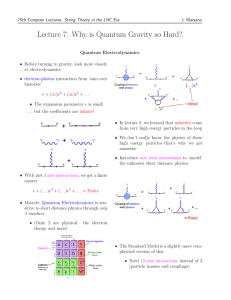
Zealey Phys-in-Cont
... For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen. They are called hydrogen, deuterium and tritium. Their particle composition is given in Table 2 and they are illustrated in Figure 2. ...
... For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen. They are called hydrogen, deuterium and tritium. Their particle composition is given in Table 2 and they are illustrated in Figure 2. ...
Applications of Quantum Field Theory in Condensed Matter
... the standard model, which has a vast and impressive body of experimental support. It was in the 80’s, however, that the efforts to produce a quantum field theory based grand unified model for the weak, strong and electromagnetic interactions, failed. This was the starting point for the attempts to u ...
... the standard model, which has a vast and impressive body of experimental support. It was in the 80’s, however, that the efforts to produce a quantum field theory based grand unified model for the weak, strong and electromagnetic interactions, failed. This was the starting point for the attempts to u ...
Lecture 33: Quantum Mechanical Spin
... particles have an additional internal degree of freedom, called ‘spin’ • The Stern-Gerlach experiment (1922): ...
... particles have an additional internal degree of freedom, called ‘spin’ • The Stern-Gerlach experiment (1922): ...
Gauge Field Theories Second Edition - Assets
... class of symmetries of the physical system. Let us consider a Lie group of continuous global (x-independent) infinitesimal transformations (here we restrict ourselves to unitary transformations; conformal transformations are discussed in ...
... class of symmetries of the physical system. Let us consider a Lie group of continuous global (x-independent) infinitesimal transformations (here we restrict ourselves to unitary transformations; conformal transformations are discussed in ...
Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking
... is an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian. This is what is called spontaneous breaking of symmetry. The Hamiltonian is perfectly symmetric under rotation of spins. However, the ground state “spontaneously” chooses a particular orientation and hence is not invariant under the symmetry (rotation). To simpli ...
... is an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian. This is what is called spontaneous breaking of symmetry. The Hamiltonian is perfectly symmetric under rotation of spins. However, the ground state “spontaneously” chooses a particular orientation and hence is not invariant under the symmetry (rotation). To simpli ...
***** 1
... The physical Hamiltonian H(ph) depends, in general, on a chosen parametrization and gauge. In particular, for the ADM parametrization and the condition N = 1 the left-hand side of this equation coincides with the lefthand side of the Wheeler − DeWitt equation. In Quantum Geometrodynamics in extended ...
... The physical Hamiltonian H(ph) depends, in general, on a chosen parametrization and gauge. In particular, for the ADM parametrization and the condition N = 1 the left-hand side of this equation coincides with the lefthand side of the Wheeler − DeWitt equation. In Quantum Geometrodynamics in extended ...
MINERVA Teacher`s Manual - HST
... The defining property of the quarks is that they carry color charge, and hence, interact via the strong force. The infrared confining behavior of the strong force results in quarks being perpetually (or at least since very soon after the start of the Big Bang) bound to one another, forming color-neu ...
... The defining property of the quarks is that they carry color charge, and hence, interact via the strong force. The infrared confining behavior of the strong force results in quarks being perpetually (or at least since very soon after the start of the Big Bang) bound to one another, forming color-neu ...