Quantum fluid dynamics approach for electronic - Prof. Shih
... based on the framework of a time-dependent Thomas–Fermi (TDTF) model [5, 6]. The TF model can be considered as a crude version of quantum fluid dynamics (QFD) where the electronic system is considered as a gas of almost free electrons and the static electron densities of many-electron systems can be ...
... based on the framework of a time-dependent Thomas–Fermi (TDTF) model [5, 6]. The TF model can be considered as a crude version of quantum fluid dynamics (QFD) where the electronic system is considered as a gas of almost free electrons and the static electron densities of many-electron systems can be ...
Document
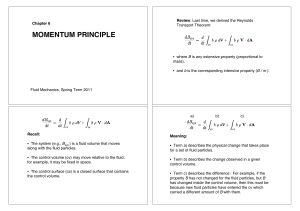
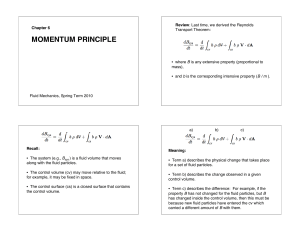
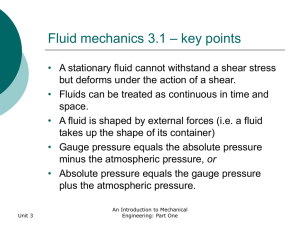
... • The steady flow energy equation can be applied to the flow of real fluids and leads to the extended Bernoulli equation that can be used to describe the losses resulting from viscous friction in a flow. • The Moody Chart can be used to estimate the frictional losses in pipe and duct flows. • The SF ...
... • The steady flow energy equation can be applied to the flow of real fluids and leads to the extended Bernoulli equation that can be used to describe the losses resulting from viscous friction in a flow. • The Moody Chart can be used to estimate the frictional losses in pipe and duct flows. • The SF ...
MEASUREMENT OF LIFETIMES OF EXCITED STATES OF THE
... measuring lifetimes of excited states of fast particles has been Wien's method, which was described in detail in 1927. [ t] In this method the lifetime is determined from the attenuation of the luminosity of a beam of excited atoms in a vacuum. Wien's experiments on measurement of the lifetimes of e ...
... measuring lifetimes of excited states of fast particles has been Wien's method, which was described in detail in 1927. [ t] In this method the lifetime is determined from the attenuation of the luminosity of a beam of excited atoms in a vacuum. Wien's experiments on measurement of the lifetimes of e ...
sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Lecture notes arXiv:1010.0682 arXiv
... Gauge theory of FL and FL* phases We want to keep better track of the charge on layer a. For this we introduce a ‘fictitious’ quantum rotor on each a lattice site. Each rotor has a periodic angular co-ordinate ϑi with period 2π; hence the states of the rotors are e inri ϑi where nri is a rotor angu ...
... Gauge theory of FL and FL* phases We want to keep better track of the charge on layer a. For this we introduce a ‘fictitious’ quantum rotor on each a lattice site. Each rotor has a periodic angular co-ordinate ϑi with period 2π; hence the states of the rotors are e inri ϑi where nri is a rotor angu ...