10.Volcanoes_and_Other_Igneous_Activity
... • A volcano is a mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material. • A crater is the depression at the summit of a volcano or that which is produced by a meteorite ...
... • A volcano is a mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material. • A crater is the depression at the summit of a volcano or that which is produced by a meteorite ...
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s plate boundaries o The boundaries Converge or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move apart Ex: Sea Floor Spreading o Rift Valley Lava pours out and volcano formed Converg ...
... Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H2O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form along the Earth’s plate boundaries o The boundaries Converge or Diverge Divergent Boundary: Plates move apart Ex: Sea Floor Spreading o Rift Valley Lava pours out and volcano formed Converg ...
Earth Science
... eruptions of basaltic lava that accumulates in layers K. A substance’s internal resistance to flow L. Large, sloping volcano built by violent eruptions of volcanic fragments and lava that accumulate in alternating layers M. Irregularly shaped pluton that is similar to a batholith, but smaller and cu ...
... eruptions of basaltic lava that accumulates in layers K. A substance’s internal resistance to flow L. Large, sloping volcano built by violent eruptions of volcanic fragments and lava that accumulate in alternating layers M. Irregularly shaped pluton that is similar to a batholith, but smaller and cu ...
How does a volcano erupt? - Germantown School District
... • Forms when uplift pushes a large body of hardened magma toward the surface • Example: Black Hills (South Dakota) ...
... • Forms when uplift pushes a large body of hardened magma toward the surface • Example: Black Hills (South Dakota) ...
Earth Science: CST Review , Day #4, CST Released Questions #28
... 1. Which of the following provides evidence for plate tectonics? ______________________________________ 2. The youngest rocks on the ocean floor are typically located near what feature? _________________ 3. A rift valley is evidence of which kind of plate boundary? ___________________ 4. The converg ...
... 1. Which of the following provides evidence for plate tectonics? ______________________________________ 2. The youngest rocks on the ocean floor are typically located near what feature? _________________ 3. A rift valley is evidence of which kind of plate boundary? ___________________ 4. The converg ...
thesis paper - The Ohio State University
... the viscosity of the magma is high and the amount of gas within the magma is large, the eruption is explosive, resulting in a cinder cone volcano (like Capulan Mountain) or a stratovolcano (like Mount Saint Helens) (Volcano Hazards, 2015). Refer to Figure 1 for the processes involved in volcano form ...
... the viscosity of the magma is high and the amount of gas within the magma is large, the eruption is explosive, resulting in a cinder cone volcano (like Capulan Mountain) or a stratovolcano (like Mount Saint Helens) (Volcano Hazards, 2015). Refer to Figure 1 for the processes involved in volcano form ...
Name Class Date 9.4 Natural Disasters Key Concepts The shaking
... areas. 5. Scientists cannot predict when earthquakes will occur, but in the United States, they occur most often in the states of and ...
... areas. 5. Scientists cannot predict when earthquakes will occur, but in the United States, they occur most often in the states of and ...
Practice04c
... Use these questions to test your understanding of Lecture 4. A. Short answer: 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools a ...
... Use these questions to test your understanding of Lecture 4. A. Short answer: 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools a ...
For Creative Minds - Arbordale Publishing
... Imagine the weight or pressure of a million rocks sitting on top of you! The deeper into the Earth, the more rocks there are so the more pressure there is. Pressure deep in the magma makes gases (like water vapor and carbon dioxide) dissolve. As the magma rises and pressure decreases, the gasses mak ...
... Imagine the weight or pressure of a million rocks sitting on top of you! The deeper into the Earth, the more rocks there are so the more pressure there is. Pressure deep in the magma makes gases (like water vapor and carbon dioxide) dissolve. As the magma rises and pressure decreases, the gasses mak ...
Homework for Volcanoes from Geology 1200
... Use these questions to test your understanding of Chapter 4. A. Short answer: 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools a ...
... Use these questions to test your understanding of Chapter 4. A. Short answer: 1. When hot particles within a nuée ardente fall to the ground and stick together, a welded _____ forms. 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools a ...
Volcanoes - Geophile.net
... • Fissure eruptions and lava plateaus – Low Viscosity, Low Volatiles, Very Large Volume – Basaltic lava extruded from crustal fractures – Incredibly large volumes of lava pour out of fissures over 2-3 million years – Can affect global climate ...
... • Fissure eruptions and lava plateaus – Low Viscosity, Low Volatiles, Very Large Volume – Basaltic lava extruded from crustal fractures – Incredibly large volumes of lava pour out of fissures over 2-3 million years – Can affect global climate ...
Shield volcanoes
... Geyser: a geothermal feature in which water erupts into the air under pressure. Hot spot: a section of the earth’s crust where plumes of magma rise weakening the crust. These are away from the plate boundaries. ...
... Geyser: a geothermal feature in which water erupts into the air under pressure. Hot spot: a section of the earth’s crust where plumes of magma rise weakening the crust. These are away from the plate boundaries. ...
The Geology of the Cabo de Gata area.
... During a quiescent period, when the sea was 200m higher relative to the land, shallow-water limestones were deposited in places around the volcanoes. Small pockets of these cream-coloured fossiliferous limestones, containing corals and shells, can be seen high on the mountain sides at this level, a ...
... During a quiescent period, when the sea was 200m higher relative to the land, shallow-water limestones were deposited in places around the volcanoes. Small pockets of these cream-coloured fossiliferous limestones, containing corals and shells, can be seen high on the mountain sides at this level, a ...
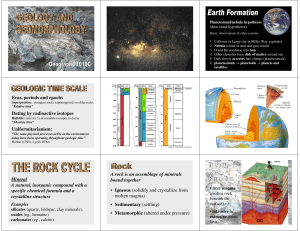
Eras, periods and epochs Dating by radioactive
... Is a major earthquake in California, Alaska or Japan of any concern thousands of kilometers away, in Hawaii? ...
... Is a major earthquake in California, Alaska or Japan of any concern thousands of kilometers away, in Hawaii? ...
Lesson 4: Volcanoes Factsheet for teachers
... Destructive plate boundaries At a destructive plate boundary (also called convergent boundaries) two plates move towards another. One plate is then pushed underneath the other. (It is the heavier plate that is forced beneath the lighter plate). The point at which one plate is forced beneath the othe ...
... Destructive plate boundaries At a destructive plate boundary (also called convergent boundaries) two plates move towards another. One plate is then pushed underneath the other. (It is the heavier plate that is forced beneath the lighter plate). The point at which one plate is forced beneath the othe ...
msword - rgs.org
... Destructive plate boundaries At a destructive plate boundary (also called convergent boundaries) two plates move towards another. One plate is then pushed underneath the other. (It is the heavier plate that is forced beneath the lighter plate). The point at which one plate is forced beneath the othe ...
... Destructive plate boundaries At a destructive plate boundary (also called convergent boundaries) two plates move towards another. One plate is then pushed underneath the other. (It is the heavier plate that is forced beneath the lighter plate). The point at which one plate is forced beneath the othe ...
Composite Volcanoes - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
... different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you wer ...
Living in an Active Zone - Penyrheol Comprehensive School Moodle
... • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction zone. • Fold mountains are created on the continental crust . • The subducted oceanic crust melts in the mantle rising up into the fold mountain to create composite volcanoes • E.g. Mount St ...
... • The subduction of the oceanic crust creates a deep sea trench and earthquakes are formed at the subduction zone. • Fold mountains are created on the continental crust . • The subducted oceanic crust melts in the mantle rising up into the fold mountain to create composite volcanoes • E.g. Mount St ...
Volcanoes A volcano is a landform (usually a mountain) where
... 2. Dormant - has been a while since it has erupted, but could at anytime. 3. Extinct, meaning it hasn't erupted in a very long, long time so it probably won't ever again. 4.2. Shapes of Volcanoes The type of magma in the earth creates four different types volcanoes: ...
... 2. Dormant - has been a while since it has erupted, but could at anytime. 3. Extinct, meaning it hasn't erupted in a very long, long time so it probably won't ever again. 4.2. Shapes of Volcanoes The type of magma in the earth creates four different types volcanoes: ...
Chapter 5 Deformation of the Crust
... -Mountains formed by faults where large blocks of Earth’s crust are lifted and tilted -Ex: __________________, form nearly parallel ranges every 80 km -________________- long, narrow valleys that develop when steep faults break the crust into blocks and slip downward relative to the surrounding bloc ...
... -Mountains formed by faults where large blocks of Earth’s crust are lifted and tilted -Ex: __________________, form nearly parallel ranges every 80 km -________________- long, narrow valleys that develop when steep faults break the crust into blocks and slip downward relative to the surrounding bloc ...
Volcano Review sheet - new for 2016-17
... a. Granite-based magma will be a major portion of shield volcanoes, like in Hawaii, and its additional percentage of silica will make it erupt more gently. b. Basalt will float on granite and volcanoes made with a lot of basalt will erupt gently c. Basalt is the best choice to make a stratovolcano, ...
... a. Granite-based magma will be a major portion of shield volcanoes, like in Hawaii, and its additional percentage of silica will make it erupt more gently. b. Basalt will float on granite and volcanoes made with a lot of basalt will erupt gently c. Basalt is the best choice to make a stratovolcano, ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.