... Tectonic plates move because of convection currents in the asthenosphere. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid—that is, a liquid or a gas. When a region of a fluid absorbs heat energy, that region expands and becomes lighter. The warm fluid floats upward as cooler, heavier ...
... Tectonic plates move because of convection currents in the asthenosphere. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid—that is, a liquid or a gas. When a region of a fluid absorbs heat energy, that region expands and becomes lighter. The warm fluid floats upward as cooler, heavier ...
Layers of the Earth - Mrs. Rasmussen Science Class
... the one that we live in—the atmosphere. The atmosphere contains all the air we breathe and the weather we experience. Although we often use the term “air,” the atmosphere is made out of many gases like: nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and other gases like argon and carbon dioxide (1%). Since there isn ...
... the one that we live in—the atmosphere. The atmosphere contains all the air we breathe and the weather we experience. Although we often use the term “air,” the atmosphere is made out of many gases like: nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and other gases like argon and carbon dioxide (1%). Since there isn ...
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials
... of sediment? What types of environments are characterized by the tremendous heat and pressure that produces metamorphic rocks? ...
... of sediment? What types of environments are characterized by the tremendous heat and pressure that produces metamorphic rocks? ...
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials
... of sediment? What types of environments are characterized by the tremendous heat and pressure that produces metamorphic rocks? ...
... of sediment? What types of environments are characterized by the tremendous heat and pressure that produces metamorphic rocks? ...
Earth`s Interior (pages 6–13)
... scientists must learn about Earth’s interior, or inside, in other ways. • Scientists use drills to get rock samples from inside Earth. The rock samples help scientists learn what conditions were like inside Earth when the rocks formed. • Scientists study how seismic waves travel through Earth. Seism ...
... scientists must learn about Earth’s interior, or inside, in other ways. • Scientists use drills to get rock samples from inside Earth. The rock samples help scientists learn what conditions were like inside Earth when the rocks formed. • Scientists study how seismic waves travel through Earth. Seism ...
Rocks
... silt, clay, or other materials. The grains in this sample are mostly the feldspar and quartz minerals, which probably accumulated near the granite from which they were eroded. ...
... silt, clay, or other materials. The grains in this sample are mostly the feldspar and quartz minerals, which probably accumulated near the granite from which they were eroded. ...
notes
... silt, clay, or other materials. The grains in this sample are mostly the feldspar and quartz minerals, which probably accumulated near the granite from which they were eroded. ...
... silt, clay, or other materials. The grains in this sample are mostly the feldspar and quartz minerals, which probably accumulated near the granite from which they were eroded. ...
Unit One
... Put on your fur parka and head to the frozen Arctic wasteland, or south to the equally frigid Antarctic ice sheet, and you might think you’d be alone. But in the pressurized ice here are tiny cracks filled with salt water, and – you guessed it – living things. Psychrophiles or cryophiles are the nam ...
... Put on your fur parka and head to the frozen Arctic wasteland, or south to the equally frigid Antarctic ice sheet, and you might think you’d be alone. But in the pressurized ice here are tiny cracks filled with salt water, and – you guessed it – living things. Psychrophiles or cryophiles are the nam ...
Inside Planet Earth!
... 1. How long are the crystals that formed here? 40 feet long 2. How did these crystals form? An underground lake was boiled by magma. Crystals grew from the minerals that were dissolved in the water. 3. There are seven massive sections that make up the Earth’s crust. These sections are known as plate ...
... 1. How long are the crystals that formed here? 40 feet long 2. How did these crystals form? An underground lake was boiled by magma. Crystals grew from the minerals that were dissolved in the water. 3. There are seven massive sections that make up the Earth’s crust. These sections are known as plate ...
The Layered Earth - Starry Night Education
... factors such as distance from the epicenter and hypocenter, local geology and type of construction used in the area. ...
... factors such as distance from the epicenter and hypocenter, local geology and type of construction used in the area. ...
The$Earth`s$Interior The$Earth`s$Interior
... Continental drift hypothesis • Supercontinent called Pangaea began breaking apart about 200 million years ago • Continents "drifted" to present positions • Continents "broke" through the ocean crust Figure 7.25 ...
... Continental drift hypothesis • Supercontinent called Pangaea began breaking apart about 200 million years ago • Continents "drifted" to present positions • Continents "broke" through the ocean crust Figure 7.25 ...
On page of your notebook create the following chart.
... tectonic plates has created rift valleys- long valleys between parallel ridges of mountains. This creation of new crust would increase the Earth’s size, except that it is balanced by the folding and colliding of plates elsewhere. Earthquakes and Tsunamis: Plate movement can cause a break in Earth’s ...
... tectonic plates has created rift valleys- long valleys between parallel ridges of mountains. This creation of new crust would increase the Earth’s size, except that it is balanced by the folding and colliding of plates elsewhere. Earthquakes and Tsunamis: Plate movement can cause a break in Earth’s ...
Unit 1 Plate Tectonics UNIT 2: LAYERS OF THE EARTH STUDY
... The inner core is also made of iron and nickel. It is liquid due to the tremendous pressure upon it. There are two types of crust: oceanic crust and continental crust. ...
... The inner core is also made of iron and nickel. It is liquid due to the tremendous pressure upon it. There are two types of crust: oceanic crust and continental crust. ...
First Hour Exam, Fall, 1998
... 24. Flocculation is a process whereby a. minerals in a magma crystallize out at different temperatures, yielding rocks with many different grain sizes in them. b. clays in suspension in waters clump together due to the presence of salt, and settle more rapidly than they would otherwise. c. sediments ...
... 24. Flocculation is a process whereby a. minerals in a magma crystallize out at different temperatures, yielding rocks with many different grain sizes in them. b. clays in suspension in waters clump together due to the presence of salt, and settle more rapidly than they would otherwise. c. sediments ...
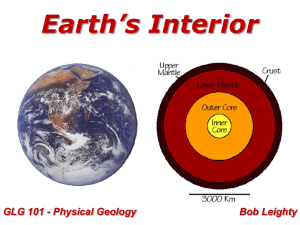
GLG101online_10B_EarthsInterior_MCC_Leighty
... These notes and web links are your primary “lecture” content in this class. Additionally, various articles are assigned each week to supplement this “lecture” information. I believe you’ll have enough information to reference without having to purchase a costly textbook. These lecture notes are ver ...
... These notes and web links are your primary “lecture” content in this class. Additionally, various articles are assigned each week to supplement this “lecture” information. I believe you’ll have enough information to reference without having to purchase a costly textbook. These lecture notes are ver ...
Fundamental Concepts in Igneous Petrology
... name of stable phase of MgSiO3 throughout most of Earth's mantle, i.e. perovskite. image source: Press and Siever (2001) ...
... name of stable phase of MgSiO3 throughout most of Earth's mantle, i.e. perovskite. image source: Press and Siever (2001) ...
Ice Age: Continental Drift
... In other examples, mountain rock in South America and Africa has the same mineral content and is the same age. This is also true for mountains in Scotland and eastern North America. There was more: Fossils of the same species of fern plant were discovered in Africa, Antarctica, Australia, India, and ...
... In other examples, mountain rock in South America and Africa has the same mineral content and is the same age. This is also true for mountains in Scotland and eastern North America. There was more: Fossils of the same species of fern plant were discovered in Africa, Antarctica, Australia, India, and ...
Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics
... Eon: The longest geologic time unit: Phanerozoic Eon includes Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Epoch: A geologic time unit longer than an age and shorter than a period. Era: A geologic time unit smaller than an eon. Extrusive: Pertaining to igneous rock which flows or is ejected onto the Earth ...
... Eon: The longest geologic time unit: Phanerozoic Eon includes Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Epoch: A geologic time unit longer than an age and shorter than a period. Era: A geologic time unit smaller than an eon. Extrusive: Pertaining to igneous rock which flows or is ejected onto the Earth ...